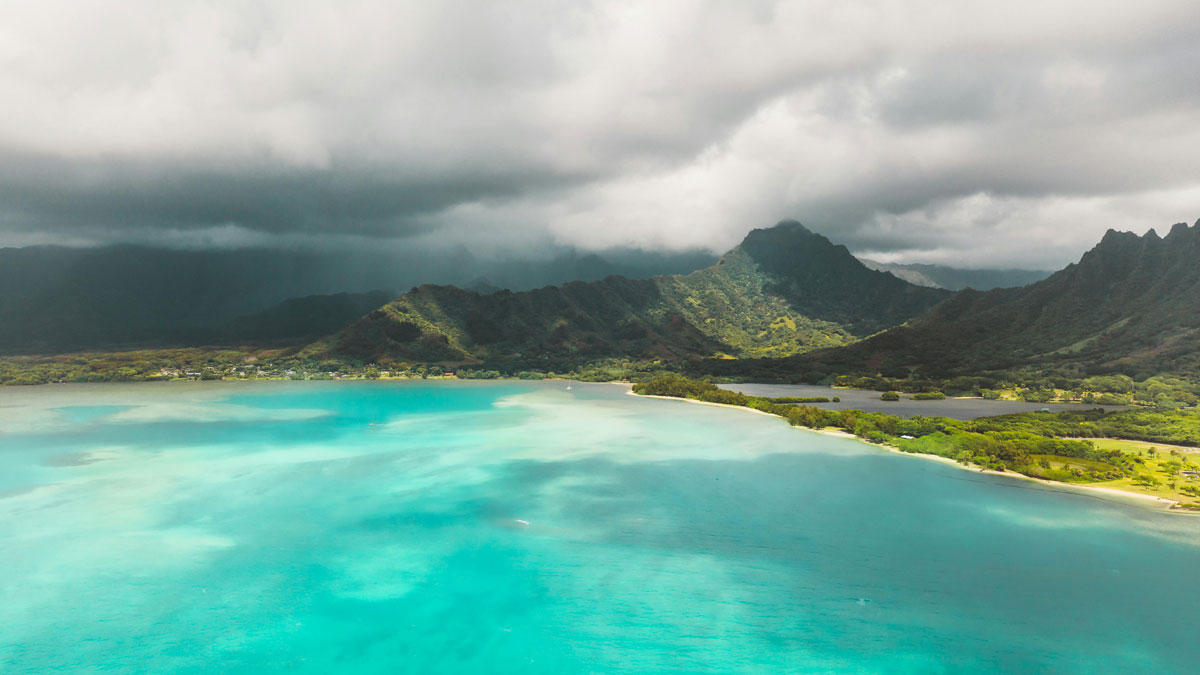
Isolated islands that depend on rainfall could benefit from improved forecasting of near-future events, and understanding the Madden-Julian Oscillation could hold an important key.
everything atmospheric
Trump Administration Plans to Break Up NCAR
The Trump administration is planning to dismantle the National Center for Atmospheric Research, one of the world’s leading climate and Earth science research laboratories, according to a statement from Russ Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, to USA Today.
Is Convection Wobbling Venus?
Venus’s rotation axis is not where it should be – but atmospheric torques, not mantle convection, are likely responsible.
