Although the total surface area of Earth’s lakes emits less methane than previously believed, it is still among the largest natural methane sources.
Sarah Stanley
Sarah Stanley, a freelance writer for Eos, has a background in environmental microbiology but covers a wide range of science stories for a variety of audiences. She has also written for PLOS, the University of Washington, Kaiser Permanente, Stanford Medicine, Gladstone Institutes, and Cancer Commons, a nonprofit that works with cancer patients.
Understanding Earthquakes Triggered by Wastewater Injection
A deep dive into a 2015 Oklahoma earthquake reveals new insights into the dynamics of quakes induced by wastewater injection, and could help inform future earthquake hazard modeling.
Los microbios podrían comer minerales magnéticos en un sitio de derrame de petróleo
Nuevos experimentos en un antiguo sitio de derrames de petróleo en Minnesota sugieren que los procesos no biológicos por sí solos no pueden explicar la disminución de la magnetización.
Microbes Might Munch Magnetic Minerals at Oil Spill Site
New experiments at an old oil spill site in Minnesota suggest that nonbiological processes alone may not account for decreased magnetization.
Earthquake Modelers Unite to Compare and Improve Code
International community–driven efforts lend confidence to fault-slip simulations while highlighting key discrepancies.
Road Salts Linked to High Sodium Levels in Tap Water
Use of deicing agents may sometimes raise sodium levels in drinking water beyond healthy limits for people on salt-restricted diets.
Probing the Mysteries of Deep, Dense Antarctic Seawater
Twelve freely drifting Deep Argo floats reveal year-round dynamics of bottom water flow in the Australian-Antarctic Basin.
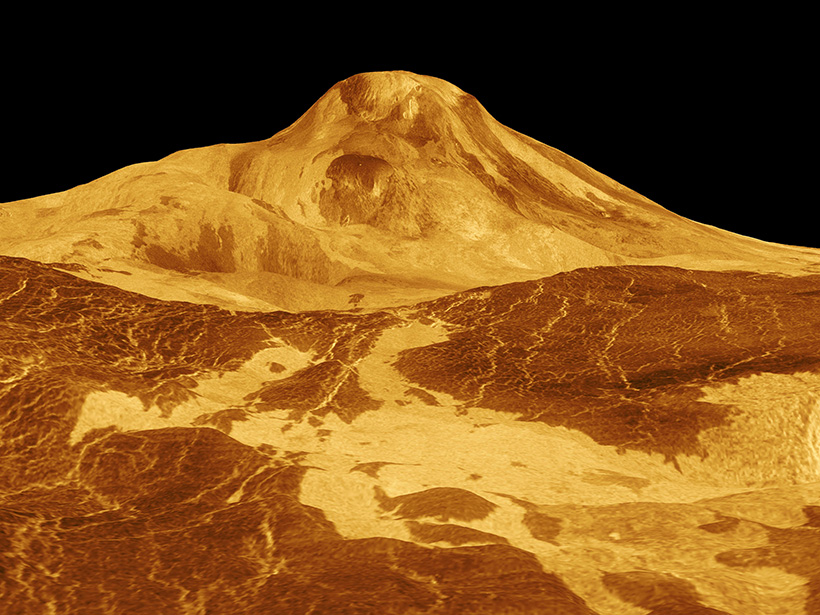
¿Es Venus volcánicamente activo? Nuevo enfoque podría proporcionar una respuesta
Una estrategia que combina la cartografía geológica con datos sobre cómo la superficie del planeta emite y absorbe la radiación de microondas podría potencialmente identificar flujos de lava recientes.
Rising Trend Predicted for Conditions Linked to Severe Storms
Climate modeling predicts that conditions conducive to severe thunderstorms will arise more often as Earth warms.