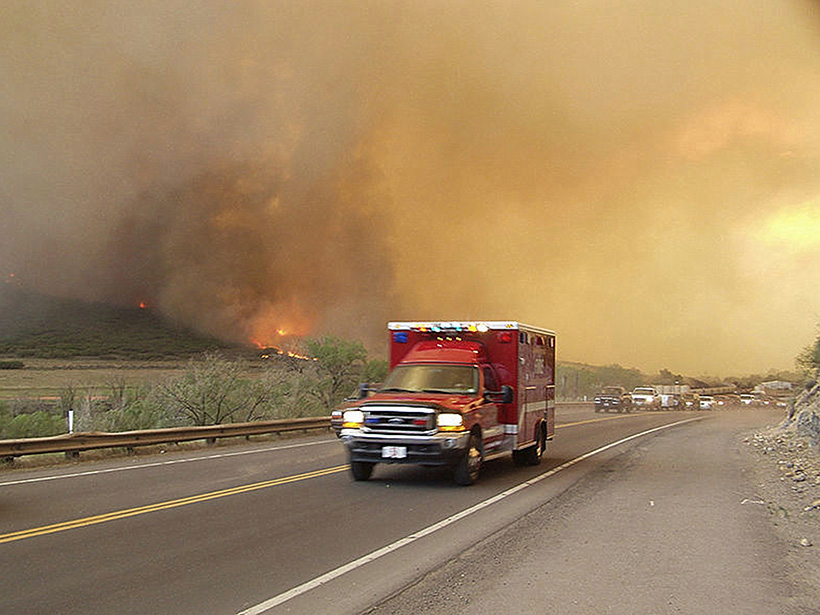
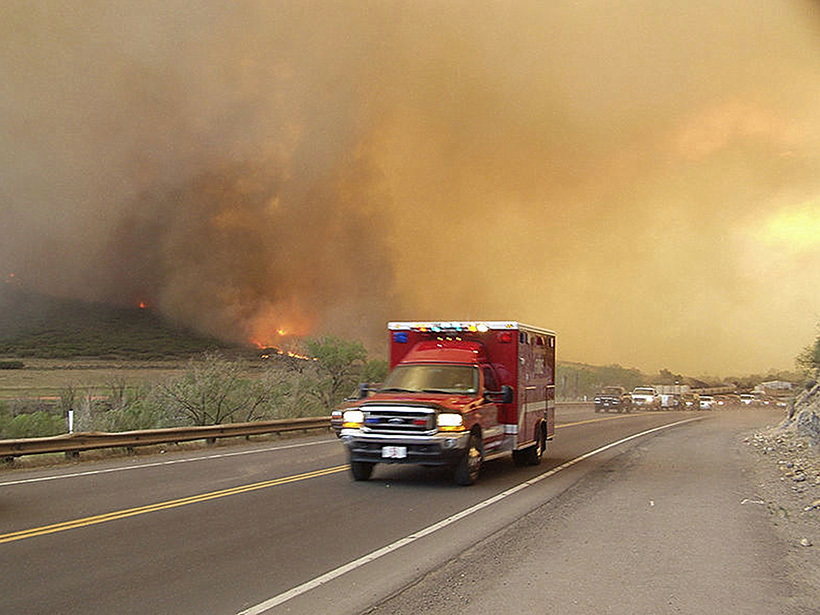
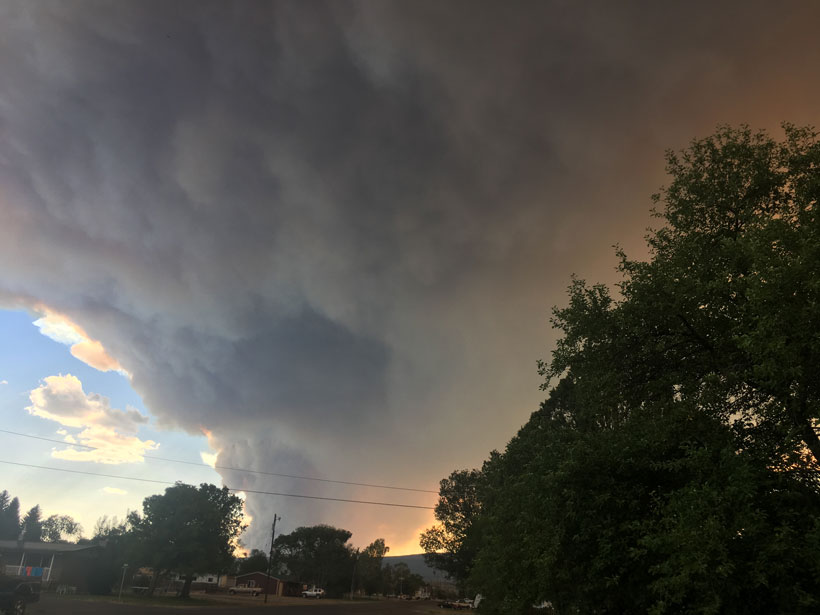
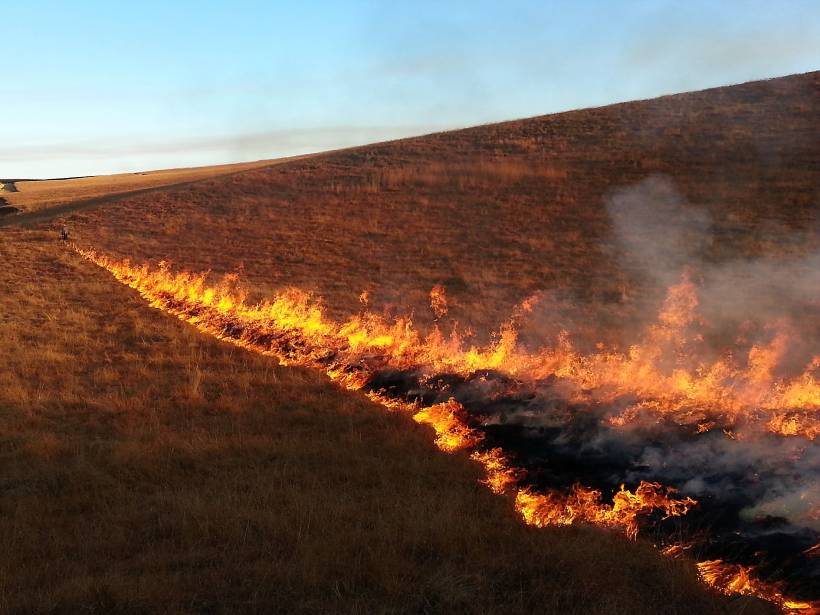
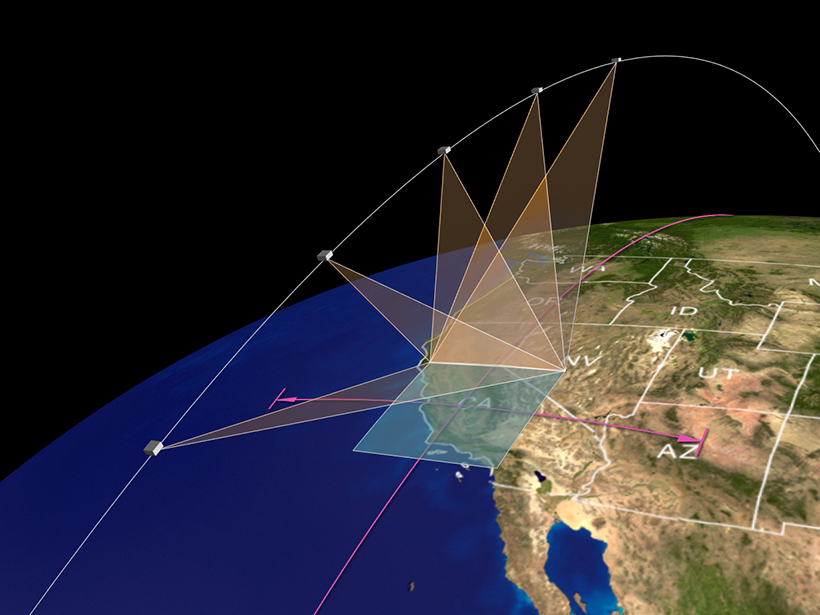
How does a large volcanic cloud get into the stratosphere? Scientists model how volcanic debris injected into the lower stratosphere can be lofted high into the middle stratosphere.
aerosols & particles
Establishing a Link Between Air Pollution and Dementia
A new study examines the relationship between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and dementia, finding that air pollution may be responsible for up to 2 million dementia cases each year.
How Hospitals Respond to Wildfires
A new study tracks intensive care unit admissions after periods of wildfire smoke pollution. A prolonged or severe smoke event has the potential to strain hospital resources.
Taking Flight to Study Clouds and Climate
A new mission involving synchronized aircraft observations is collecting data vital for improving our understanding of how aerosol particles and clouds influence each other.
The Promise of Spaceborne High Spectral Resolution Lidar
New spaceborne high spectral resolution lidar measurements provide a new view of global aerosols.
Los Incendios forestales podrían exacerbar el asma en el oeste de los Estados Unidos
Un nuevo estudio predice que para la década de 2050, el humo de los incendios forestales hará que la región gaste $850 millones más cada año para tratar el asma.
Using Satellite Data to Map Air Pollution and Improve Health
NASA scientists will be teaming up with epidemiologists in the agency’s first health-focused mission. With satellite data, they’ll find out how air pollution affects health in cities around the world.
Zooming In on Small Fires in Africa
By analyzing high-resolution satellite images, researchers found that fires burning in Africa were undercounted by as much as 80%.
Aerosol Scientists Try to Clear the Air About COVID-19 Transmission
“We are basically doing what a public health agency should be doing.”