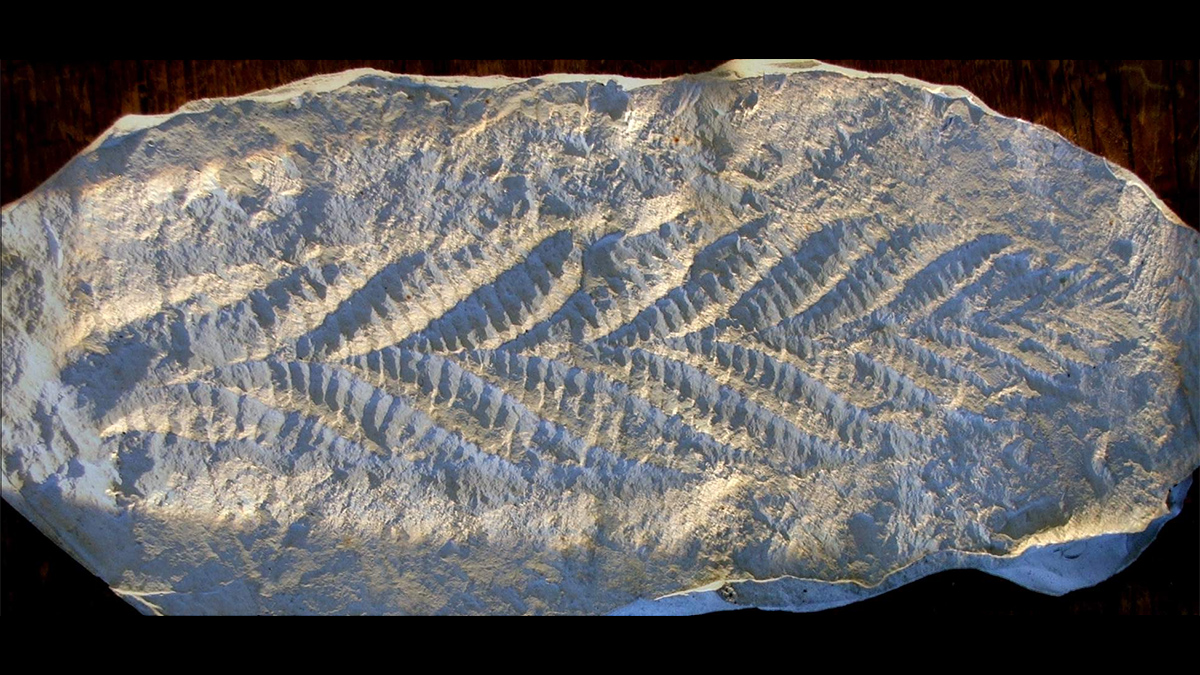
The Long and the Weak of It—The Ediacaran Magnetic Field
A roughly 70-million-year interval of anomalously weak magnetic field during the Ediacaran period could have triggered atmospheric changes that supported the rise of macroscopic life.
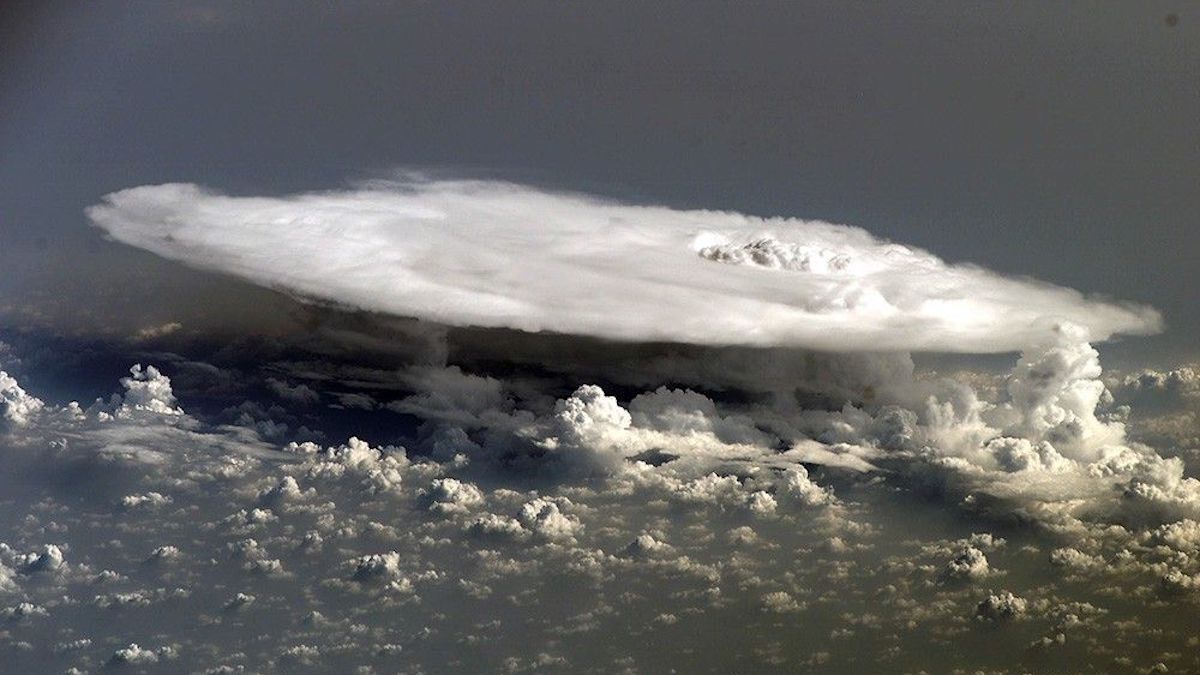
Some Summer Storms Spit Sooty Particles into the Stratosphere
Earth’s typically pristine stratosphere is filling with particles from wildfires and additional moisture due to strong convective storms.
