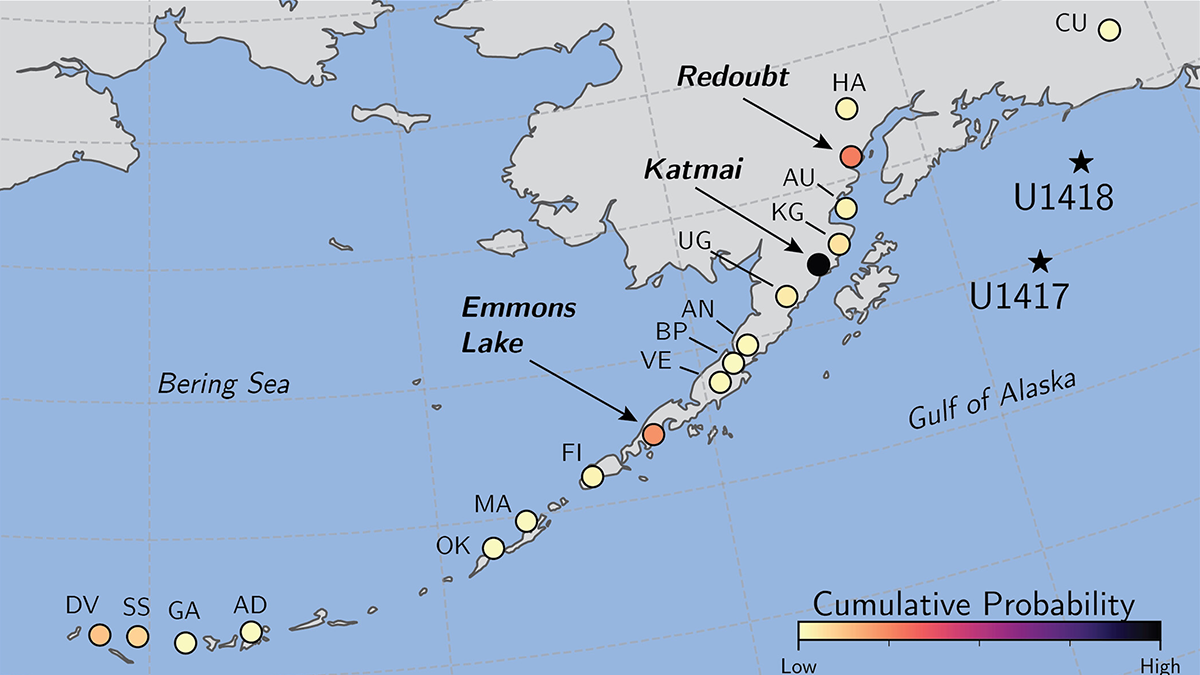
Tracing ash layers from explosive eruptions back to their source volcanoes is needed to evaluate hazards to population and aviation, a problem addressed by a new machine learning classification method.
Editors’ Highlights
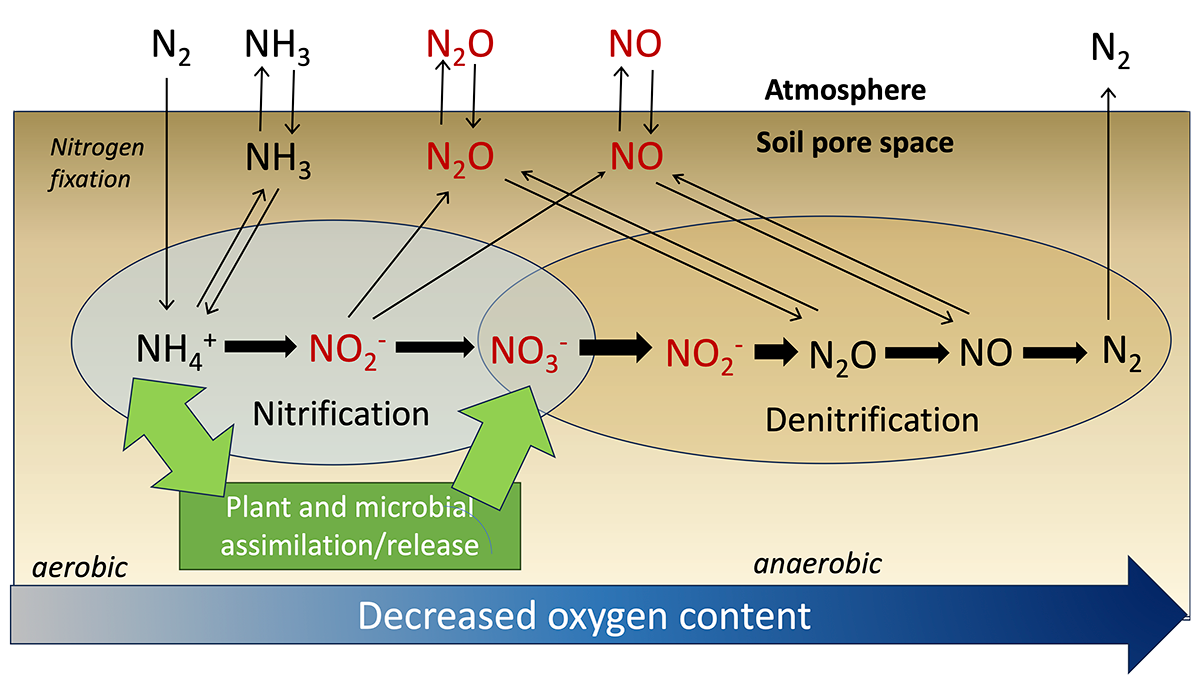
Reporting Model Results Even When They Cannot (Yet) be Tested
Models simulating the nitrogen cycle track its multiple chemical forms but tend to report a subset that can be compared with available field measurements.
Cumulus Cloud Botany in Large Domains
A new study provides a sample of shallow cumulus clouds simulated in domains 150-kilometers wide, enabling investigations of their structure and organization.
