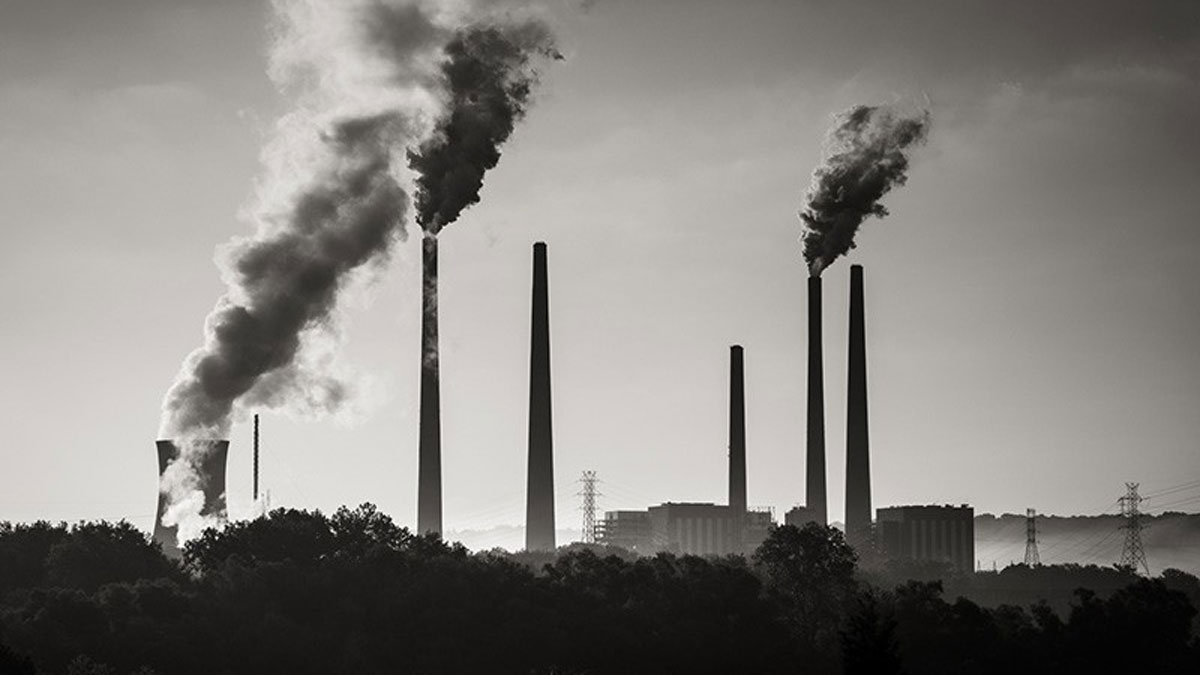
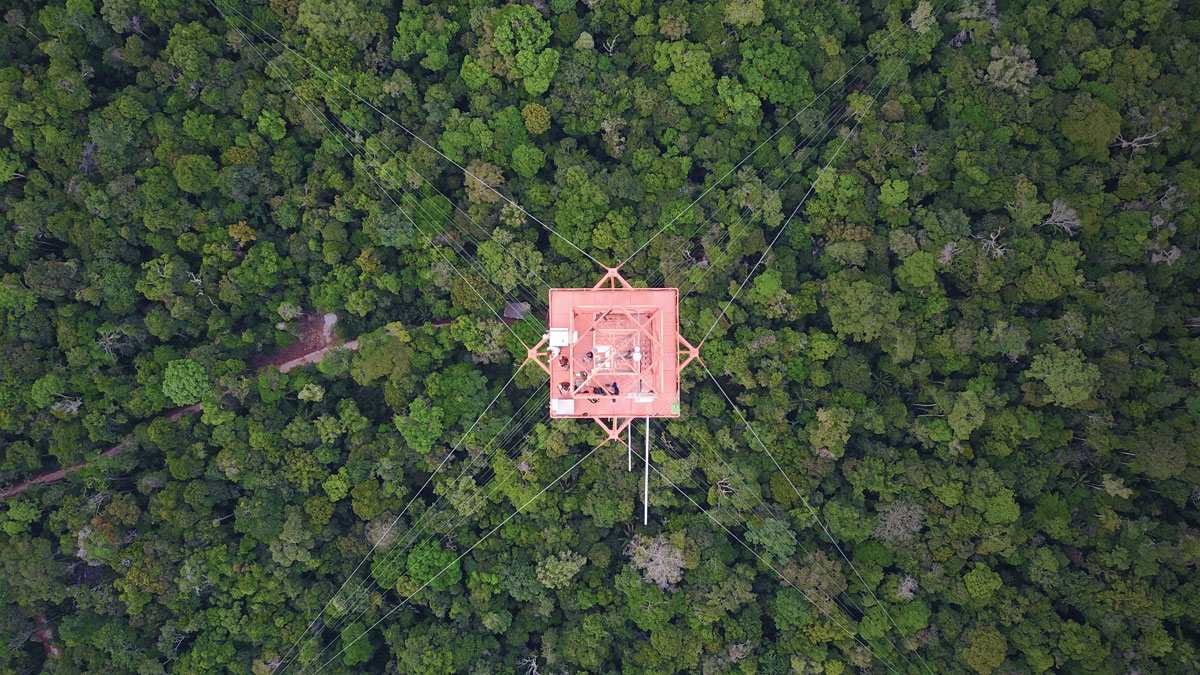
Eliminar la contaminación del aire relacionada con la energía en los Estados Unidos podría evitar aproximadamente 50,000 muertes prematuras y ahorrar miles de millones de dólares al año.
aerosols & particles
The Sun Bakes Wildfire Smoke, Changing Its Toxicity
A new study questions the narrative that dilution is the solution to pollution.
Indoor Air Pollution in the Time of Coronavirus
How aerosol scientists spread the word on the airborne transmission of COVID-19–and what it means for cleaning our indoor air.
