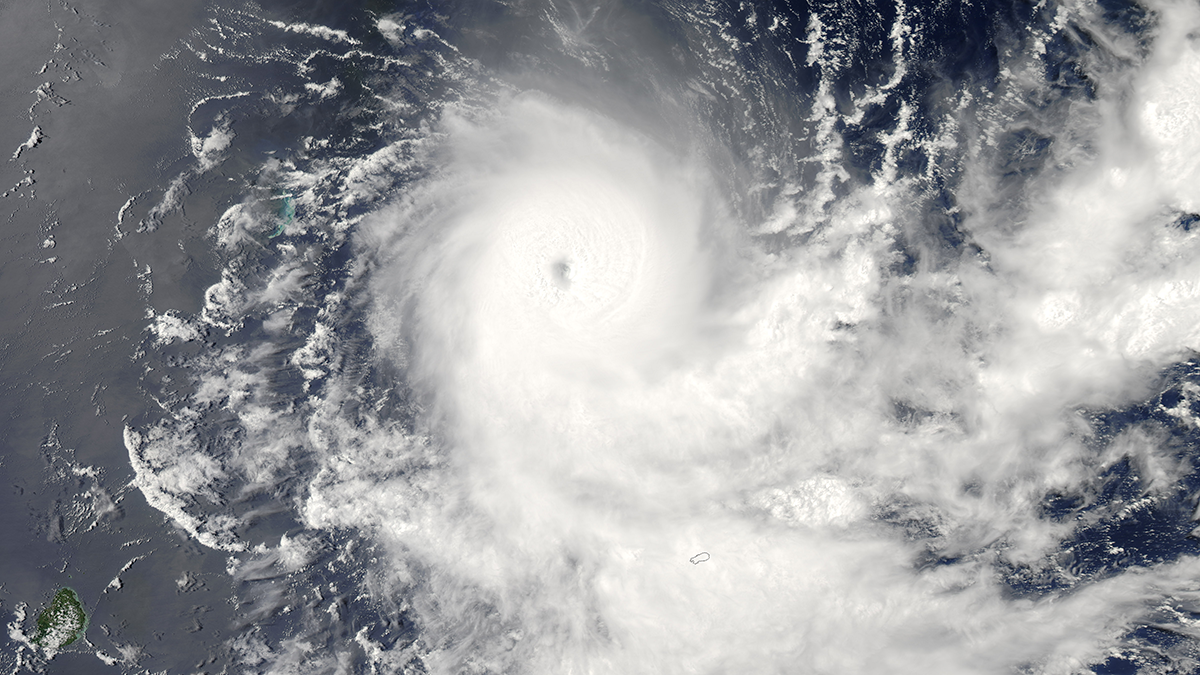
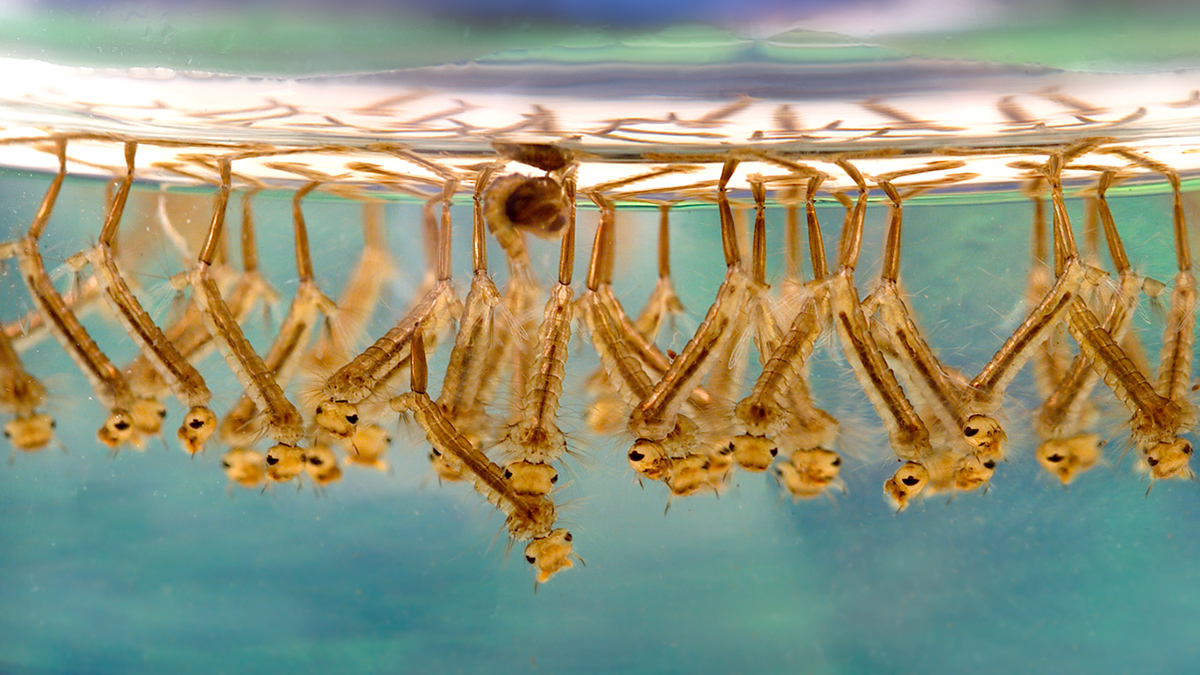
Tropopause temperature biases create major tropical cyclone differences in models; cooler air boosts storm potential intensity, raising global cyclone frequency and hurricanes in experiments.
Modeling
What do BLOBs Have to Do with Earth’s Magnetic Field? A Lot, It Turns Out
