Editors’ Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU’s journal editors.
Source: Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems
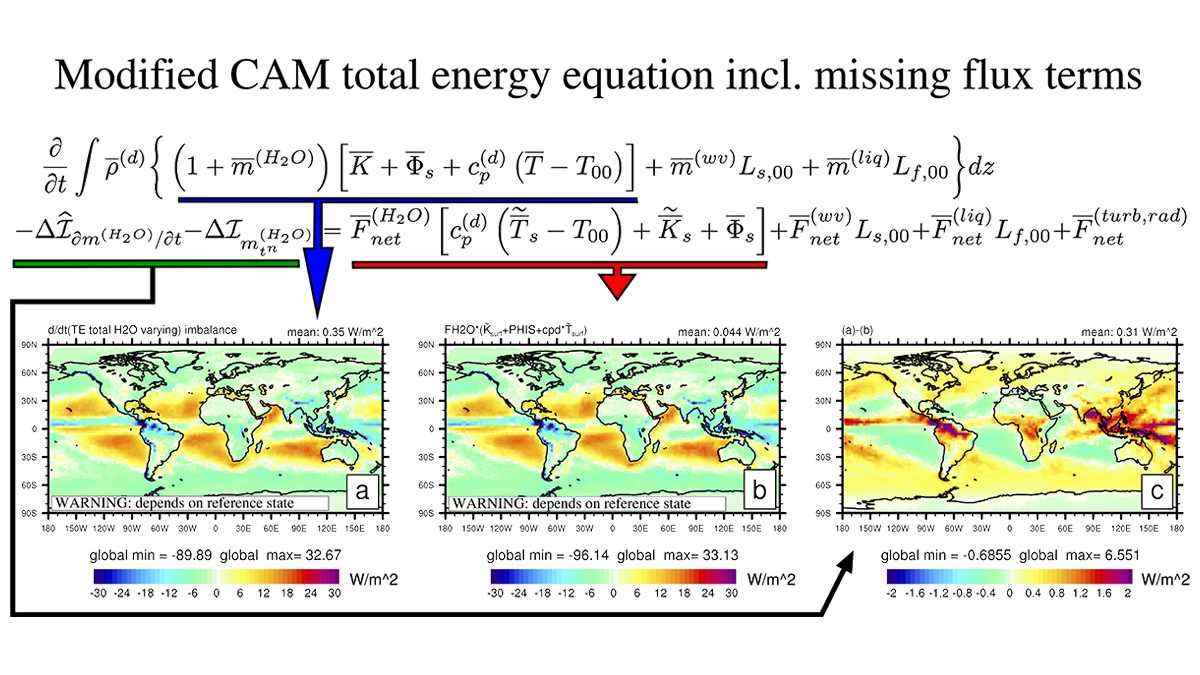
For the sake of tractability, Earth System Models make a range of approximations in their treatment of the energy budget. Consequently, diagnosing a consistent closed energy budget that captures all the processes known to be important is very difficult.
Lauritzen et al. [2022] carefully derive the energy budget for the atmospheric component of an Earth System Model and review the assumptions and approximations that are commonly made. The challenges of obtaining a consistent closed budget are discussed and illustrated using data from the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model, and some of the largest budget discrepancies are identified.
Directions and priorities for future work to improve energy budgets are discussed; these encompass the inclusion of physical processes currently neglected (such as frictional heating by falling rain), the use of a more self-consistent thermodynamic treatment, and a careful accounting for kinetic energy dissipation by the dynamical core. The article will be a valuable benchmark for future work on these topics.
Citation: Lauritzen, P.H., Kevlahan, N.K., Toniazzo, T., Eldred, C., Dubos, T., Gassmann, A., et al. (2022). Reconciling and improving formulations for thermodynamics and conservation principles in Earth System Models (ESMs). Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 14, e2022MS003117. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022MS003117
—John Thuburn, Associate Editor, Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems