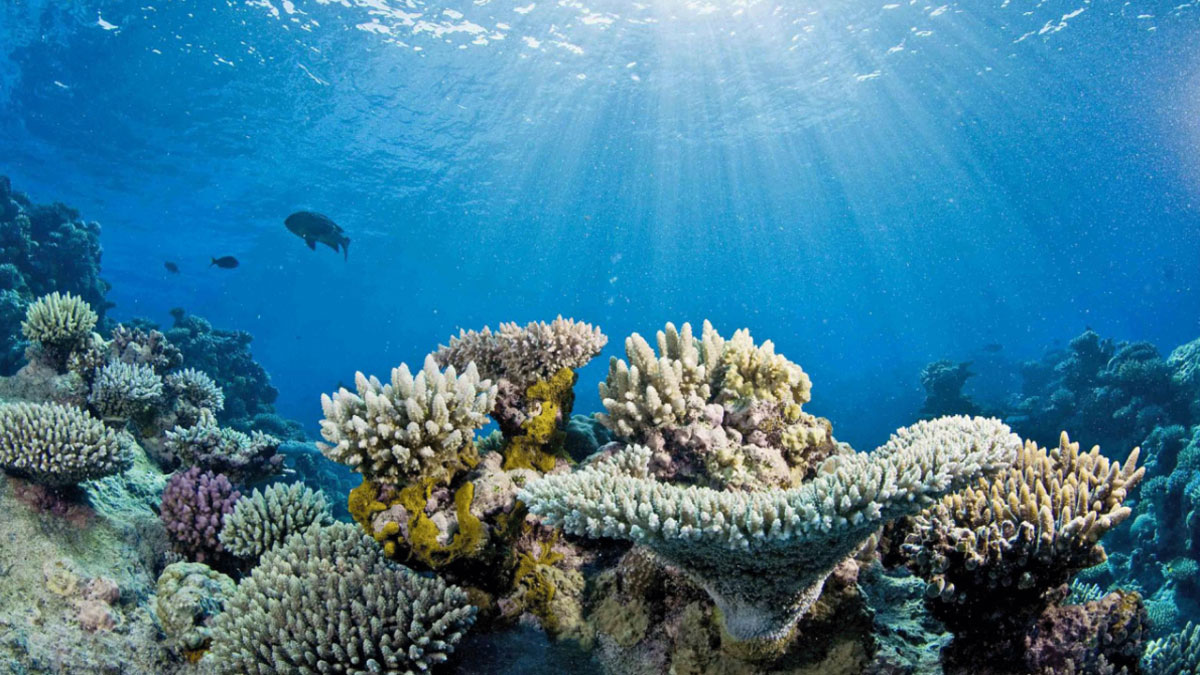
New research indicates a well-studied form of climate intervention might at least buy time for many at-risk reefs.
Modeling
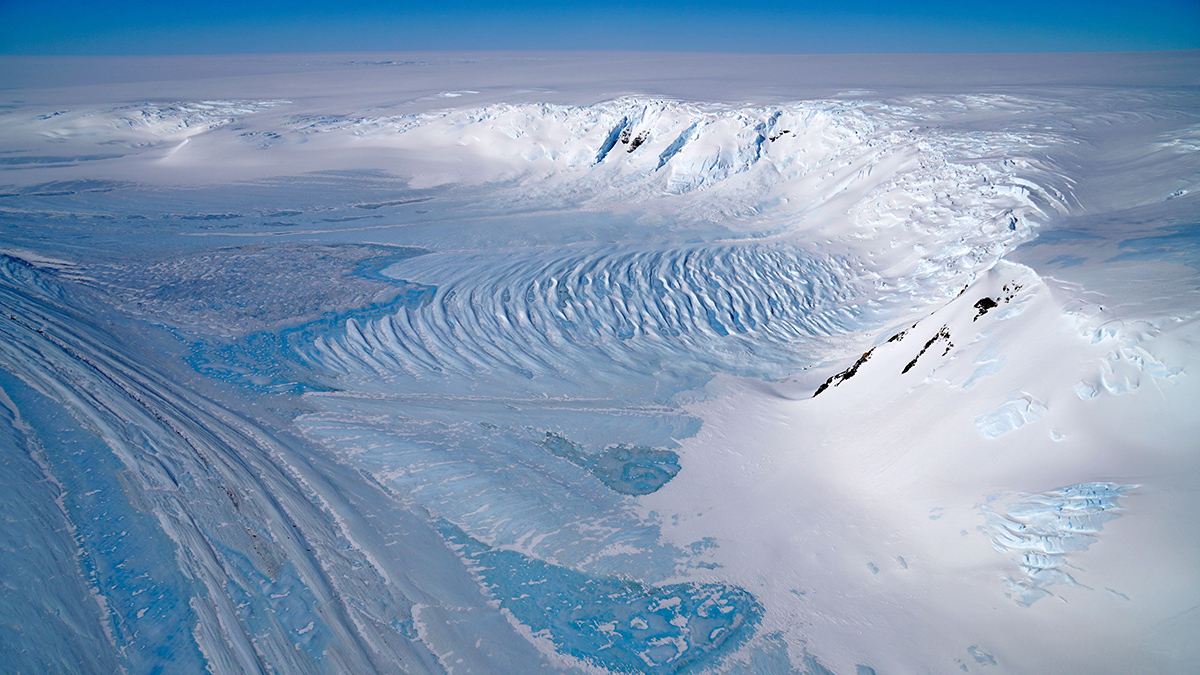
New Lessons from Old Ice: How We Understand Past (and Future) Heating
Fragments of blue ice up to 6 million years old—the oldest ever found—offer key insights into Earth’s warming cycles. Researchers are using these ancient data to refine models of our future climate.