Enormous provinces of superheated mantle exert a powerful influence over our planet’s magnetic field, researchers have discovered.
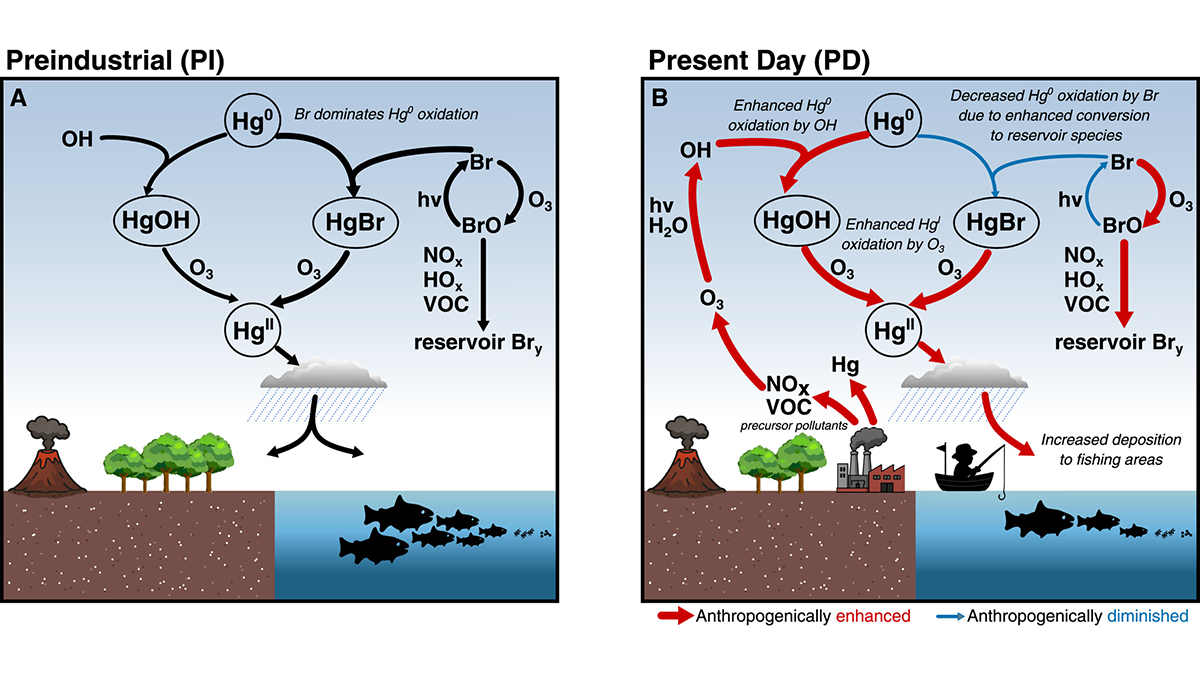
Human Effects on Background Atmosphere have Affected Mercury Chemistry
Atmospheric mercury chemistry has evolved over time due to changes in atmospheric composition, especially for changing concentrations of bromine radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and ozone.
