Unusually warm ocean waters can amplify extreme rainfall in downwind areas, leaving coastal communities—especially those in developing countries—at risk.
everything atmospheric
Understanding Aerosol-Cloud Interactions is Pivotal for Improving Climate Predictions
Global cooperation and knowledge sharing are essential to improve our understanding of cloud formation and evolution through aerosol-cloud interaction.
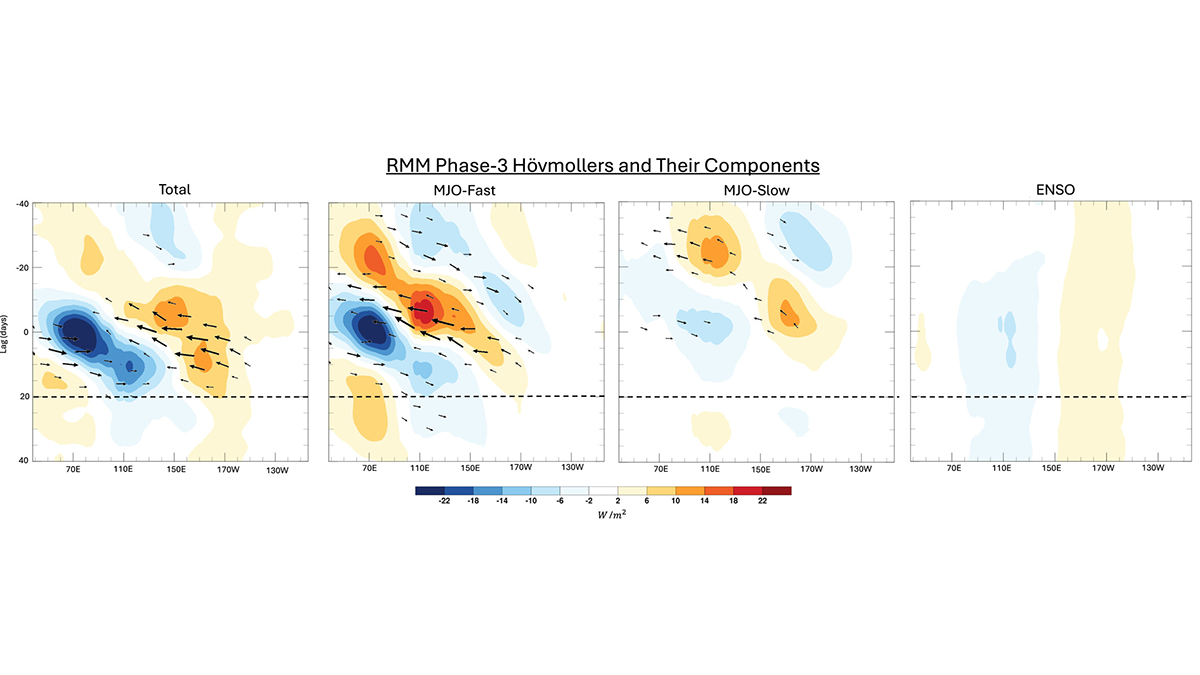
Slow and Fast Madden-Julian Oscillation Modes
The skill of Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) forecasts can be improved by identifying slow- and fast-MJO modes and their superposition.
Linking Space Weather and Atmospheric Changes With Cosmic Rays
Water-Cherenkov cosmic-ray detectors can be used as a tool for monitoring and studying changes in the lower stratosphere over Antarctica.
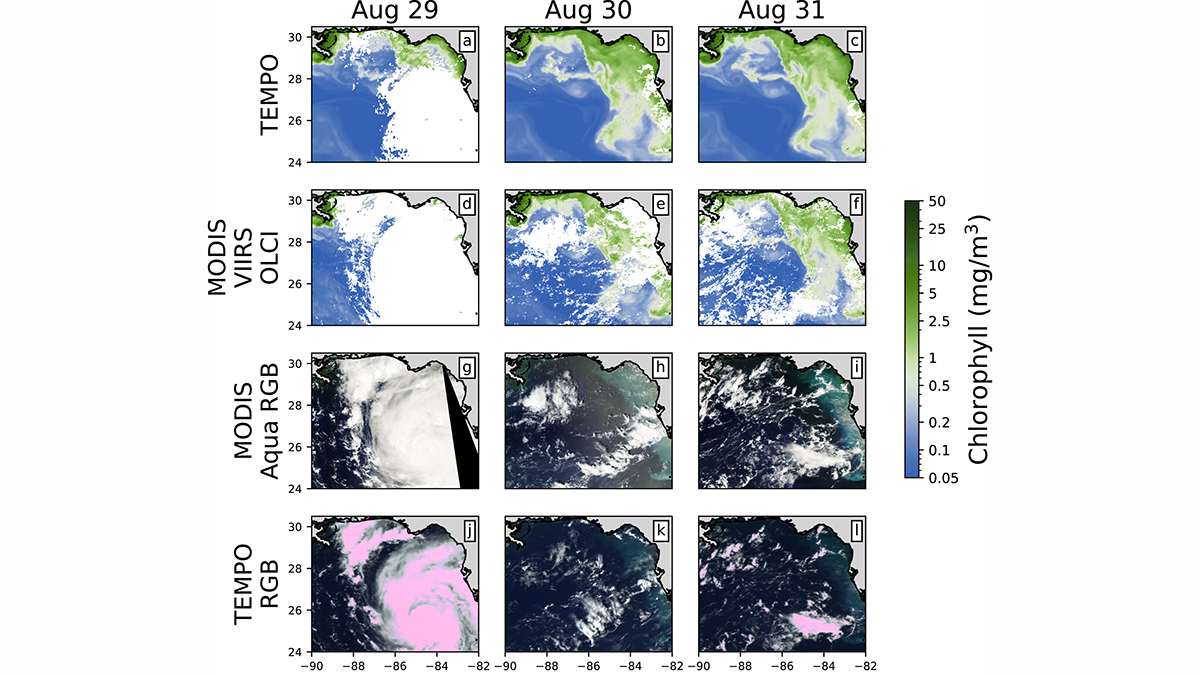
Monitoring Ocean Color From Deep Space: A TEMPO Study
Scientists apply machine learning to demonstrate that geosynchronous satellites can be used to assess the health of oceans from deep space.
