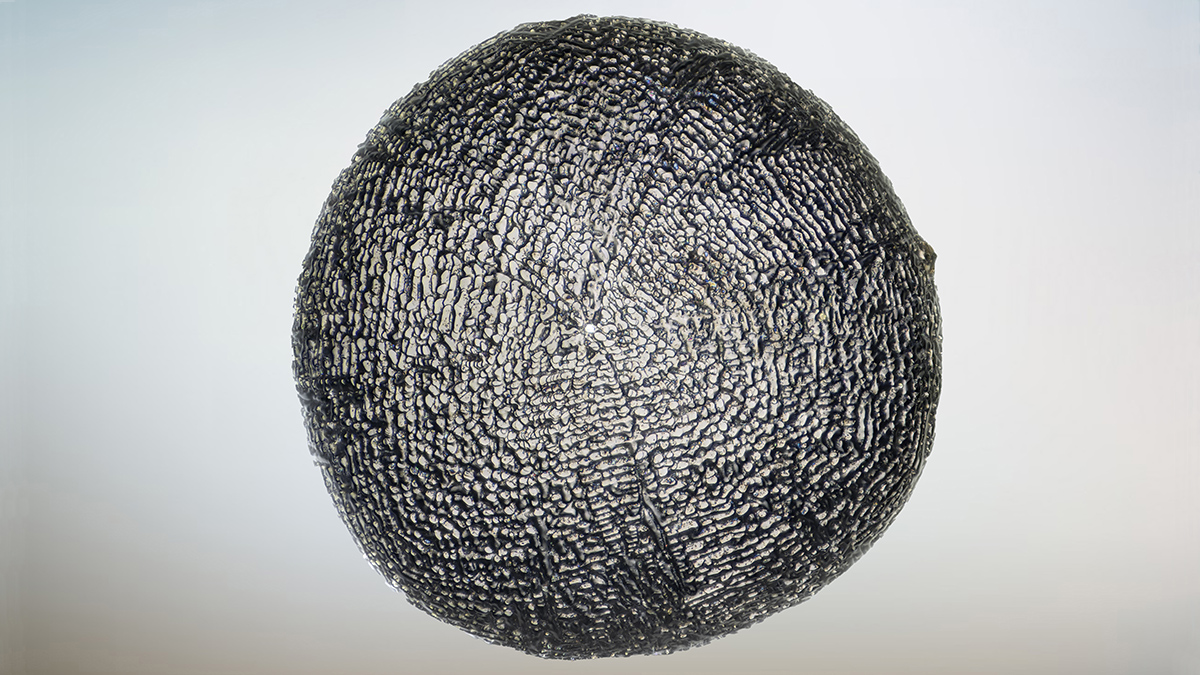
A cadre of iron-rich extraterrestrial particles picked up faint whiffs of our planet’s atmosphere when they fell to Earth millions of years ago.
everything atmospheric
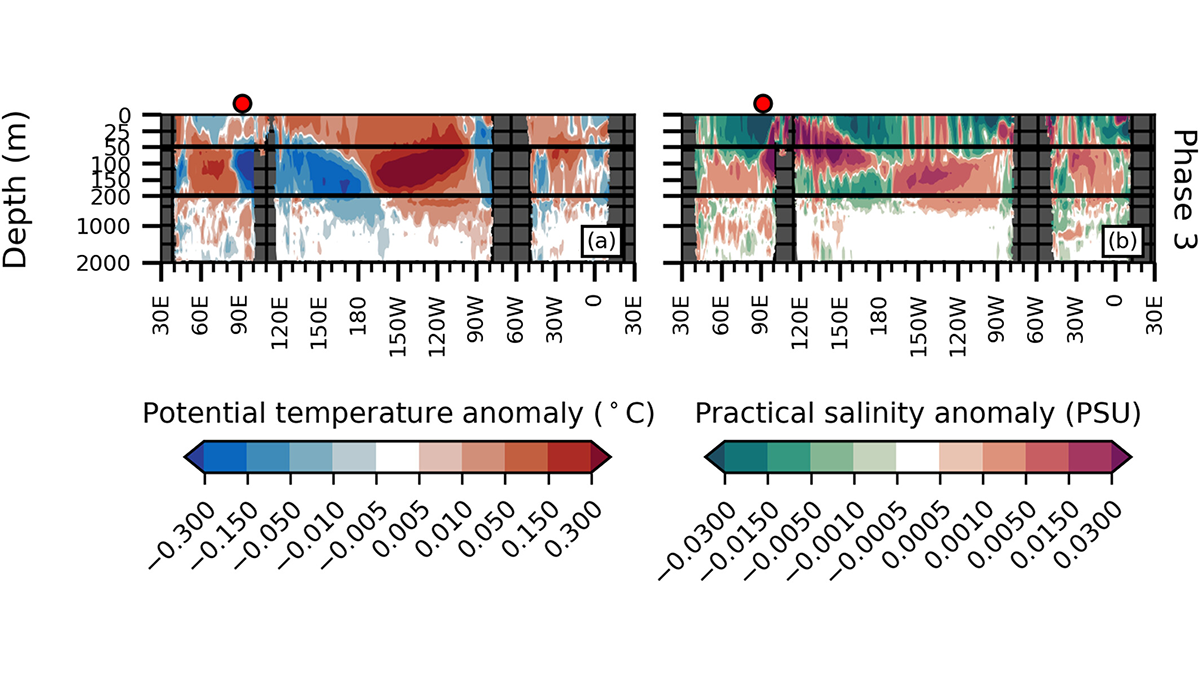
Equatorial Deep Ocean Response to the Madden-Julian Oscillation