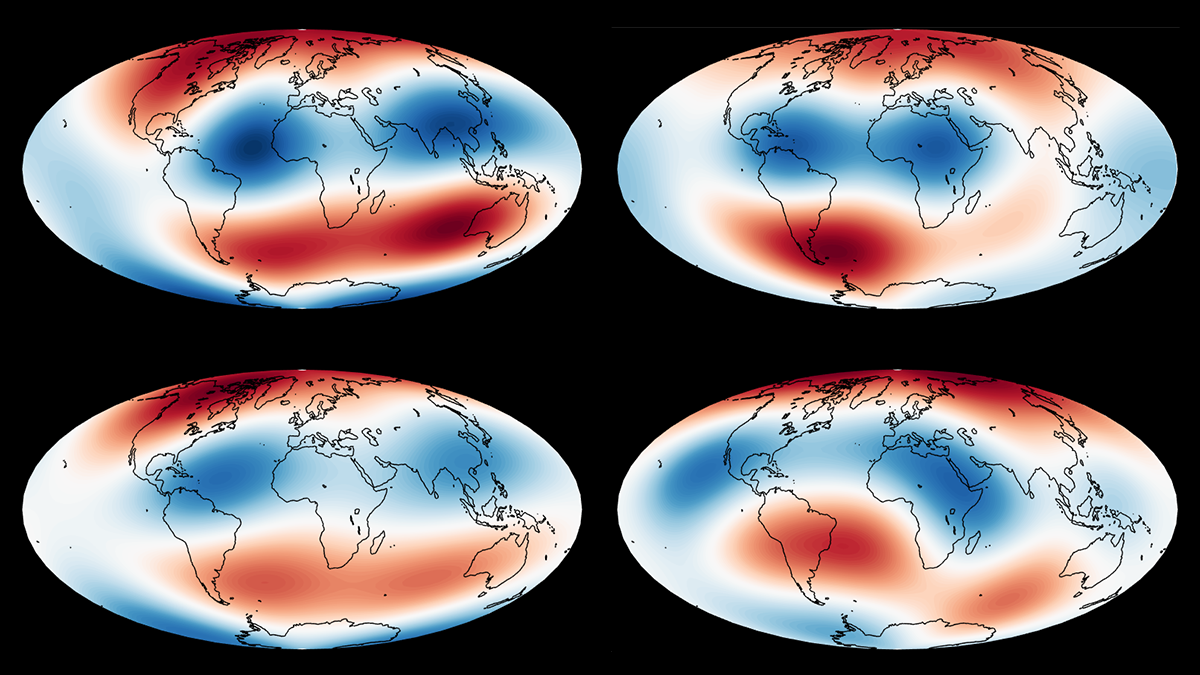
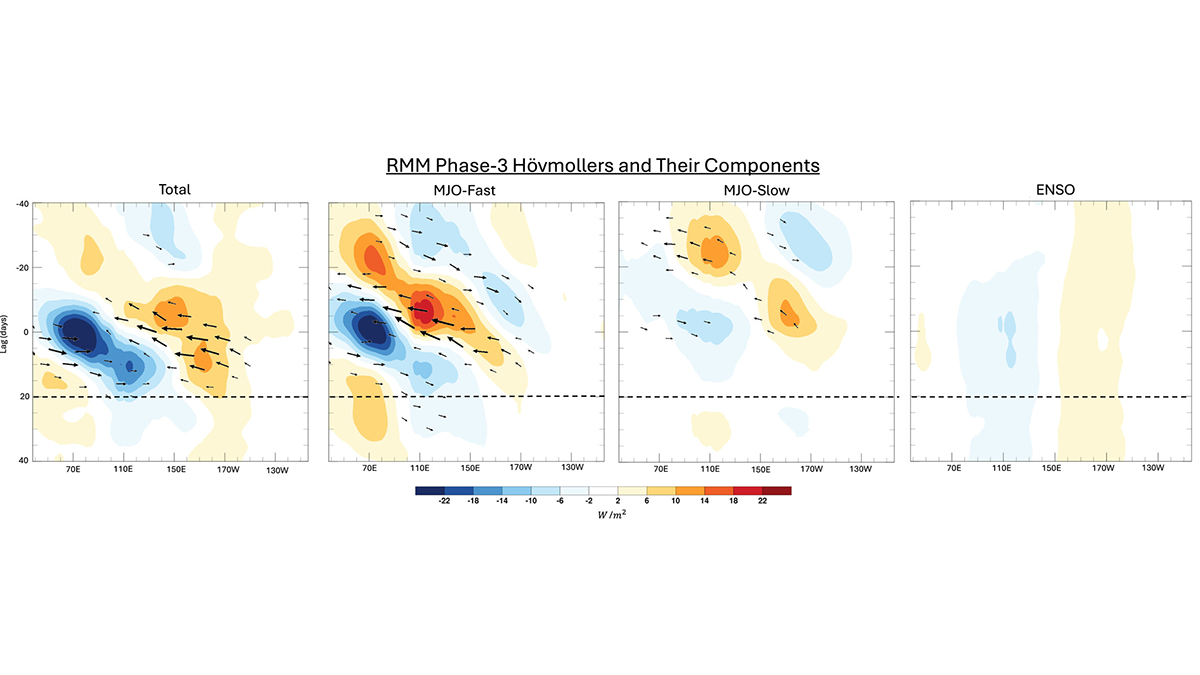
Slow and Fast Madden-Julian Oscillation Modes
The skill of Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) forecasts can be improved by identifying slow- and fast-MJO modes and their superposition.
How to Accelerate Advances in Ecological Forecasting
Developing shared cyberinfrastructure can enhance predictions of ecological change and enable improved decisionmaking for resource management and public well-being.
New Method Could Improve U.S. Forecasting of West Nile Virus