Why Are Thunderstorms More Intense Over Land Than Ocean?
A new perspective on convective instability sheds light on the factors controlling intensity in the rising motions that produce precipitation, and occasionally thunder and lightning, over land.
Tsunamis from the Sky
Not all tsunamis come from the seafloor, some are triggered by the atmosphere, driven by fast-moving storms and pressure waves, and can strike coasts with little warning.
What Americans Lose If Their National Center for Atmospheric Research Is Dismantled
Five ways dismantling NCAR will cost the American people, and two ways to save it.
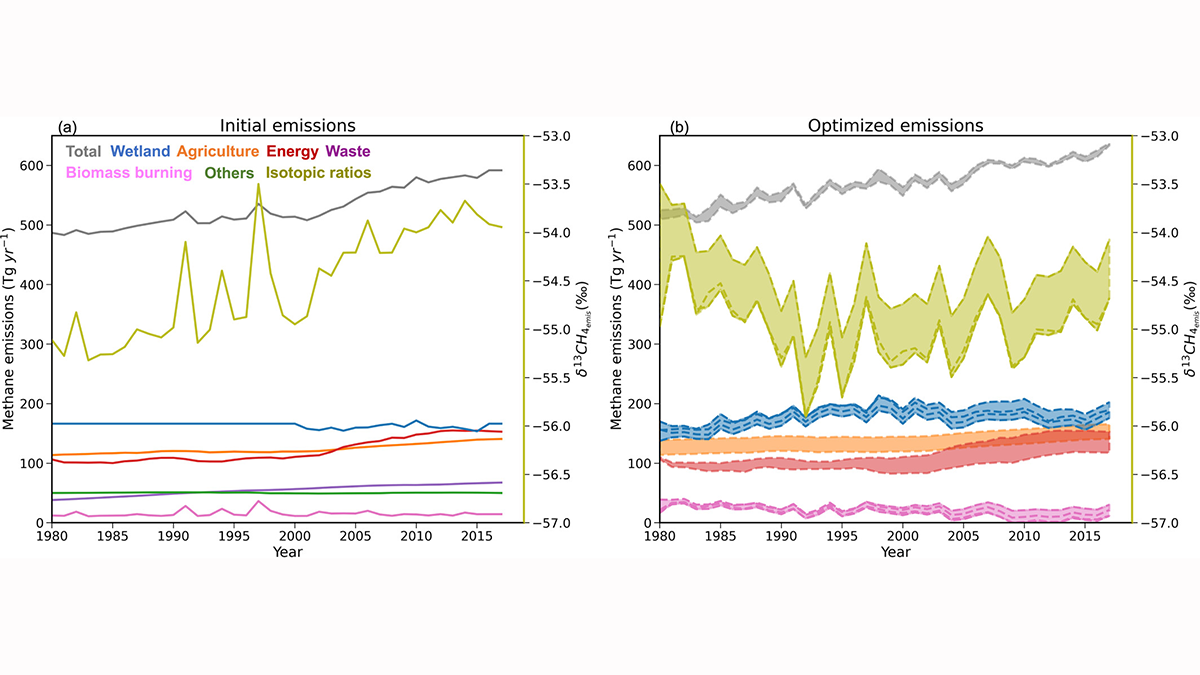
Cows, Coal, and Chemistry: The Role of Photochemistry in Methane Budget
Recent increases in atmospheric methane are a result of changing natural and manmade sources, climate, and other less-understood factors linked to its role in the atmosphere’s self-cleaning mechanisms.
New Insights into the Foggy Role of Contrails Within Clouds
New research helps clarify how frequently contrails form within clouds and what that means for their effect on the climate.