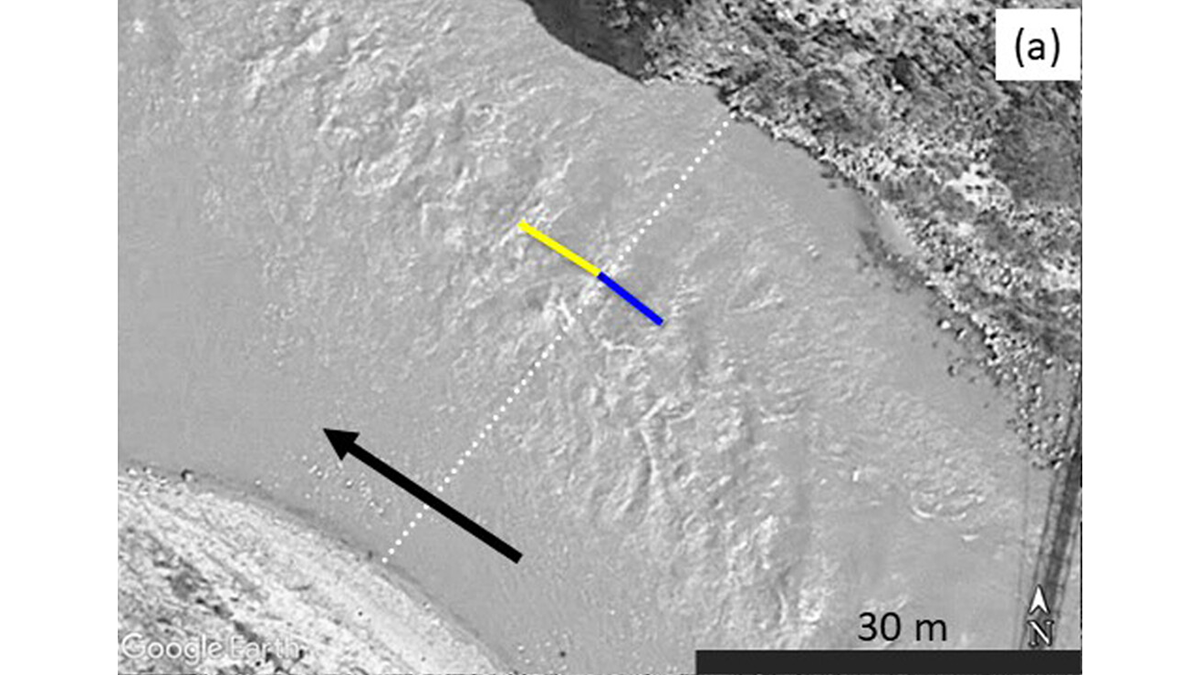
Critical flow theory can predict river discharge based on the spacing of standing waves captured by Google Earth images.
Guiling Wang
Associate Editor, Geophysical Research Letters
Pre-Season Wet Soil Produces Fire-Prone Conditions
The SMAP satellite shows that wetter-than-normal soil five months prior to wildfires in the western United States increases fuel availability and fire activity when desiccation occurs.
Warming Reduces Relative Humidity Through Soil Moisture
Relative humidity over land decreases in a warmer climate as a result of interactive soil moisture response.
Wet Conditions Delay Wildfire Detection
When accompanied by a considerable amount of rainfall, ignition of wildfire by lightning over forested land may not be detected until days later.
Greening of Loess Plateau Increases Water Yield