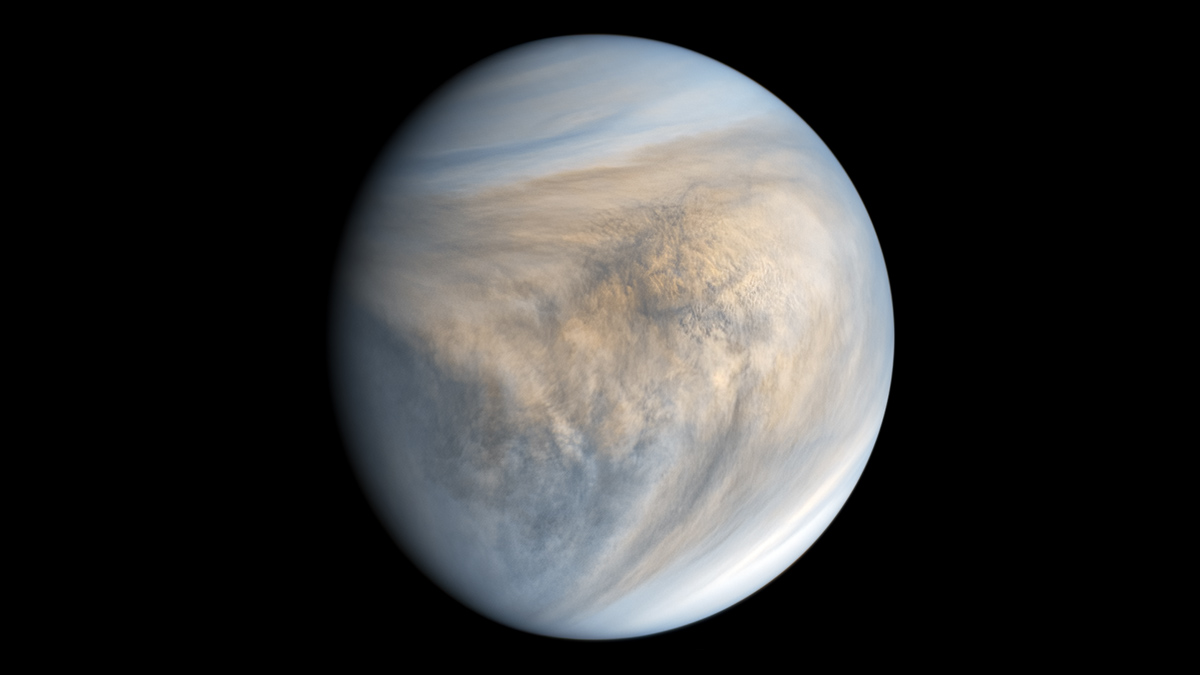
Key Driver of Extreme Winds on Venus Identified
A new study suggests that a once-daily atmospheric tidal cycle may be a bigger driver of rapid Venusian winds than previously thought.
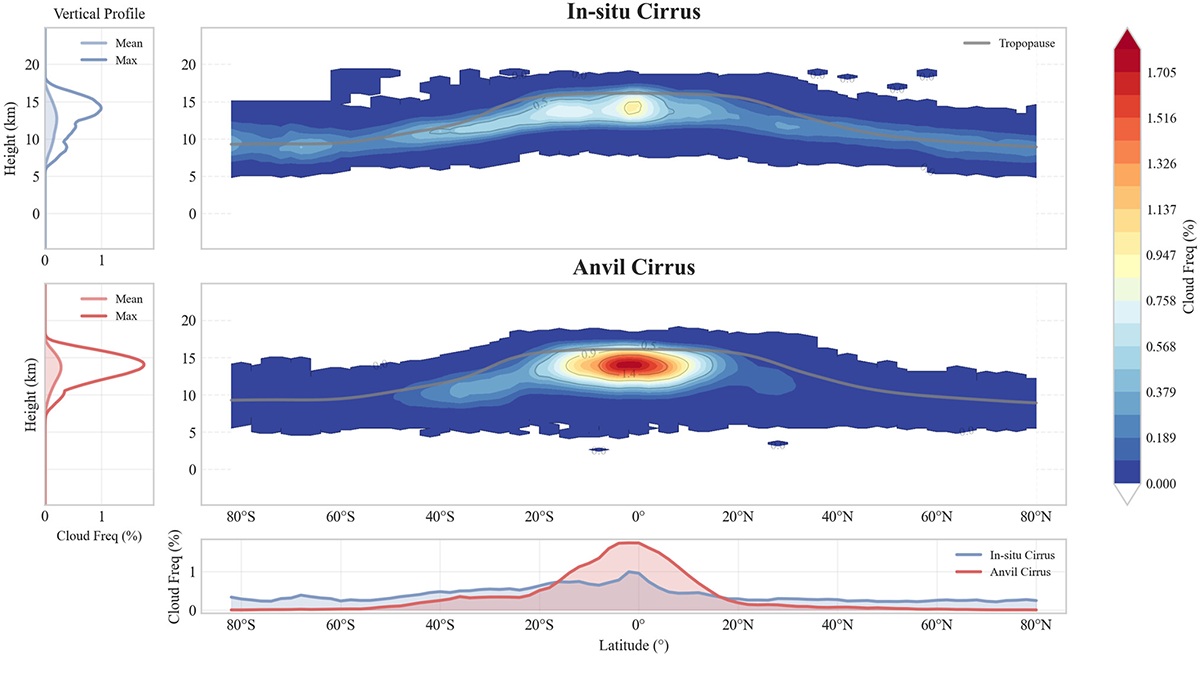
Understanding Relative Atmospheric Roles of Anvil and In-situ Cirrus Clouds
New framework for separating anvil and in-situ cirrus clouds provides a pathway for modeling cirrus and how regional shifts in convection could reshape global cirrus distributions and their radiative impact.
Understanding Cloud Droplets Could Improve Climate Modeling
The microphysical structure of cloud droplets affects behavior like precipitation. Current models may be underestimating how much these structures can vary within a single cloud.
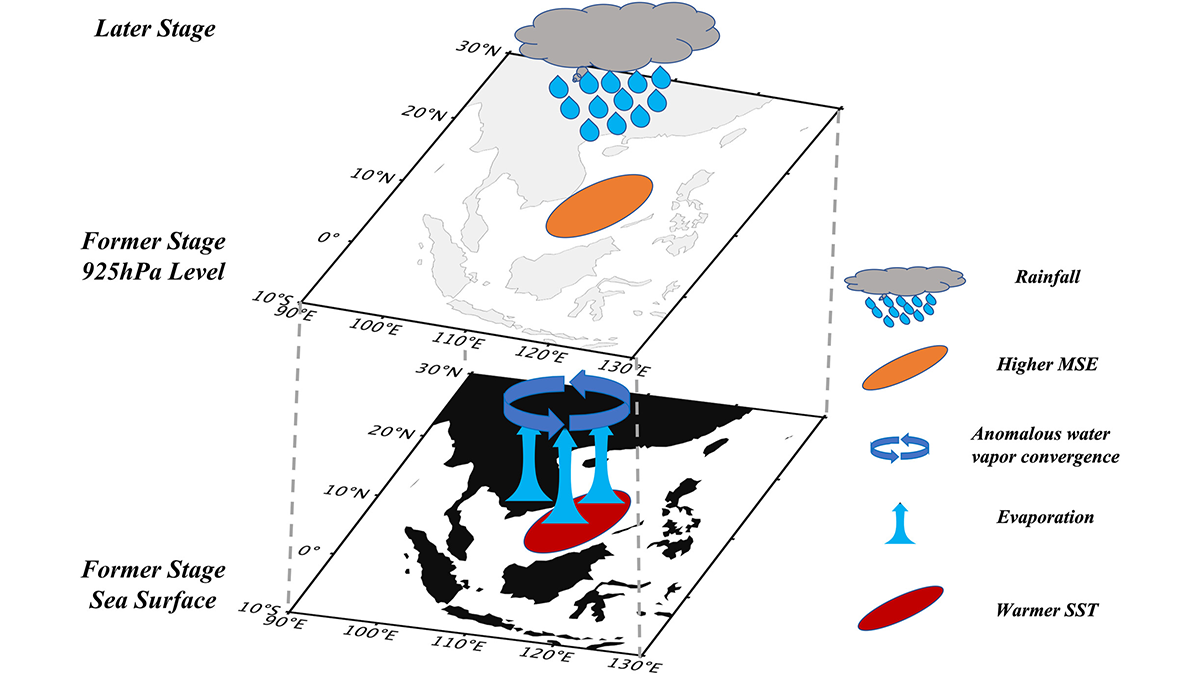
Marine Heatwaves Reshape Precipitation Patterns
Most marine heatwaves experience reduced precipitation throughout their lifetime, but warmer events in the early stage can trigger increased precipitation after reaching peak intensity, causing faster decay.
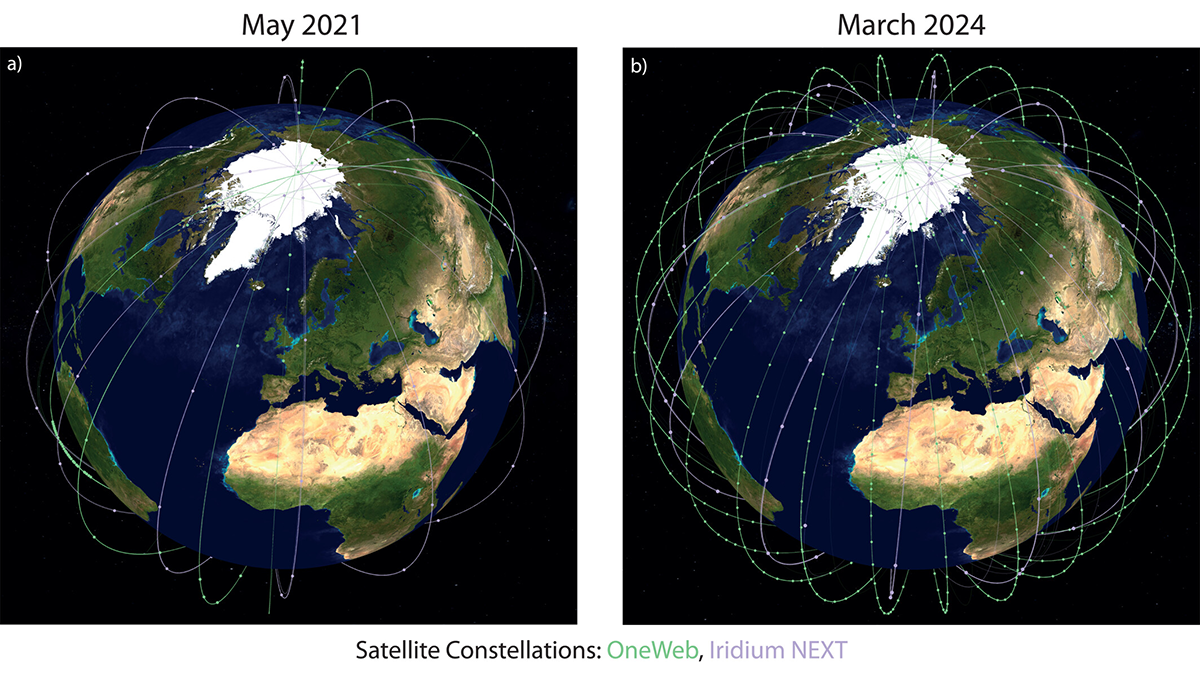
Space Weather Monitoring from Commercial Satellite Mega-Constellations
Enabling unprecedented monitoring of key electric current systems in low-Earth orbit using commercial satellite mega-constellations advances space weather monitoring.