The changes in Madden-Julian Oscillation wind can trigger a response in the deep equatorial Pacific and Indian Ocean.
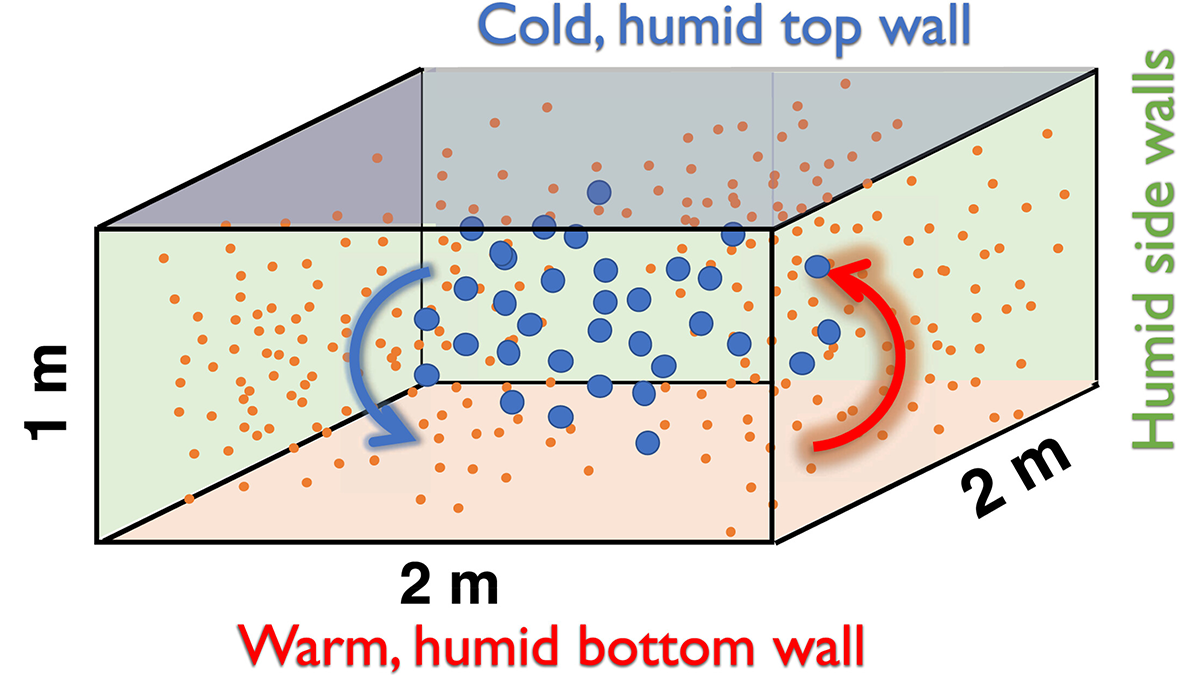
From Aerosols to Clouds: Testing Models with a Convection Cloud Chamber
Researchers benchmark seven cloud models against cloud chamber measurements to reveal how well models capture aerosol-cloud-turbulence interactions and where models still diverge.
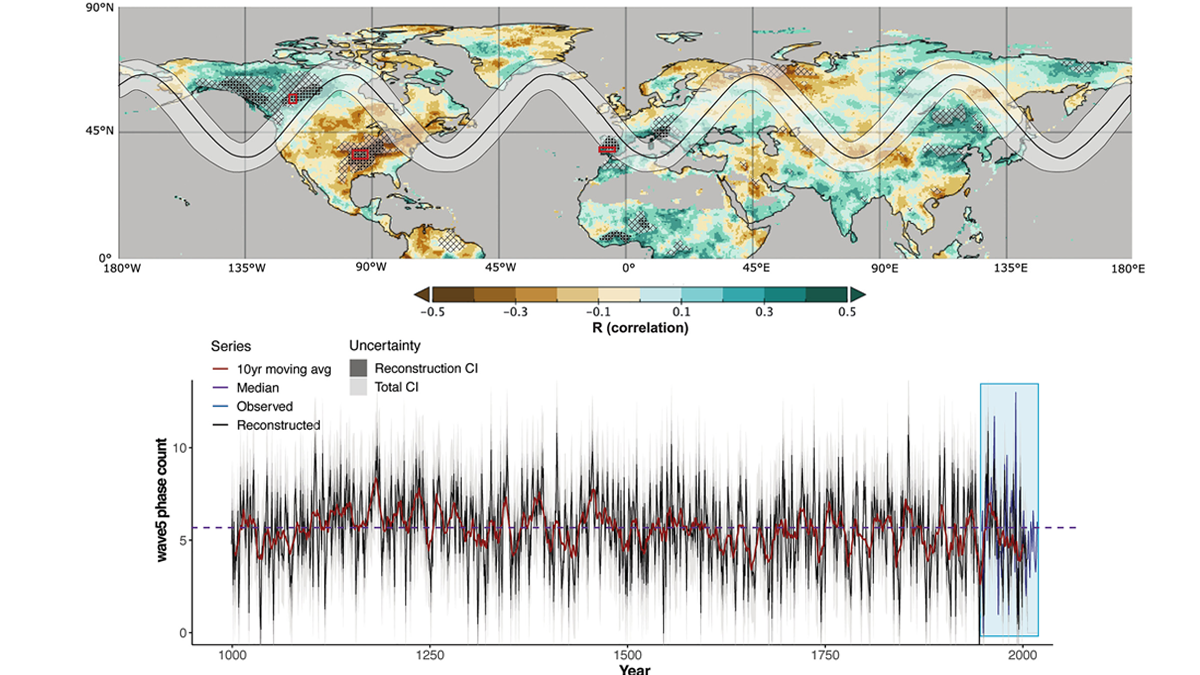
Tree Rings Record History of Jet Stream-Related Climate Extremes
Persistent spatial patterns of summer weather extremes in the northern hemisphere recorded in tree ring growth records provide a thousand-year history of jet stream ‘wave5’ dynamics.