Should I Stay or Should I Go…To Another Paleomagnetic Site?
When collecting a finite number of paleomagnetic samples, having more sites, each with only one sample, achieves superior results compared to sites with multiple samples.
Grow-Fast-Die-Young Strategy Increases Swiss Forest Biomass
Climate change and CO2 fertilization can increase both growth and mortality of trees. The net effect on forest biomass depends on that trade-off, which long-term studies in Switzerland reveal.
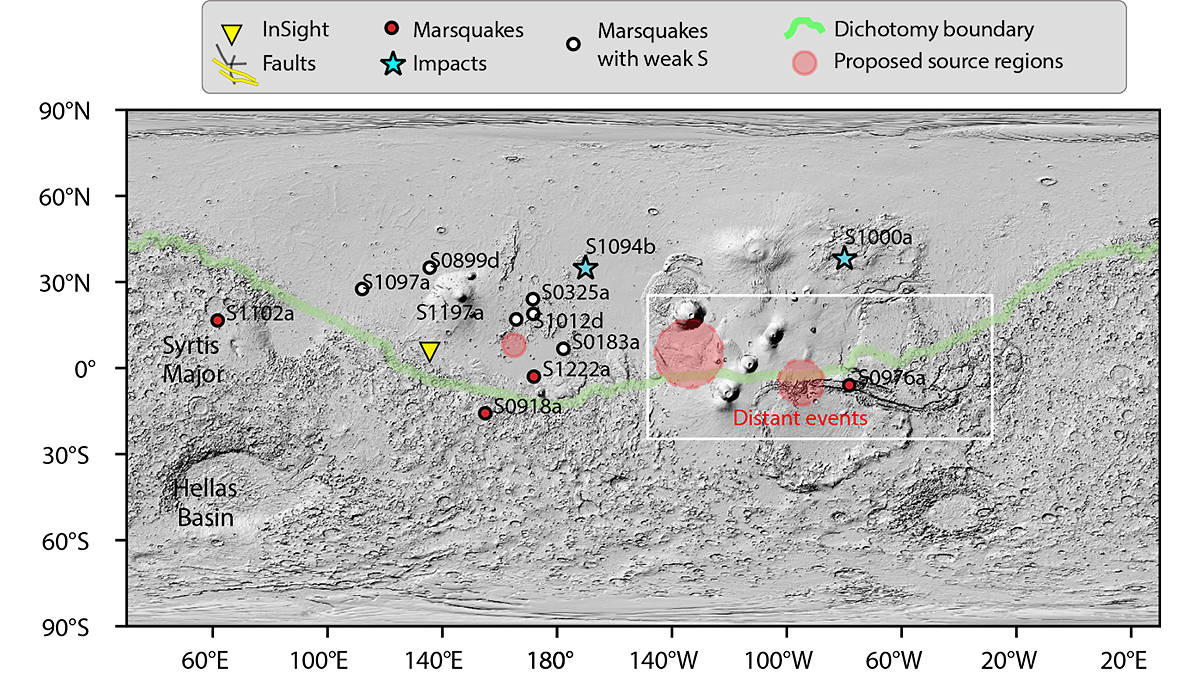
Where the Wild Marsquakes Are
A new analysis of the seismic data gathered by the InSight lander reveals that marsquakes occur across a much larger area of the planet than previously believed.
