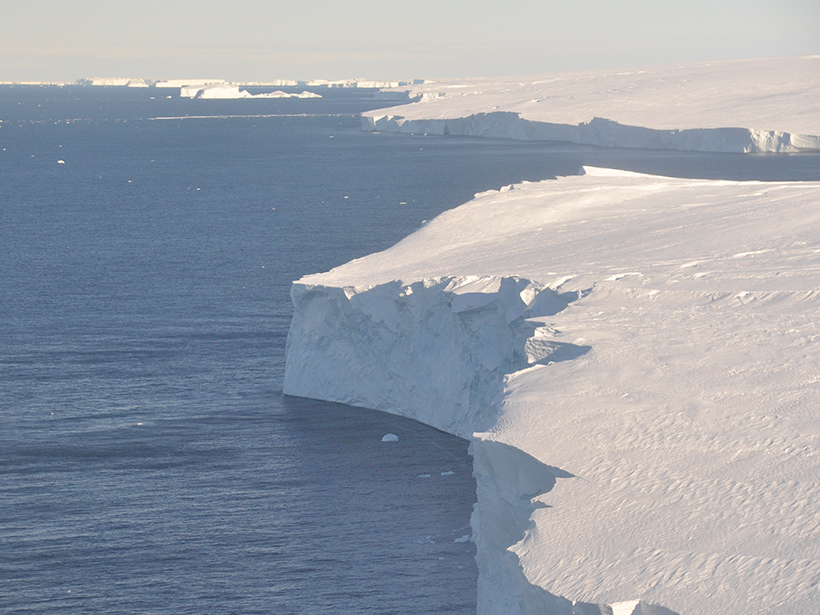
These seismic events, triggered by icebergs capsizing and ramming into Thwaites, reveal that the glacier has lost some of its floating ice shelf.
CC BY-NC-ND 2020
How Does Climate Respond to Different Forcings?
Global temperature responds in the same way to carbon dioxide as it does to methane or aerosol changes if the concept of effective radiative forcing is used to quantify the forcing strength.
Wine Grape Diversity Buffers Climate Change–Induced Losses
By mixing up which wine grape varieties are planted where, the wine industry can better ride out the effects of a warming climate, new research reveals.
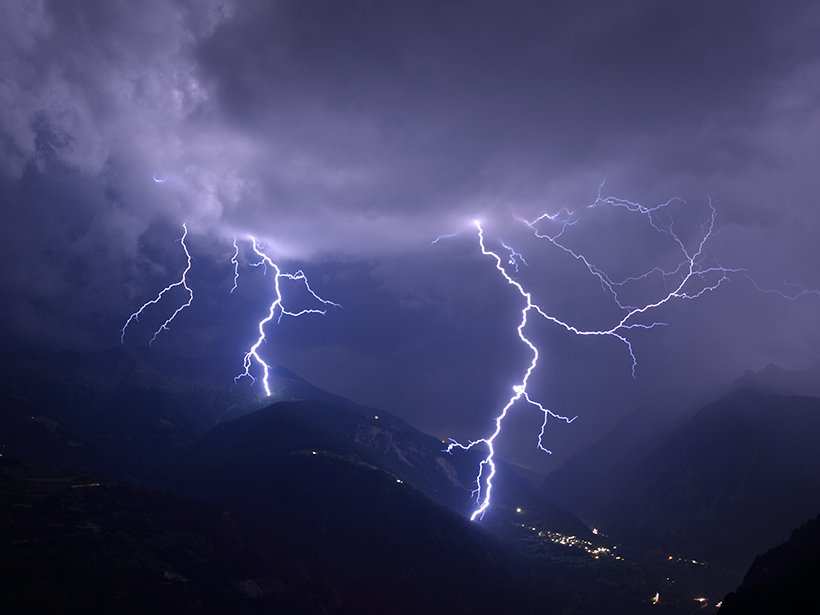
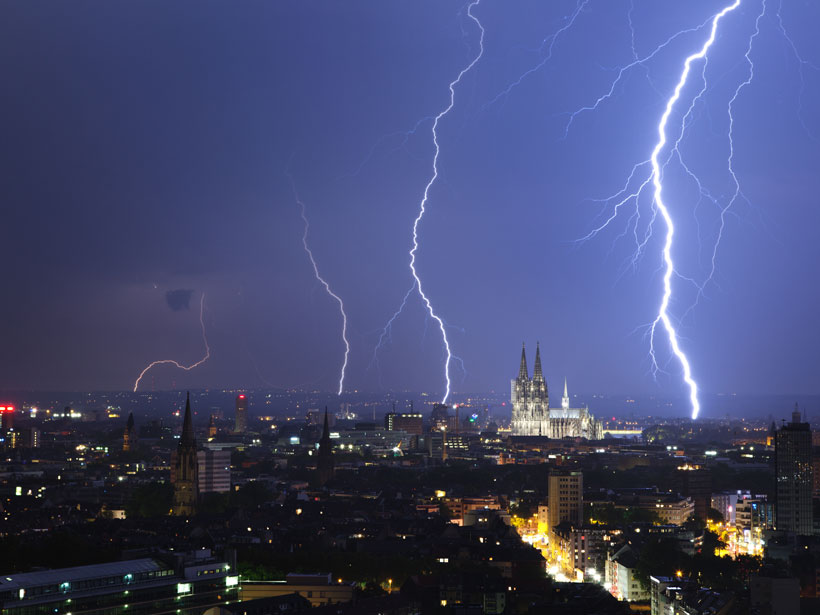
New Study Hints at Bespoke Future of Lightning Forecasting
Researchers used machine learning to develop a model that can predict lightning strikes to within 30 minutes of their occurrence and within 30 kilometers of a weather station by using just four simple atmospheric measurements.
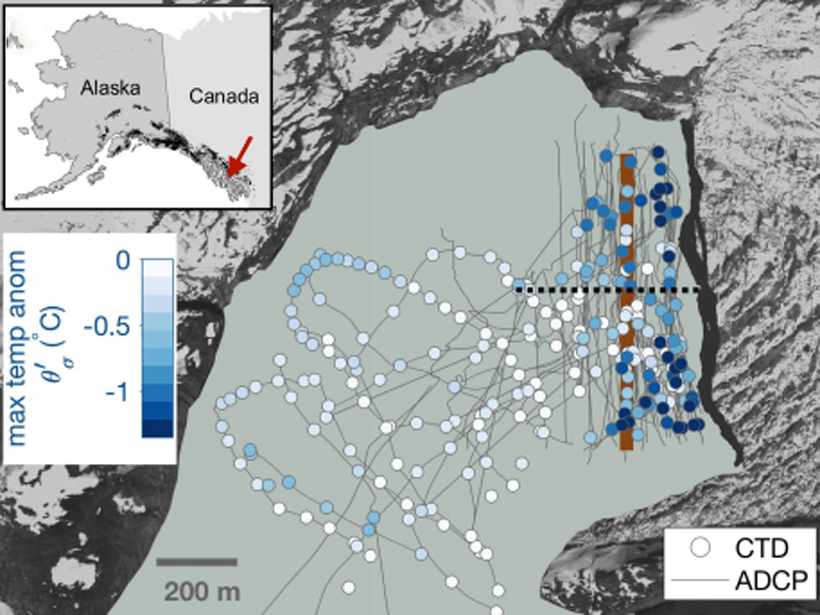
First Field Observations of Ocean Melting a Tidewater Glacier
Using autonomous kayaks, researchers carried out measurements of water properties near the terminus of LeConte Glacier and showed that ice/ocean interactions are more complex than thought.
Northern Europe Set for Increases in Lightning
As the climate warms across Europe, a rise in severe thunderstorms could bring a dramatic increase in related hazards, including lightning and hailstones.
New Clean Water Act Rule Leaves U.S. Waters Vulnerable
A revised definition of which waters can be protected from pollution by the federal government ignores established science.
The Give and Take of Mercury in Glacial Landscapes
As glacial ice melts, toxic mercury is released into the environment. But a new study shows vegetation may be an effective cleanup crew.
Where Do Natural Gas Hydrates Come from and Why Should We Care?
A new generation of models, laboratory, and field studies is helping scientists answer important questions about this mysterious substance.
Understanding Tropical Rainfall Projections Under Climate Change
A new mechanism explains changes in the probability distribution of tropical rainfall, which is not expected to change uniformly in a warming climate.