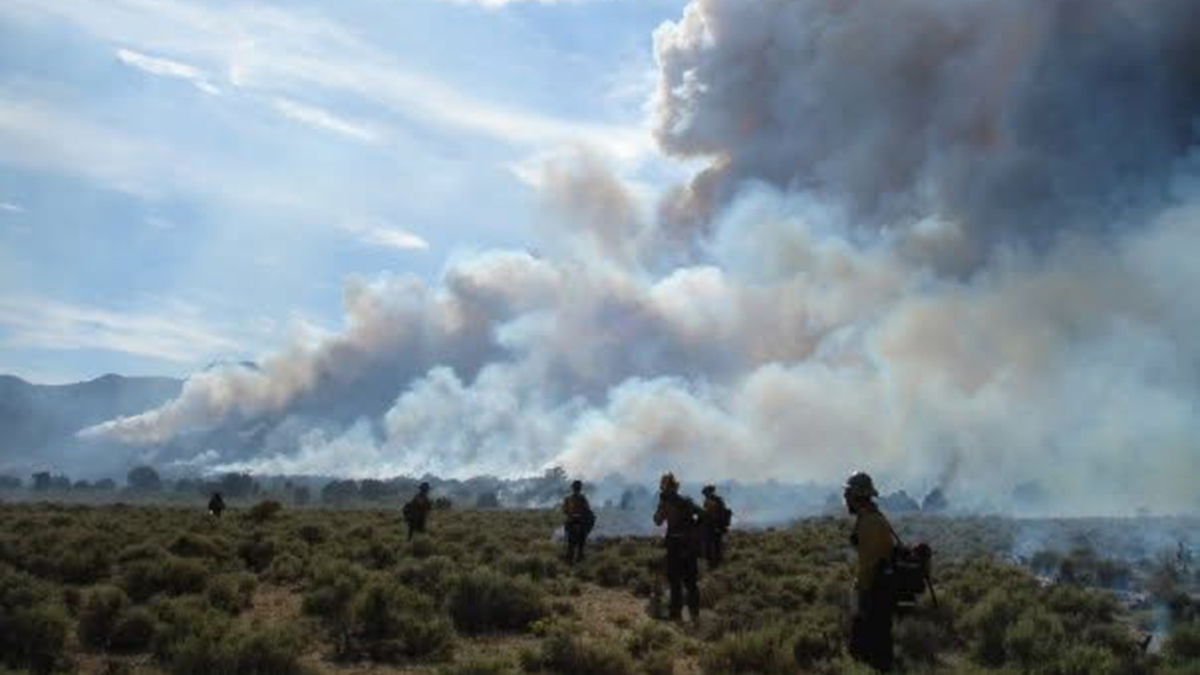
Twenty years of data from around the world show that areas that are not too dry and not too wet are most conducive to wildfire burning.
AGU Advances
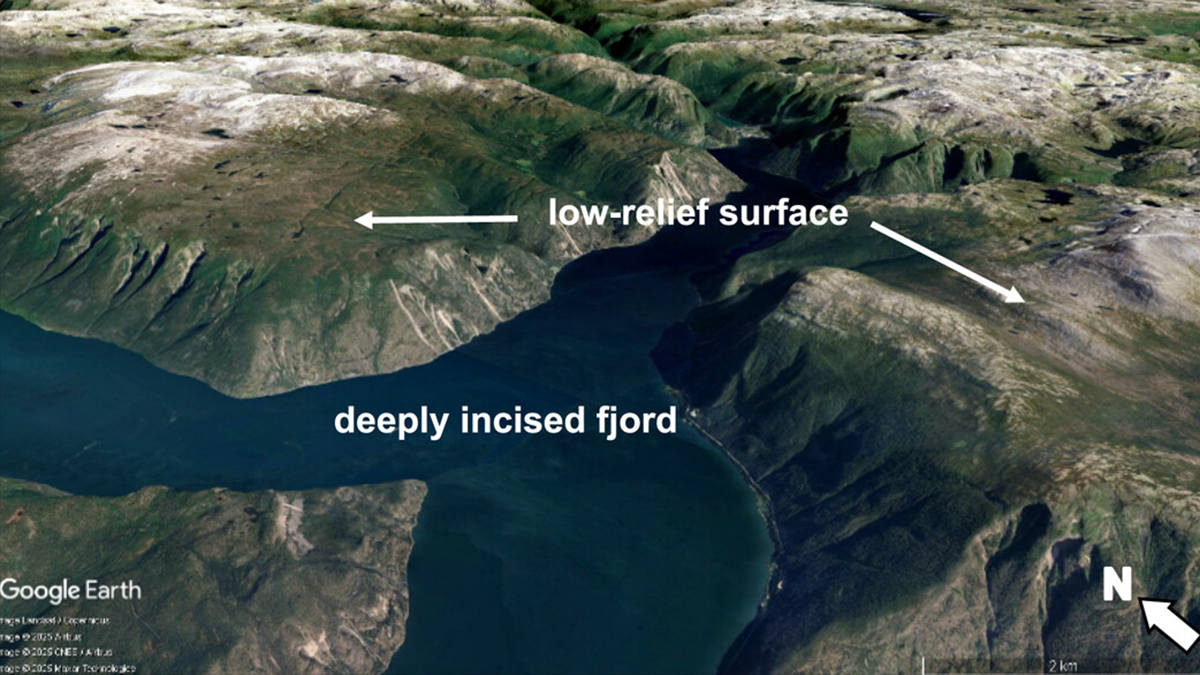
High Relief, Low Relief — Glaciers Do It All
Contrary to conventional wisdom that glaciers just carve landscapes, they can also form low-relief surfaces by sheltering rock from erosion, enriching understanding of how mountain landscapes evolve.
Former Department of Energy Leader Reflects on a Changing Landscape
