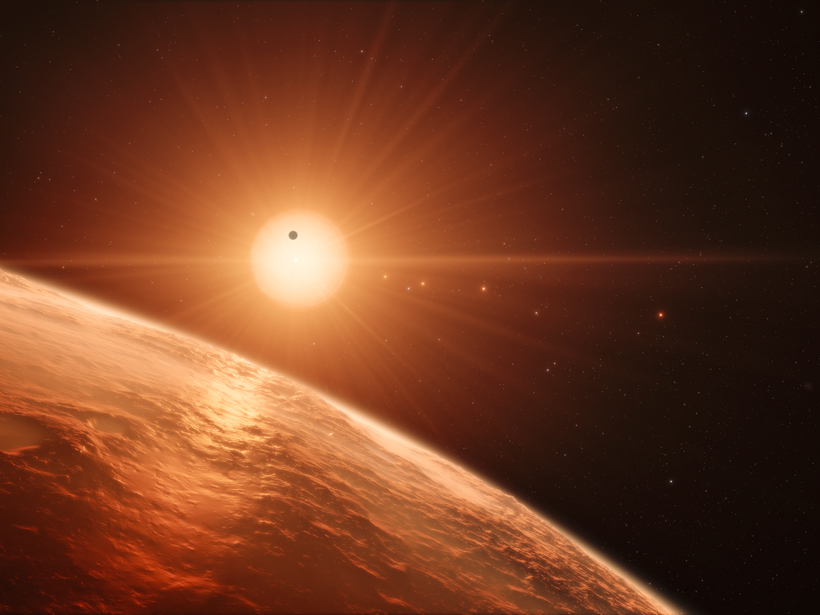
The proposed formation scenario relies on unconventional processes to account for a bevy of seven Earth-sized exoplanets recently found orbiting an unlikely star.
S. Hall
Shannon Hall, a freelance science journalist, covers topics ranging from geysers to galaxies. Over the past 8 years she has received four degrees—two bachelor’s degrees in astronomy and philosophy and two master’s degrees in astronomy and science journalism—and has lived in eight different states. For the moment she has settled down in Hanover, N.H., happy to be a tiny dot in a big landscape.
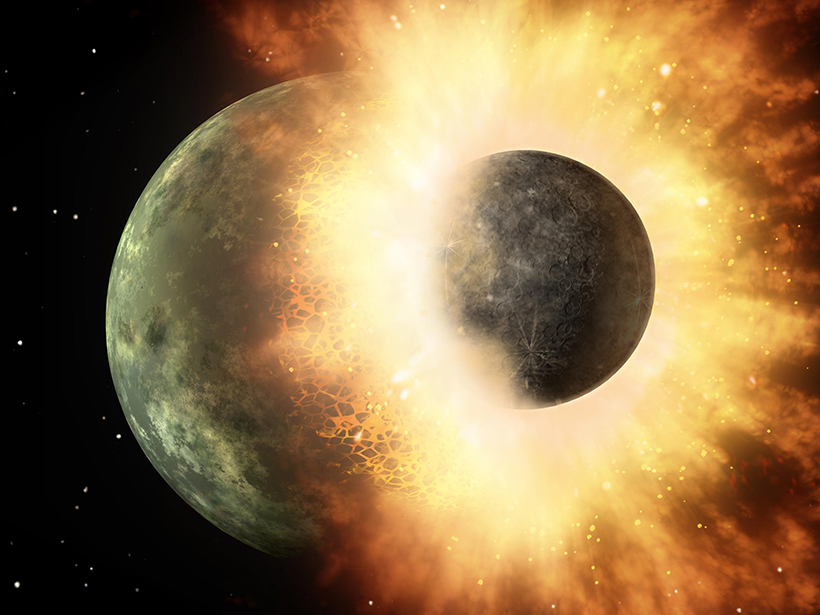
New Insight into Silica Explains Planetary Smashup
A better equation of state for silica will help planetary scientists accurately constrain the giant impacts that have shaped our solar system.
A New Model to Improve Gravity Models
Data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission gets a new and improved look.
Modeling Rainfall Runoff
New framework unifies existing models for better analysis of the flowing water produced by heavy rain events.
Groundwater: A Hidden Influence on River Shape
A new study shows how groundwater influences river dynamics and channel pattern.
Can We Predict the Future of Ocean Carbon Dioxide Uptake?
A new understanding of uncertainties in climate change models allows scientists to decide which source to tackle first in order to better forecast our planet's changing climate.
Simulating the Climate 145 Million Years Ago
A new model shows that the Intertropical Convergence Zone wasn't always a single band around the equator, which had drastic effects on climate.
Eliminating Uncertainty One Cloud at a Time
The impact of clouds on climate change has been a scientific mystery for decades. Now researchers are fighting to gain the upper hand.
Seismological Models Are Biased, but Scientists Have a Solution
Many seismic wave models are based on an erroneous assumption about the Earth's interior. A new technique corrects this by eliminating false signals produced by models.
A Flip-Flopping Climate Could Explain Mars's Watery Past
A new hypothesis might reconcile two opposing theories that have tried to explain Mars's mysterious history for more than 40 years.