Quantifying the Health Benefits of a U.S. Clean Energy Transition
Eliminating energy-related air pollution in the United States could prevent roughly 50,000 premature deaths and save billions of dollars per year.
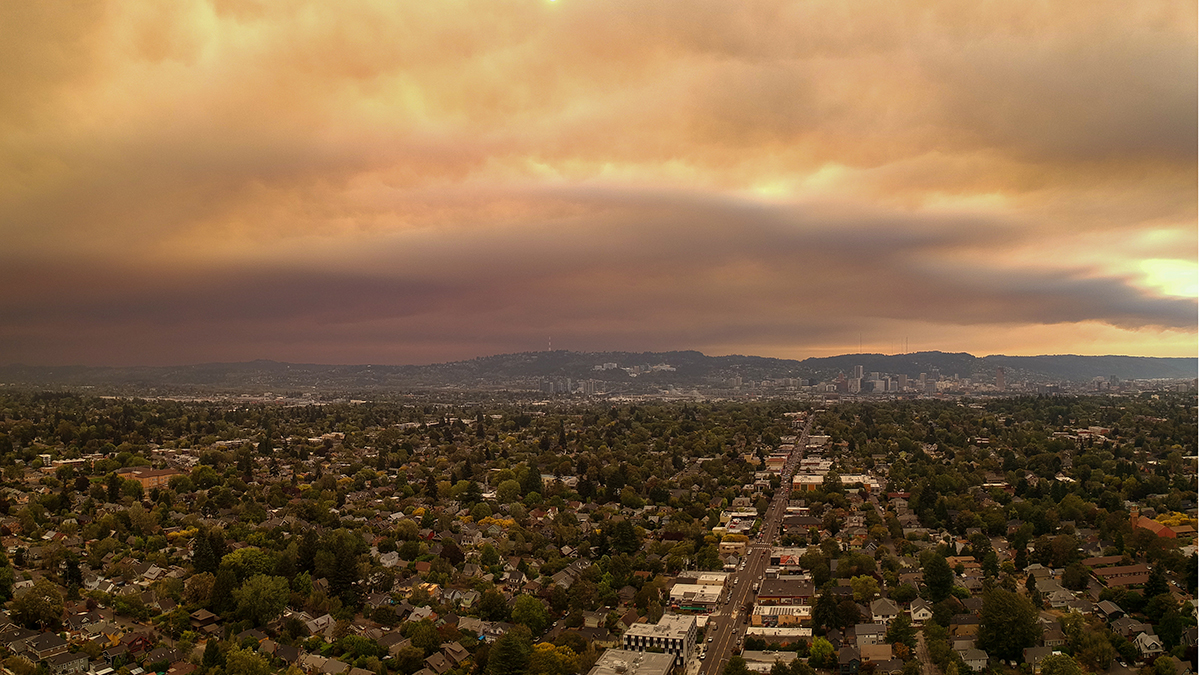
Unhealthy Air Could Become Routine in the Pacific Northwest
If the world stays on fossil fuels, fine particle pollution from wildfire smoke could more than double in the late summer to early fall in the U.S. Pacific Northwest by 2100.