Understanding Flux, from the Wettest Ecosystems to the Driest
Pulses of activity, from tides to precipitation swings, play a crucial, changing role in ecosystems worldwide.
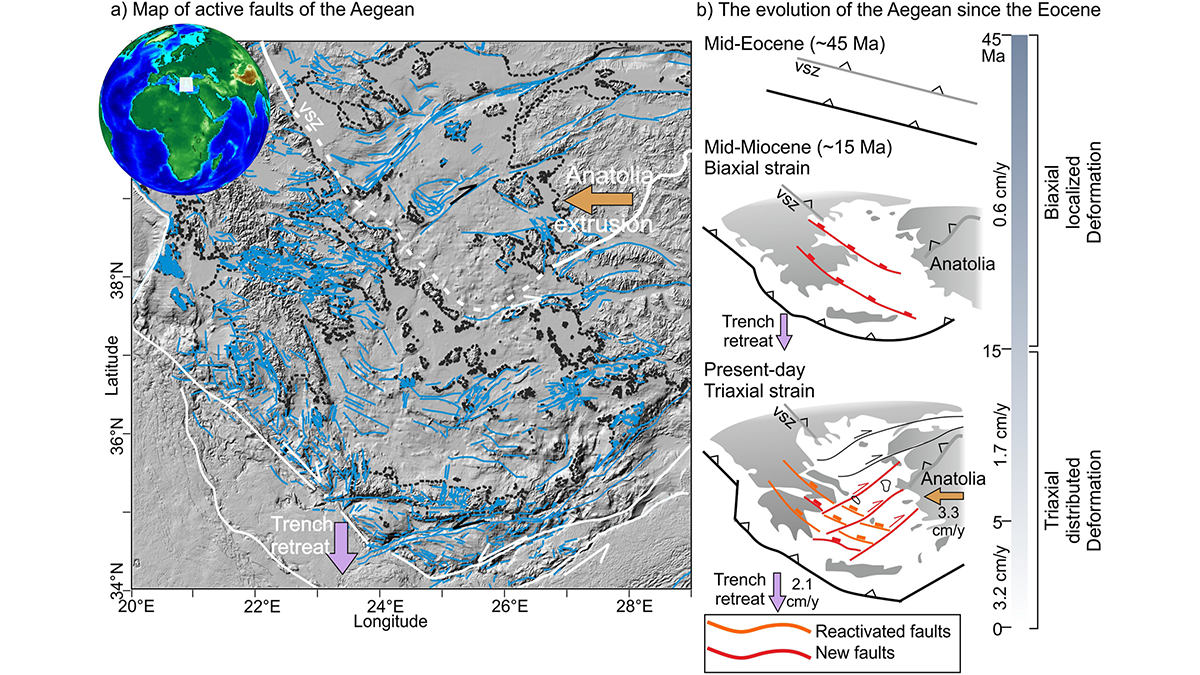
The Language of the Crust: Investigating Fault-to-Fault Interactions
Faults don’t just form—they respond, resist, and reshape the crustal narrative.