An innovative model uses regional climate data and records of West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease to outperform existing forecasts, potentially helping communities prepare.
Earth’s Climate May Go from Greenhouse to Hothouse
Uncertainty in climate models could mean Earth systems are perilously close to their tipping points, scientists warn.
The AMOC of the Ice Age Was Warmer Than Once Thought
An analysis of sediment cores indicates that North Atlantic waters were relatively warm and continued to circulate even under major climate stress during the Last Glacial Maximum.
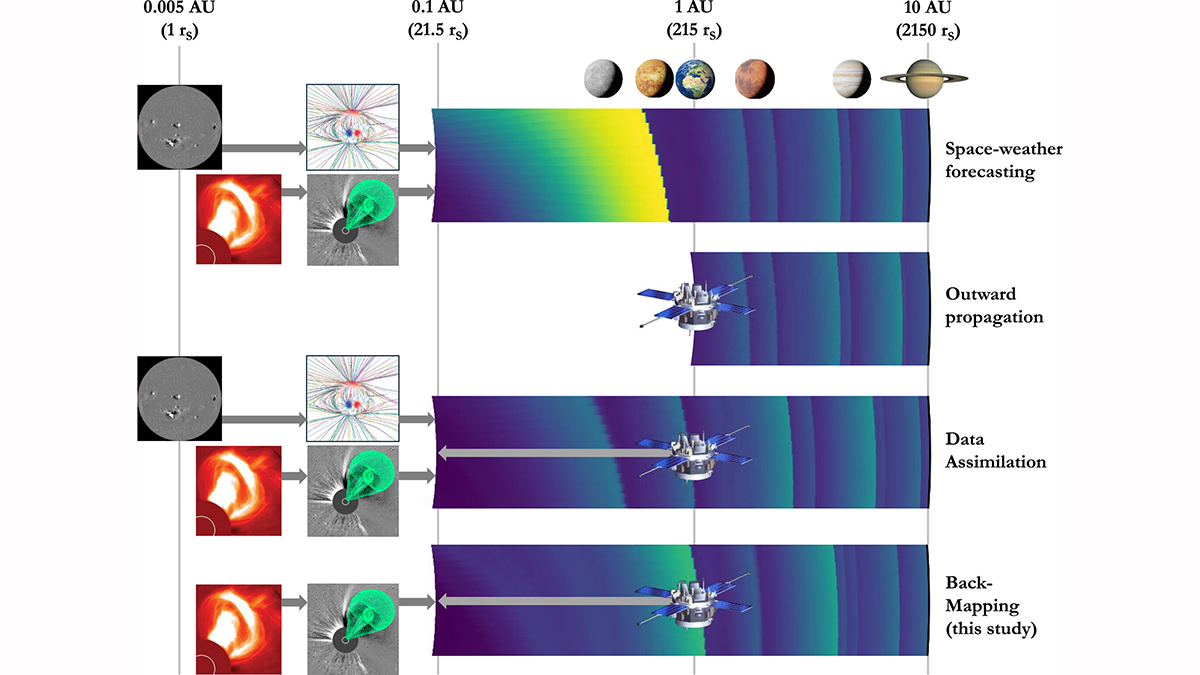
From Measurements to Solar Wind Model Initial Conditions
A new method shows how solar wind measurements at Earth can be used to define initial conditions for solar wind models to reduce their need for solar magnetic maps and decrease their uncertainty.
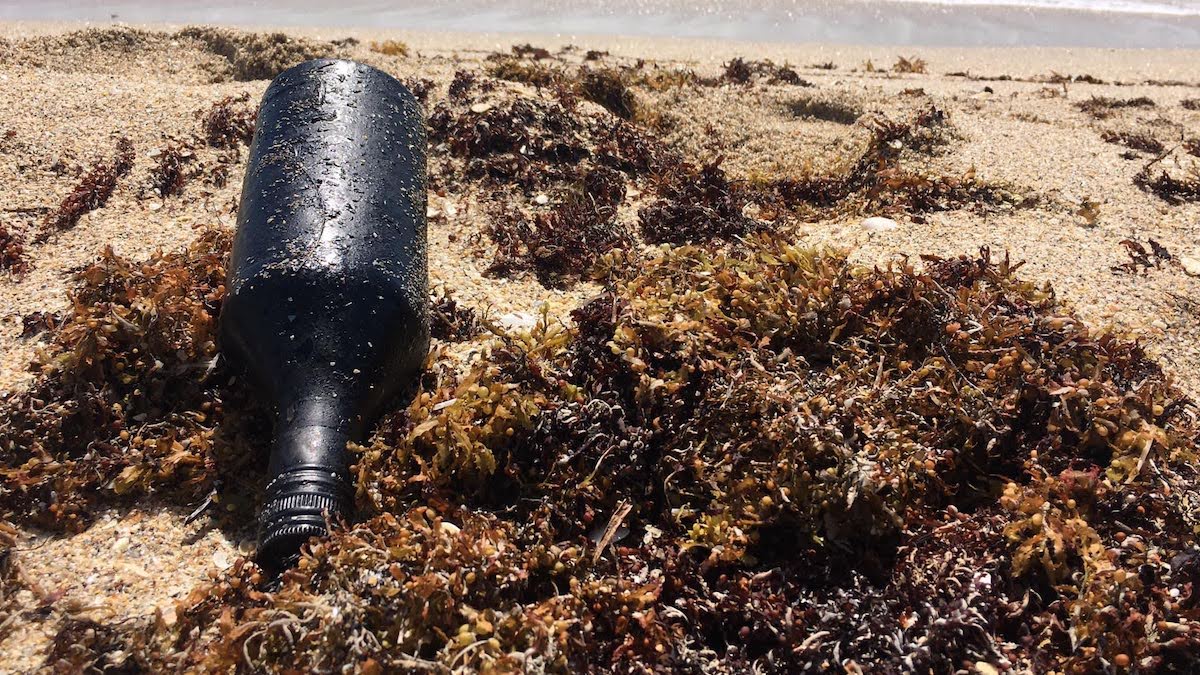
Plastic Debris Helps Oil Residues Reach Farther Across the Ocean
Scientists matched oil residues found in Florida to a Brazilian spill thousands of miles away.