Australian Wildfires Linked to Ozone Layer Depletion
New research shows that the Black Summer bushfires damaged the ozone layer, eliminating a decade’s worth of progress.
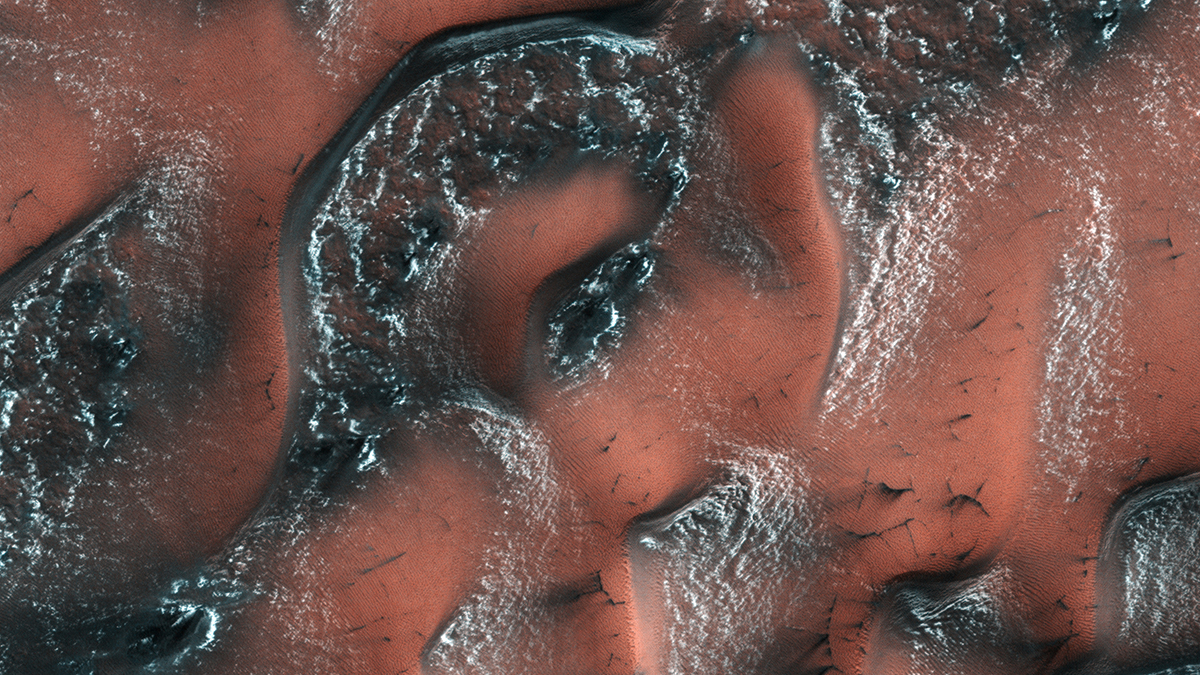
Mars’s Dust Cycle Controls Its Polar Vortex and Snowfall
On Earth, the water cycle is a dominant climate force. On Mars, it’s the dust.
The Alps Are Dusted with Nanoplastics
A new study finds the lofted pollutants came from major European cities, but further study is required to fully understand the plastics’ transport and deposition processes.
Africa’s Earth, Wind, and Fire Keep the Amazon Green
Jet streams sprinkle North African dust over the Amazon, providing the rain forest with much needed nutrients. Changing wind patterns and increasing smoke may shift the system.
The Surprising Greenhouse Gas That Caused Volcanic Summer
Extended periods of volcanism known as flood basalt eruptions lead to volcanic winters, which are often followed by an extended period of warming. But it was more than just carbon dioxide that warmed the globe.