Remote sensing measurements for water vapor isotopic composition enable us to assess how convective aggregation influences the atmospheric hydrological cycle.
Editors’ Highlights
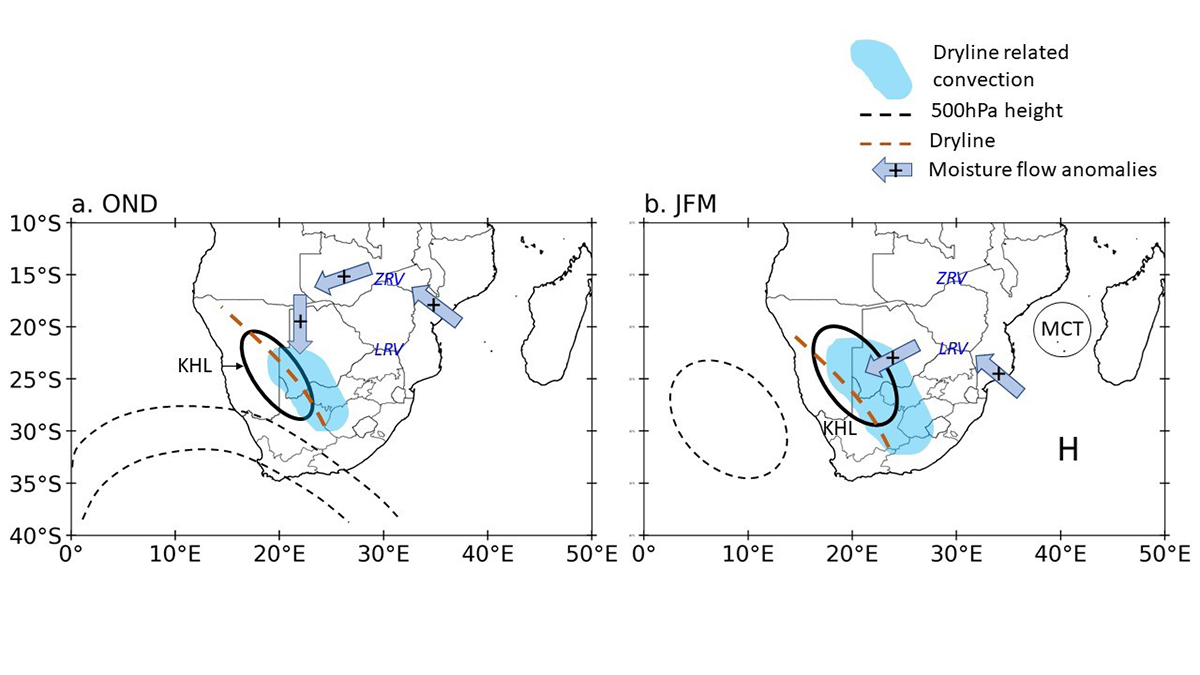
Dryline-Induced Thunderstorms Over the Southern Africa Plateau
Scientists present the first comprehensive study of dryline formation and associated thunderstorms over the southern African plateau from 2010 to 2021.
Northern Ecosystems are Shaped by Snow
Changing climate in the Arctic leads to a shorter snow season but deeper snow in the depths of winter. Under the insulating snow, biological processes are accelerated leading to higher nutrient availability and carbon losses.