The first person of color and first Earth scientist to serve as director of the Department of Energy’s Office of Science reflects on her career as the new administration works to dismantle key diversity programs.
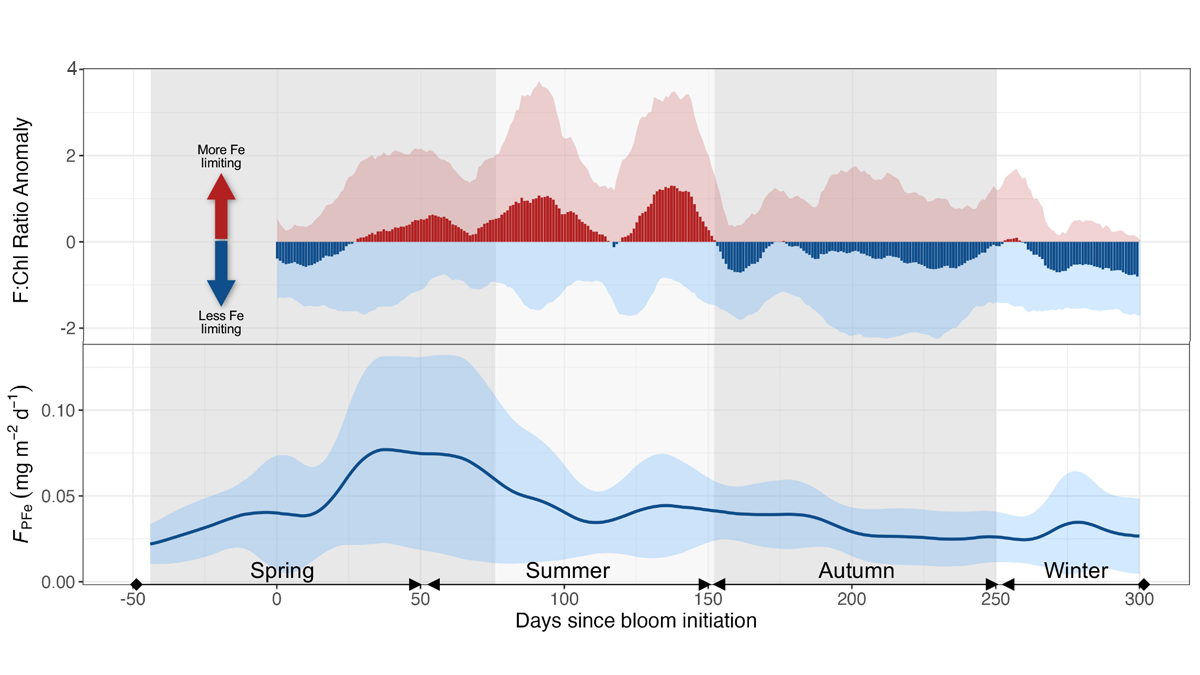
Seasonal Iron Cycle and Production in the Subantarctic Southern Ocean
Long-term monitoring at a site in the subantarctic region south of Australia combined with ship-based observations reveals three distinct phases between cycles of phytoplankton productivity and dissolved iron.