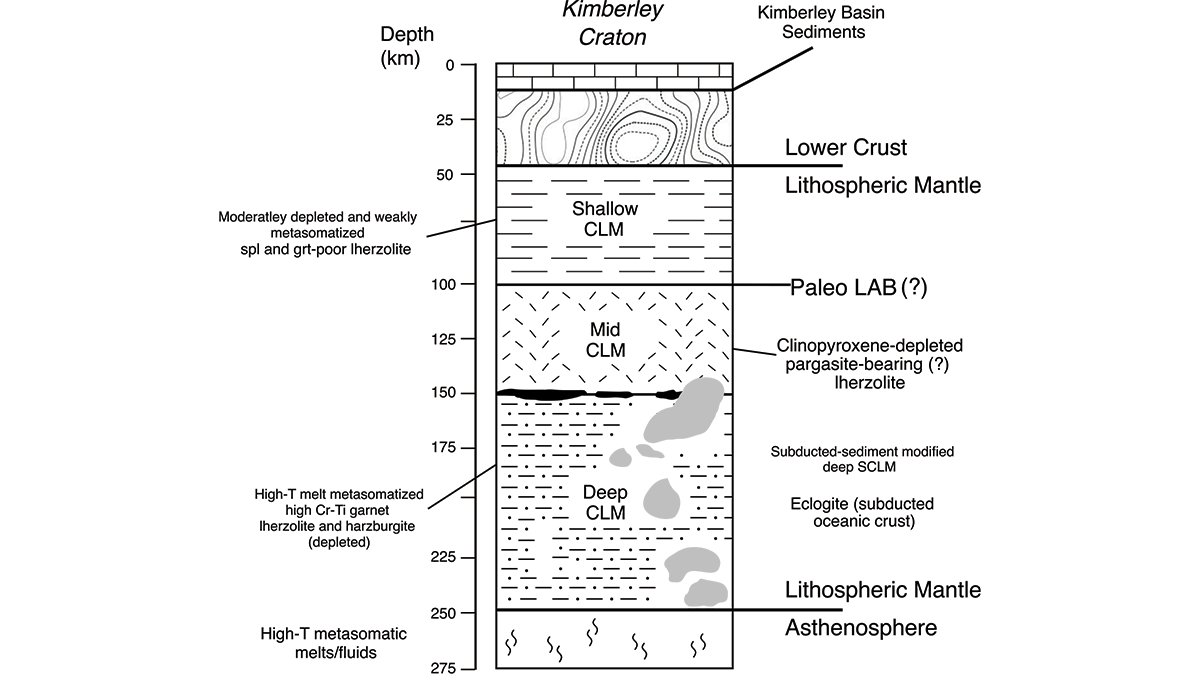
Piecing Together the Roots of the Ancient Australian Continent
Mineral compositions from numerous volcanic rocks that sample the mantle keel beneath Western Australia’s Kimberley Craton reveal the temperature and mineralogy that explain its long-lived stability.
New Aerosol Model Better Represents Black Carbon Properties
An improved representation for black carbon microphysical and optical properties alleviates overestimations of aerosol absorption efficiency in global climate models.
Rift-to-Ridge: Mid-Atlantic Ridge Segments Imprinted During Rifting
A new seismic study shows that magmatism along the eastern North American rift margin was segmented, and that rift discontinuities influence formation of fracture zones along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Ultra-High-Resolution Age Model in Clams Yields Daily Paleo-Data
Using geochemical techniques, scientists identify daily cycles in fossilized giant clams, which permits climate reconstructions at the weather timescale.