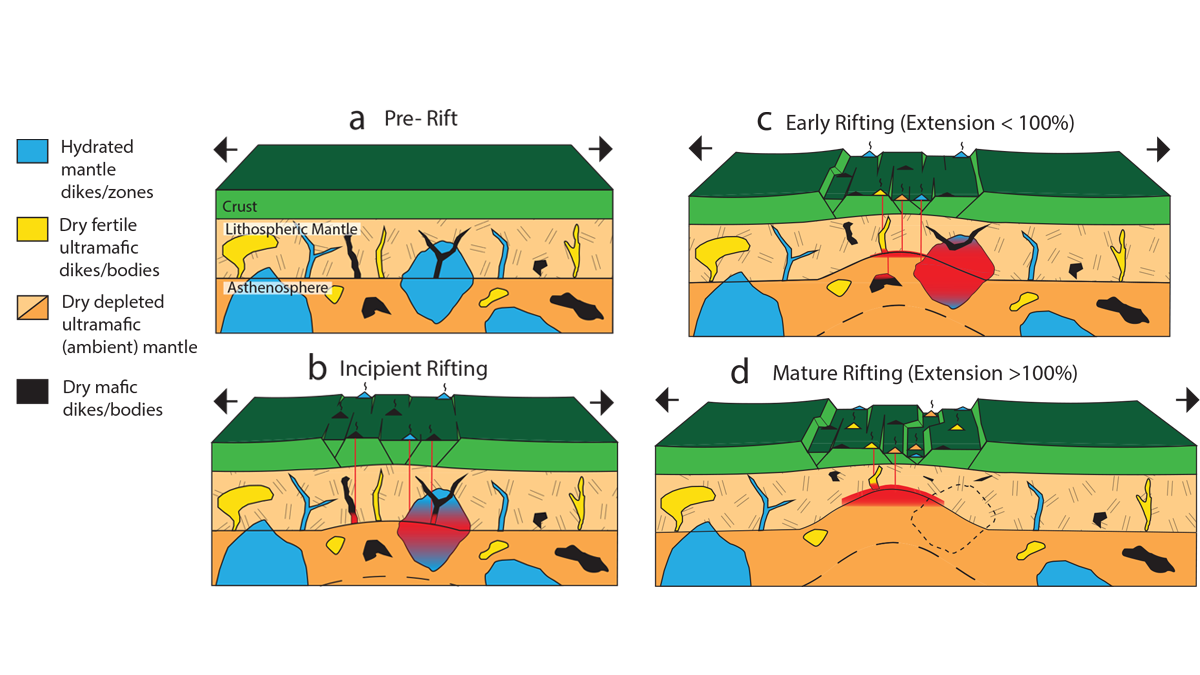
Uncovering Mantle Heterogeneities Beneath Drifting Continents
Computational models of the composition and volumes of magmas during continental rifting evolution provide clues on the heterogeneities of the deep melting mantle.
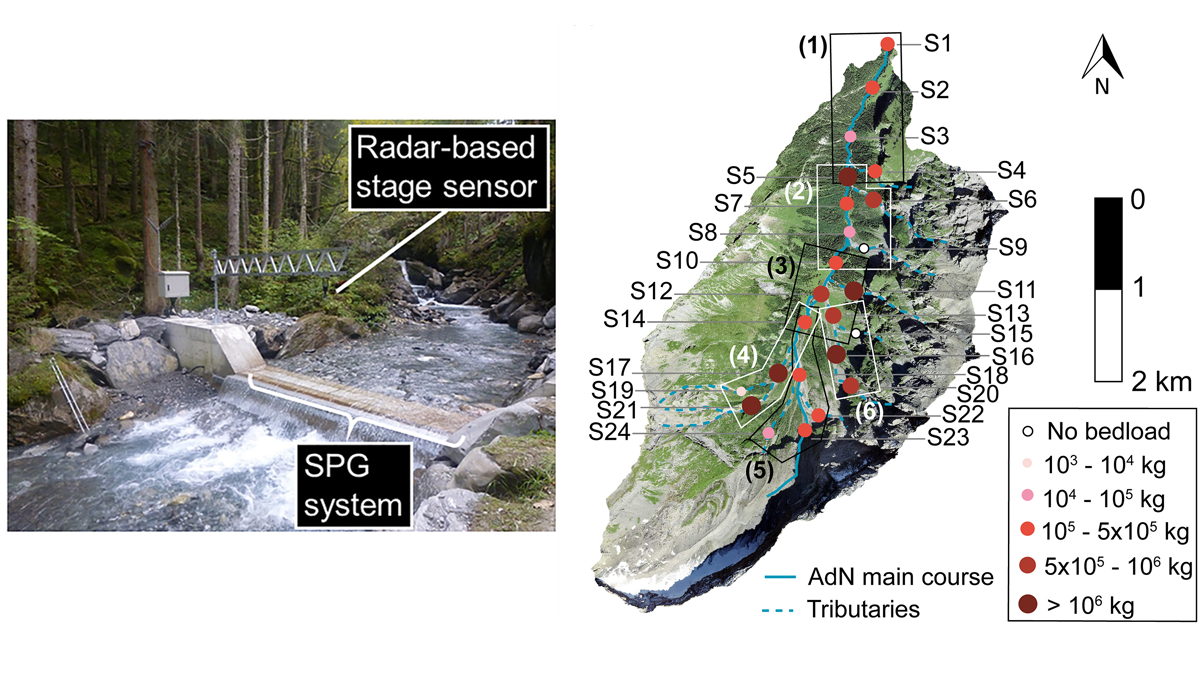
Seismometers Listening at Rivers to Measure Sediment Transport
Bedload sediment, transported throughout an alpine catchment by a flood, was remotely tracked in detail by analyzing the ground vibrations recorded by a network of 24 seismic sensors.