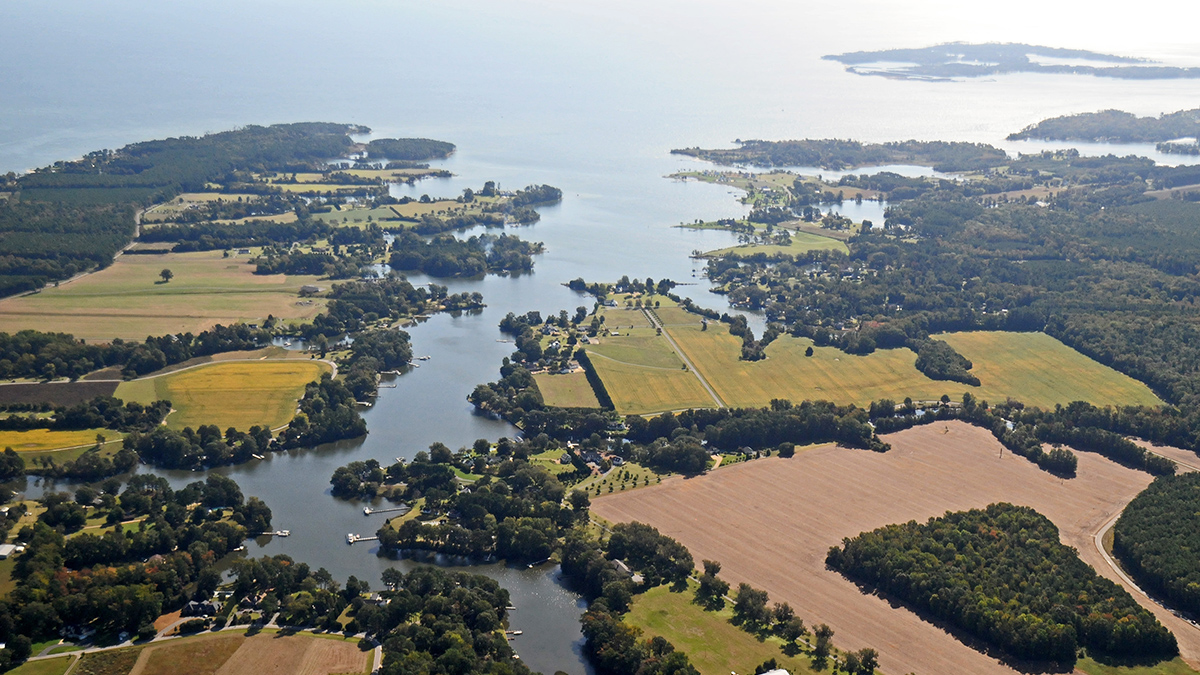
River Alkalinization and Ocean Acidification Face Off in Coastal Waters
Factors ranging from rainfall to nutrient runoff to changing mining and agricultural practices drove decades-long pH trends in the Chesapeake Bay.