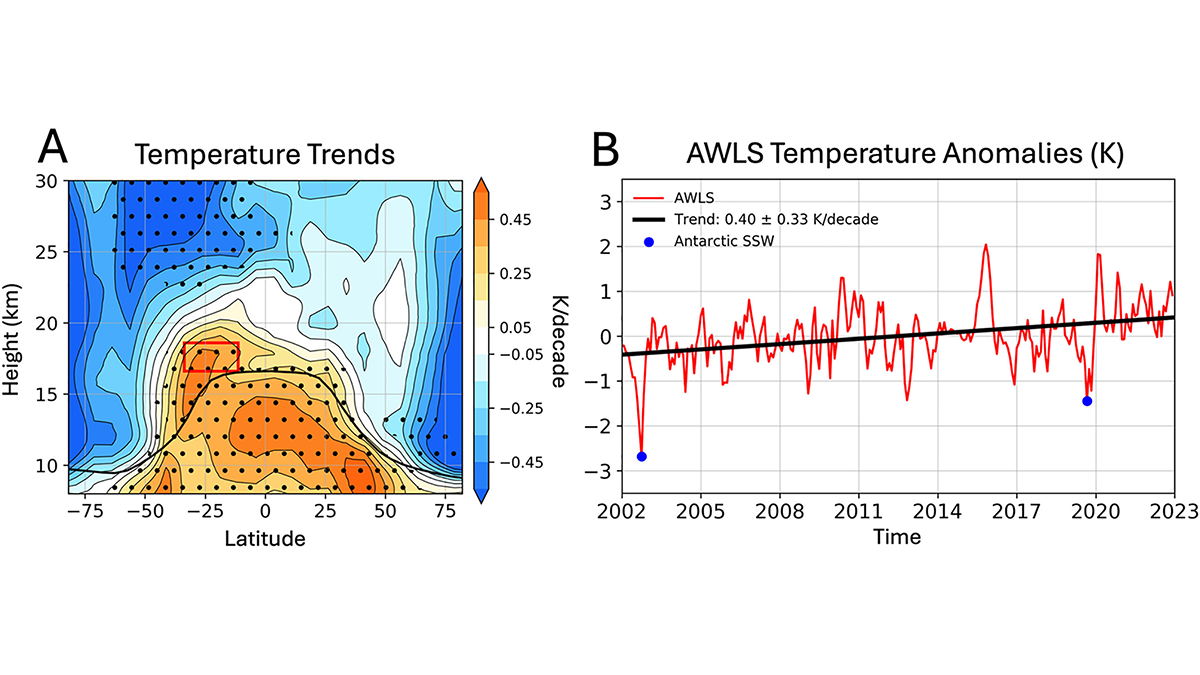
Southern Hemisphere Subtropical Lower Stratosphere is Warming
Warming of the Southern Hemisphere (SH) subtropical lower stratosphere is due to slowing of Brewer-Dobson Circulation, thus cooling the Antarctic lower stratosphere and masking anticipated ozone recovery.
Can Microorganisms Thrive in Earth’s Atmosphere, or Do They Simply Survive There?
A bottom-up modeling approach could bring scientists closer to understanding communities of microbes in the atmosphere.
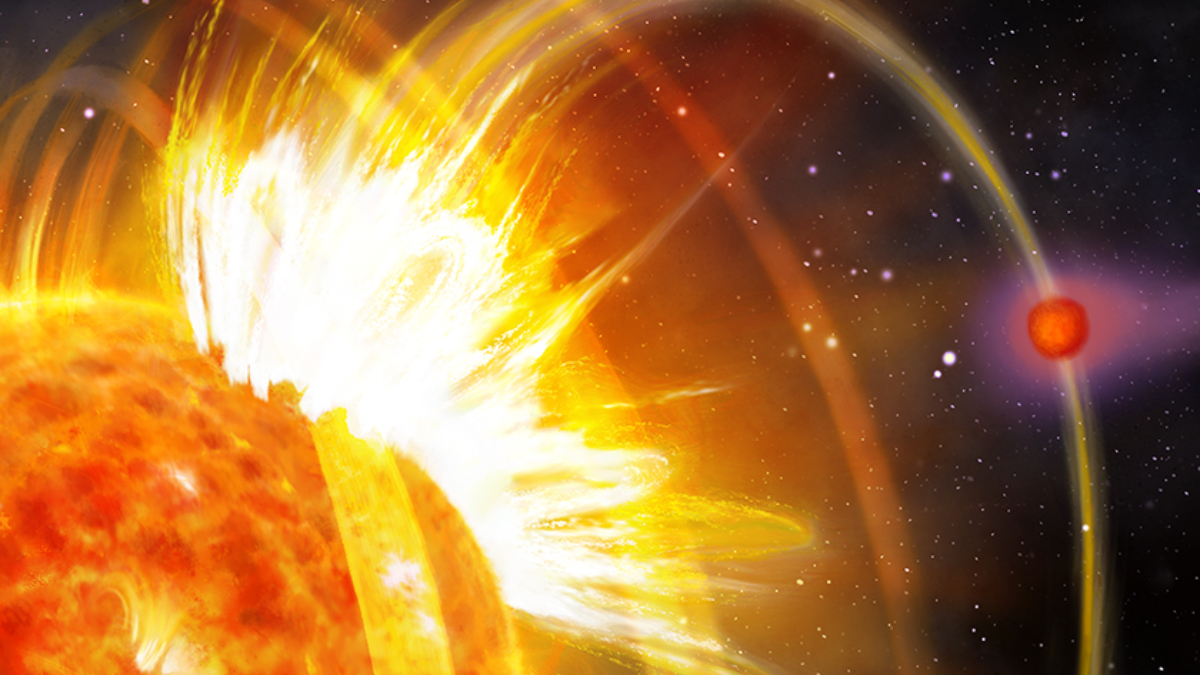
Exoplanet Triggers Stellar Flares and Hastens Its Demise
HIP 67522 b can’t stop blasting itself in the face with stellar flares, a type of magnetic interaction that scientists have spent decades looking for.