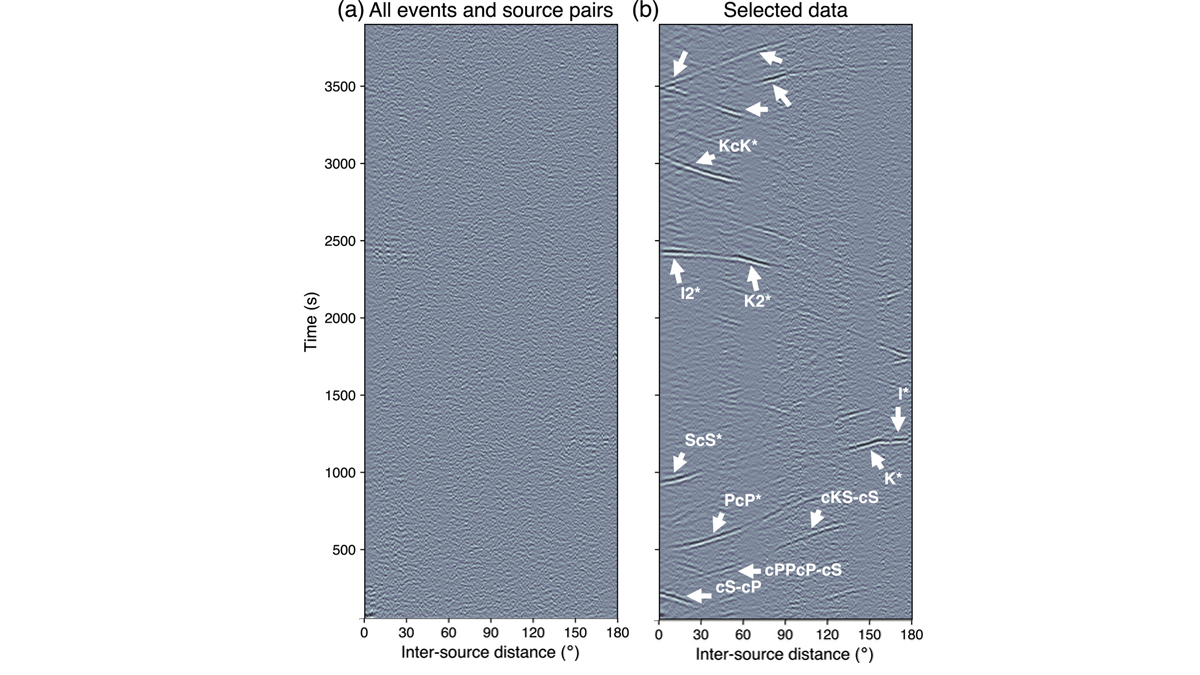
Source Selection Essential to Inter-Source Cross-Correlation
Inter-source correlograms yield coherent signals upon careful consideration of source mechanisms and source-receiver geometry, affording new means of characterizing planetary interiors.
Pliocene Conveyer Belt in the Pacific
Ocean Drilling Program cores and helium isotopes put better constraints on the ocean circulation in the north Pacific.
Low-Frequency Quakes Have Modest Effect on Slow Earthquake Cycle
Slow slip phenomena on subdaily scales, captured by seismic and GNSS data, show that low-frequency earthquakes are incidental to larger magnitude slow earthquakes, in which aseismic slip dominates.
Wet Conditions Delay Wildfire Detection
When accompanied by a considerable amount of rainfall, ignition of wildfire by lightning over forested land may not be detected until days later.
Barnacles Help Reconstruct Drift Path of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370
Careful calibration of isotopes in a barnacle shell growing on ocean debris – in this case an airplane part – informs a new forensic method to identify its most probable drift path.