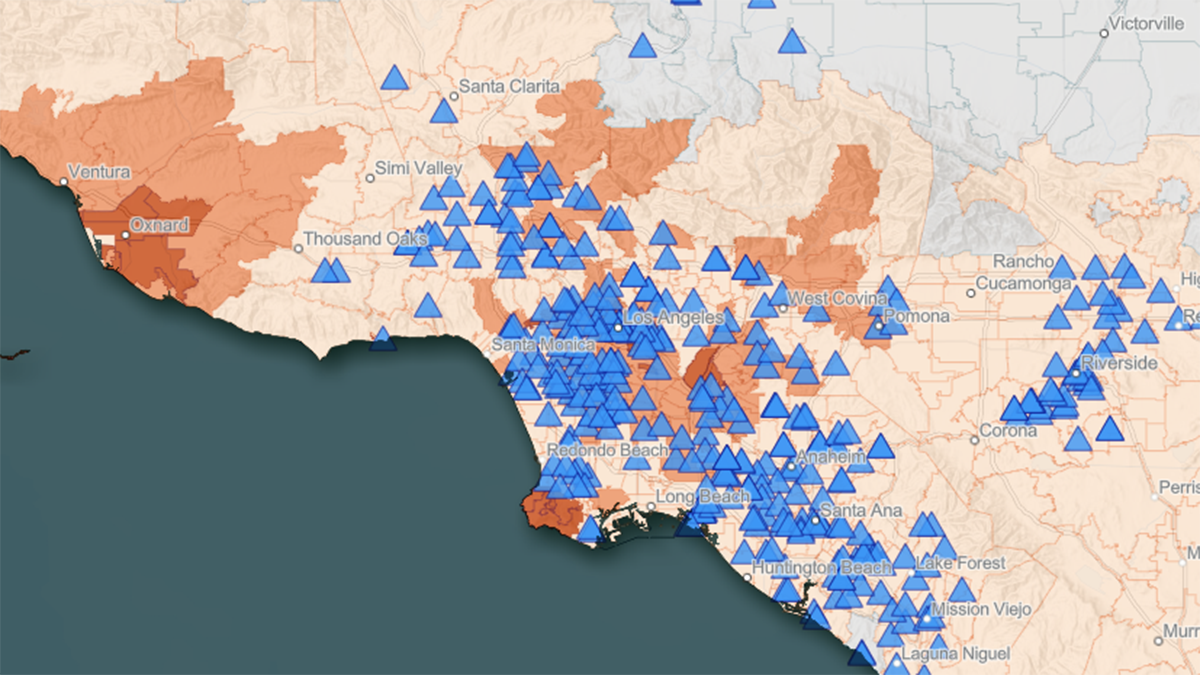
New Tool Maps the Overlap of Heat and Health in California
CalHeatScore creates heat wave warnings for every zip code in California, using temperature data, socioeconomic indicators, and the history of emergency room visits, to predict heat-related health risk.
全球气候模型需要全面纳入氮循环
氮在气候变化、人类健康和农业等领域发挥着重要作用。一位研究人员认为,气候模型若能更全面地纳入氮的影响,将会受益匪浅。
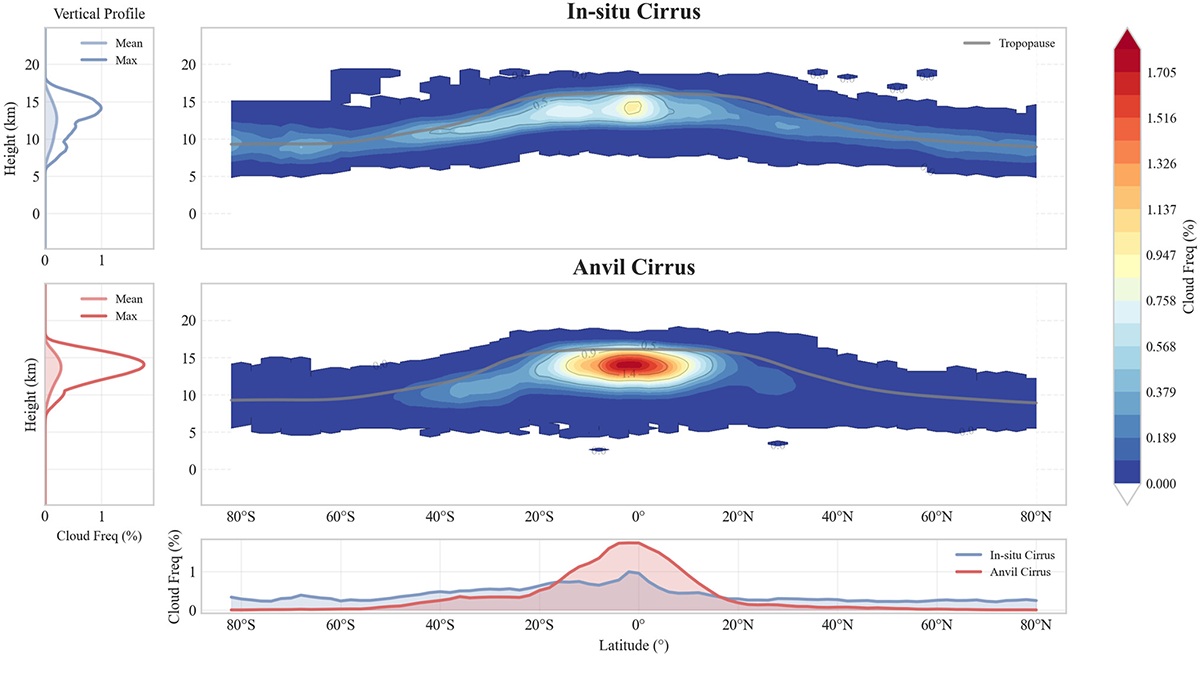
Understanding Relative Atmospheric Roles of Anvil and In-situ Cirrus Clouds
New framework for separating anvil and in-situ cirrus clouds provides a pathway for modeling cirrus and how regional shifts in convection could reshape global cirrus distributions and their radiative impact.
