In forest experiments in which artificial warming mimicked future climate conditions, heat-tolerant ants thrived, leaving other populations unstable.
animals
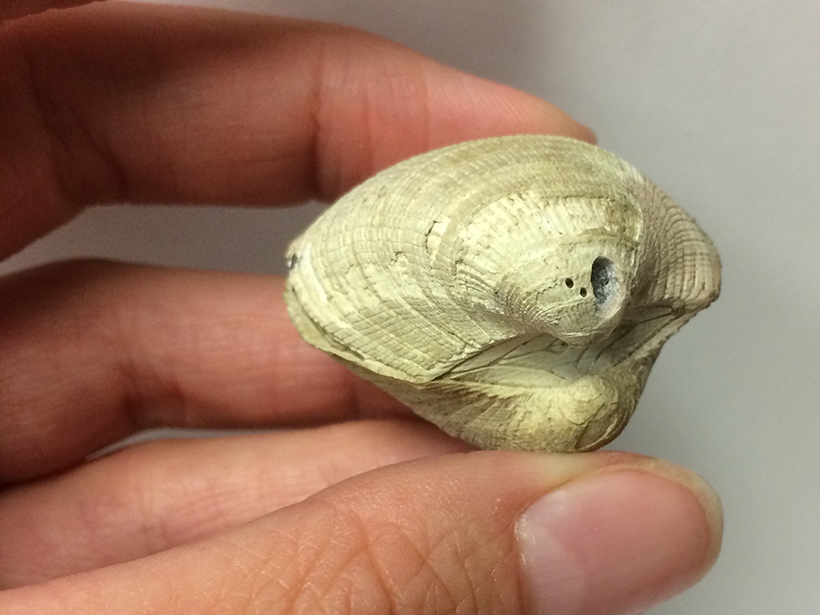
Rock-Chomping Bees Burrow into Sandstone
A previously unknown species of rock-excavating bees, discovered 40 years ago but not reported in the scientific literature, finally gets the spotlight.
Elephant Seals' Dives Show Slowdown in Ocean Circulation
Data from instruments mounted on elephant seals reveal that melting ice flushes fresh water into the Southern Ocean, suppressing an important arm of the global ocean circulation belt.
Climate Warming May Have Helped Kill the Dinosaurs
New evidence indicates ancient warming spells that coincided with prodigious volcanism and a powerful meteorite impact, both seen as possible causes of mass extinctions about 66 million years ago.
Habitat Fragmentation Prevents Migration During Climate Change
East Coast species will face the most difficulty finding routes to cooler homes as climate change forces migration.
What Does the Pacific Arctic's New Normal Mean for Marine Life?
Climate change has reconfigured Arctic ecosystems. A 5-year project focuses on the relationships among oceanographic conditions and the animals and other life-forms in this region.
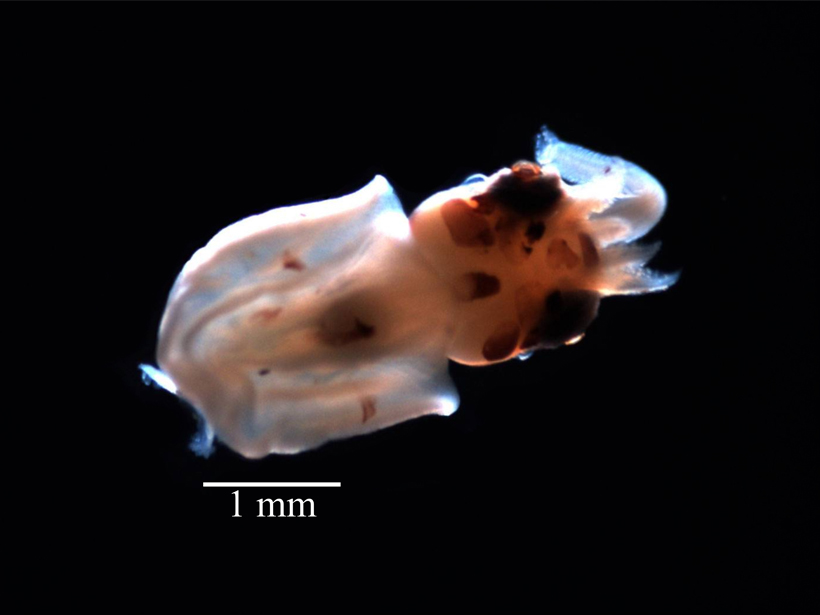
Understanding the Distribution of Juvenile Jumbo Squid
An expanding zone of shallow, oxygen-depleted water in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean may be vertically restricting the habitat of this important source of food, according to a recent study.
Bark Beetles Cause Big Tree Die-Offs, but Streams Flow Steadily
Recent beetle epidemics have driven tree die-offs across North America, and previous studies predicted an increase in annual streamflow would follow—but a new study shows this may not be the case.
More Acidic Oceans Could Reduce Fertility for Algae Eaters
New research shows that increased levels of carbon dioxide in the oceans cause changes that alter key nutrients essential to the reproduction of animals low on the food web.
Ancient Start of Animal Evolution Wasn't Delayed by Low Oxygen
New research finds that Earth had sufficient oxygen 1.4 billion years ago for animals to evolve. Therefore, low oxygen levels probably didn't hold back evolution, as scientists have long thought.