Vegetation restoration over the Chinese Loess Plateau can enhance atmospheric moisture convergence, increasing the precipitation enough to compensate for the vegetation water consumption.
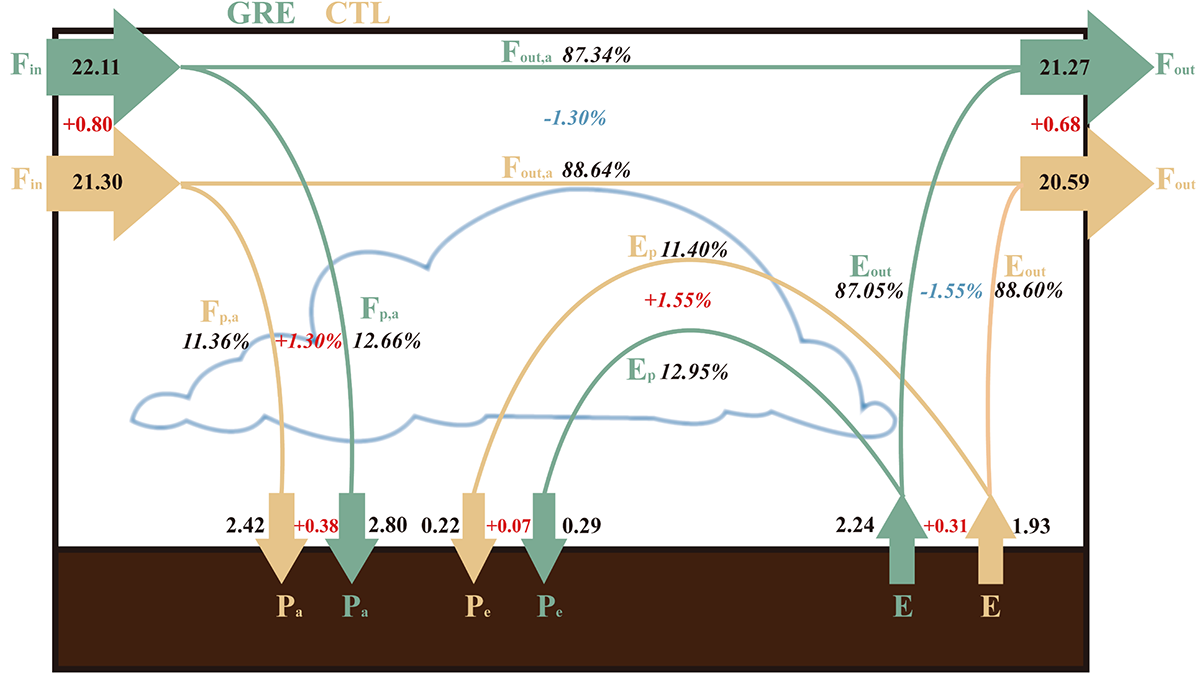
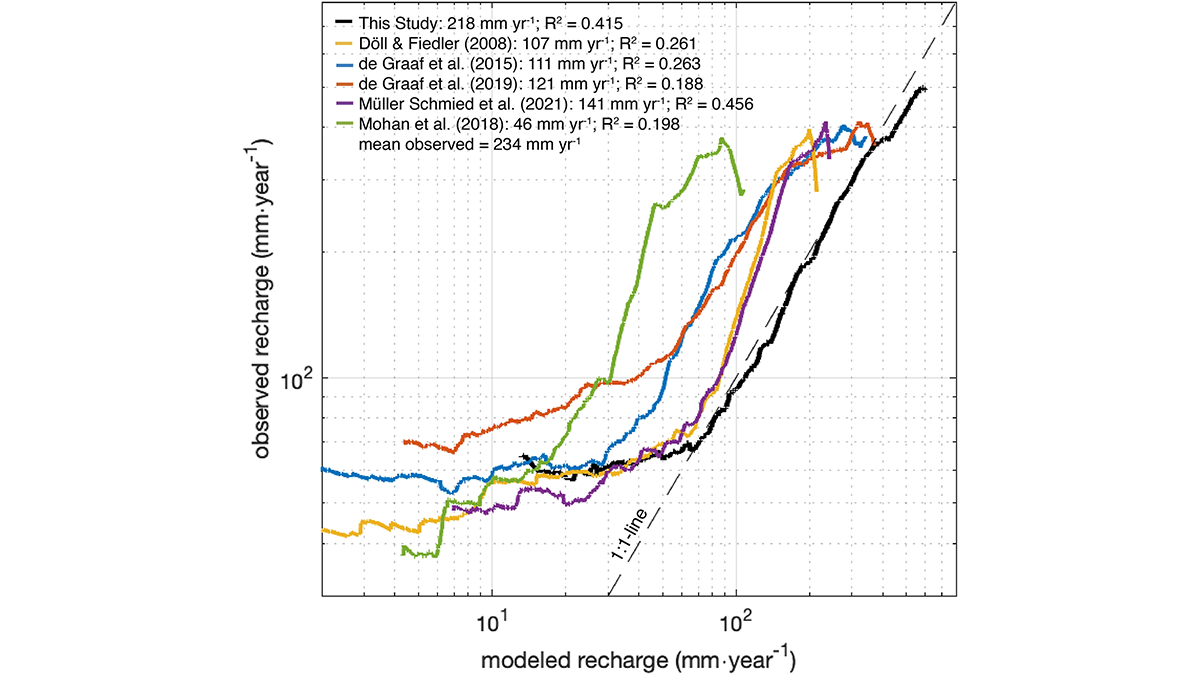
Global Models Underestimated Groundwater Recharge and Discharge
A new estimate for global groundwater recharge by rainfall and snowmelt, which dictates the upper limit of sustainable groundwater use, doubles the previous estimates from global models.
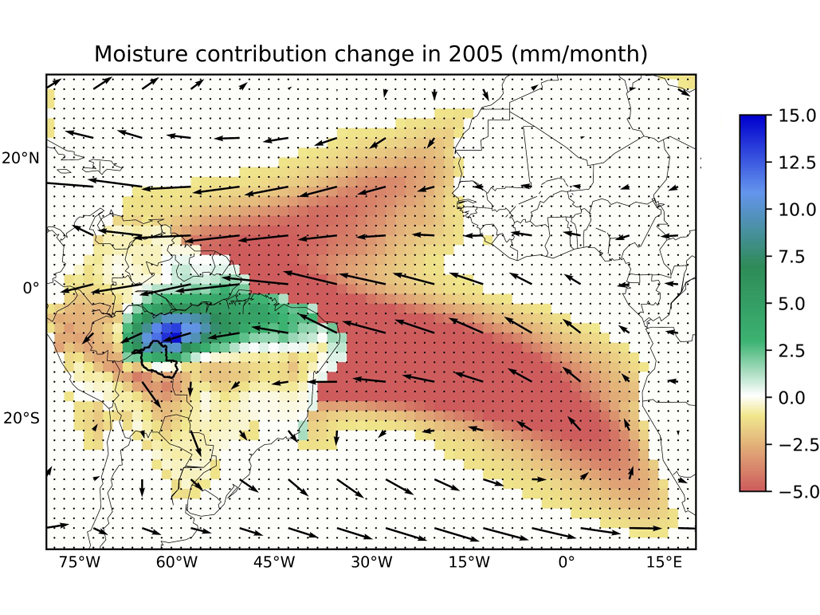
Upwind Forest Buffers Rondonia Cropland Against Regional Drought
During severe Amazonia droughts when oceanic supply of moisture failed, the magnitude of rainfall reduction over Rondonia was moderated by enhanced moisture supply from upwind forests.