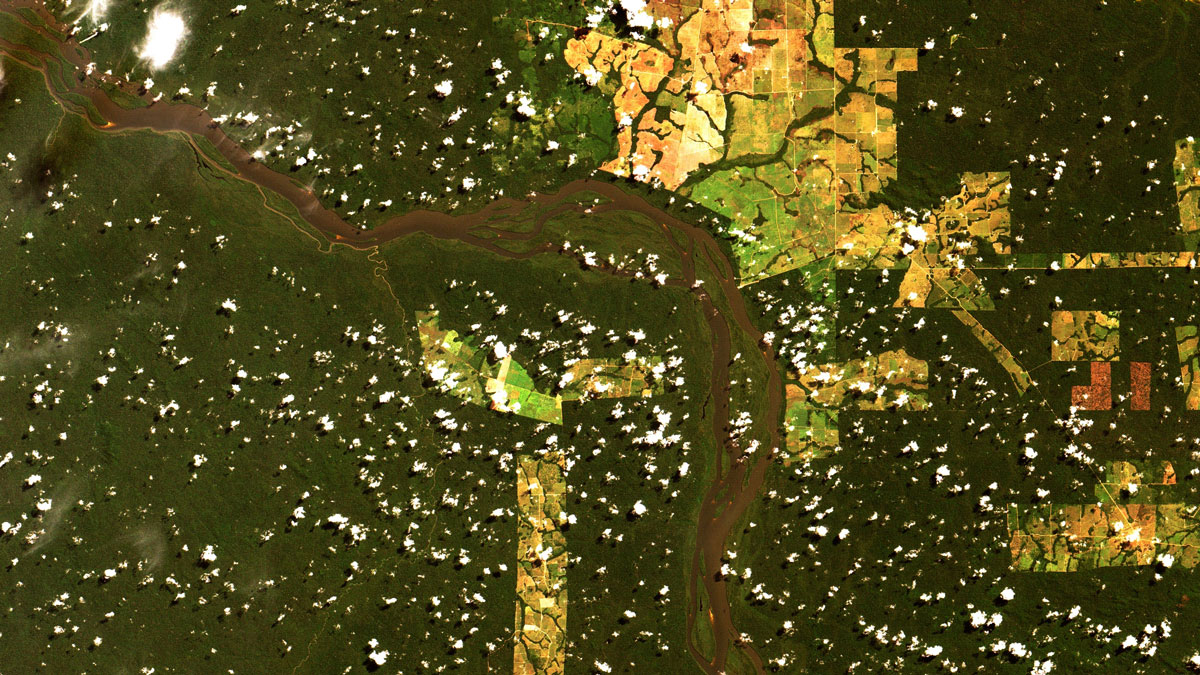
Deforestation Is Reducing Rainfall in the Amazon
Researchers found that between 2002 and 2015, a 3.2% reduction in Brazilian forest cover led to a 5.4% reduction in precipitation levels.
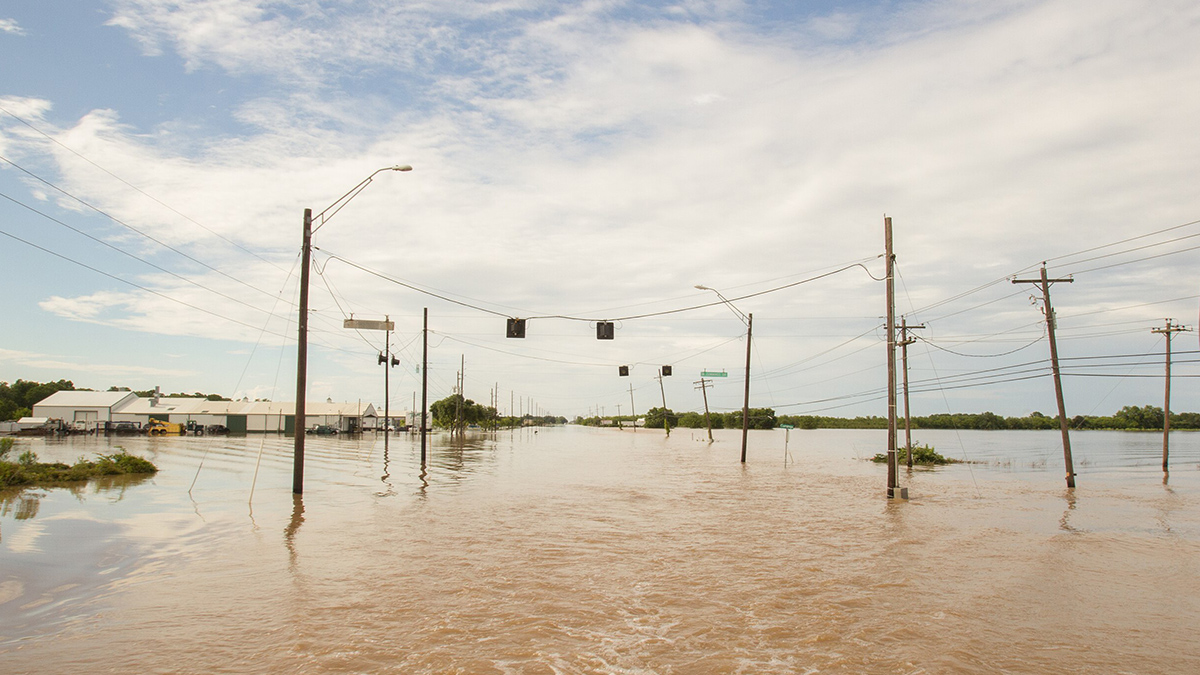
Scientists Reveal Hidden Heat and Flood Hazards Across Texas
A wider swath of the Lone Star State may be affected by more heat and flood events than previous recordkeeping suggests.