Understanding Cloud Droplets Could Improve Climate Modeling
The microphysical structure of cloud droplets affects behavior like precipitation. Current models may be underestimating how much these structures can vary within a single cloud.
Are “Day Zero Droughts” Closer Than We Think? Here’s What We Know
A new study warns that day zero droughts—when reservoirs fail to supply taps—could become common within this decade.
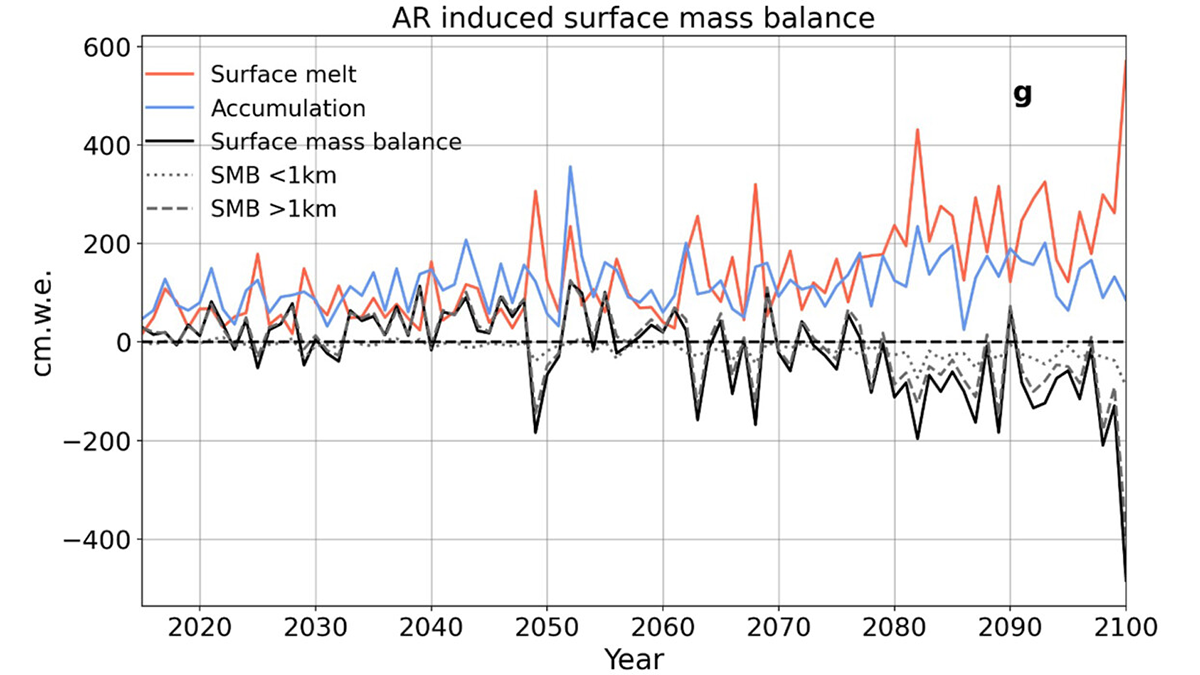
Atmospheric Rivers Shaped Greenland’s Ancient Ice
New simulations reveal how atmospheric rivers influenced Greenland’s ice sheet during the Last Interglacial—offering clues to future melt in a warming world.