Stacey Hitchcock: From Fearing Storms to Seeking Them
This atmospheric scientist digs into the details of storms to help keep people safe.
Jeff Massey: Atmospheric Science Meets the Private Sector
Expertise in weather modeling has applications in business, this atmospheric scientist found.
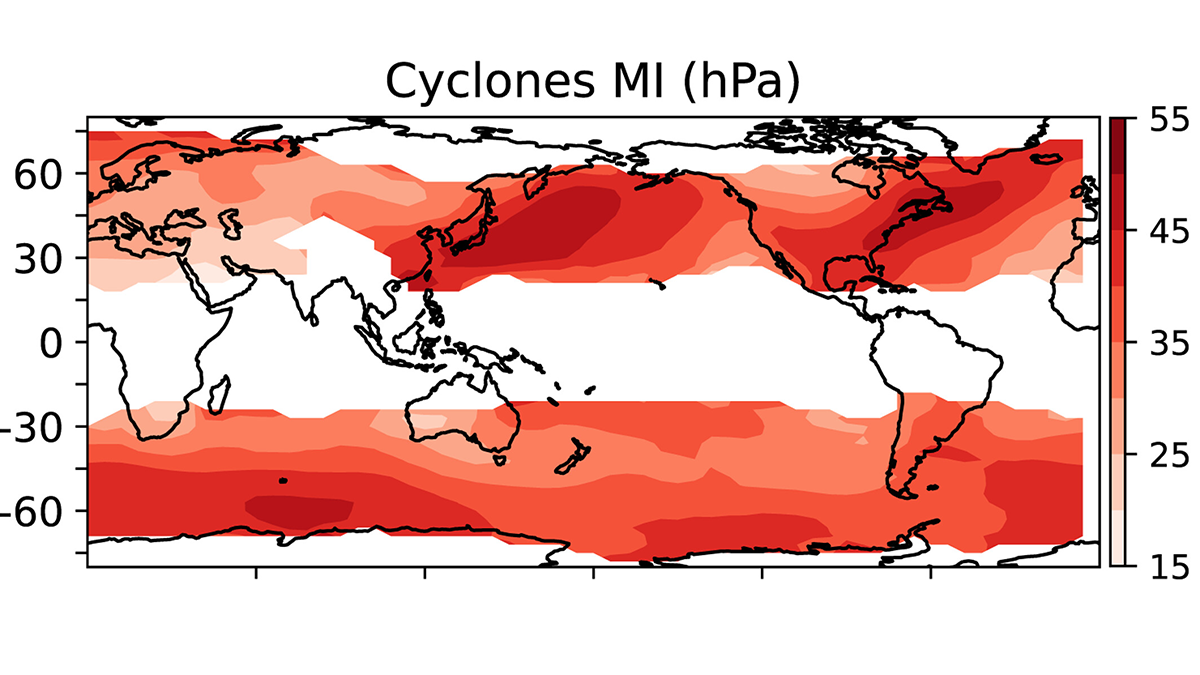
Midlatitude Storm Dynamics Better Explained by Lagrangian Analysis
Examining the growth of storms using ERA-5 reanalysis data reveals a nonlinear relationship between baroclinicity and storm activity under extreme conditions.