Old Forests in a New Climate
It’s usually cooler under a forest than outside the forest, but that natural temperature buffering didn’t make global warming any less strong during the last 45 years in an old-growth forest of Oregon.
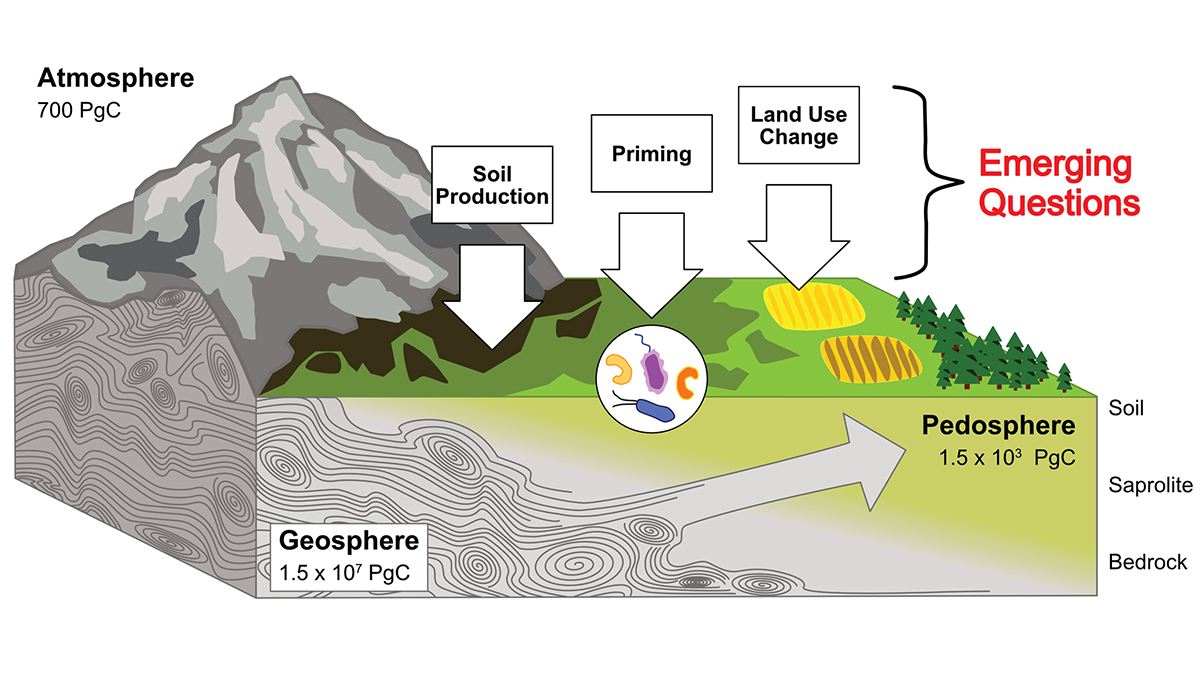
Rock Organic Carbon in Soils: Recycled or Just Passing Through
It’s often assumed that all soil organic carbon ultimately derives from recent vegetation, but researchers argue that carbon inherited from parent rocks can be important and deserves more focus.