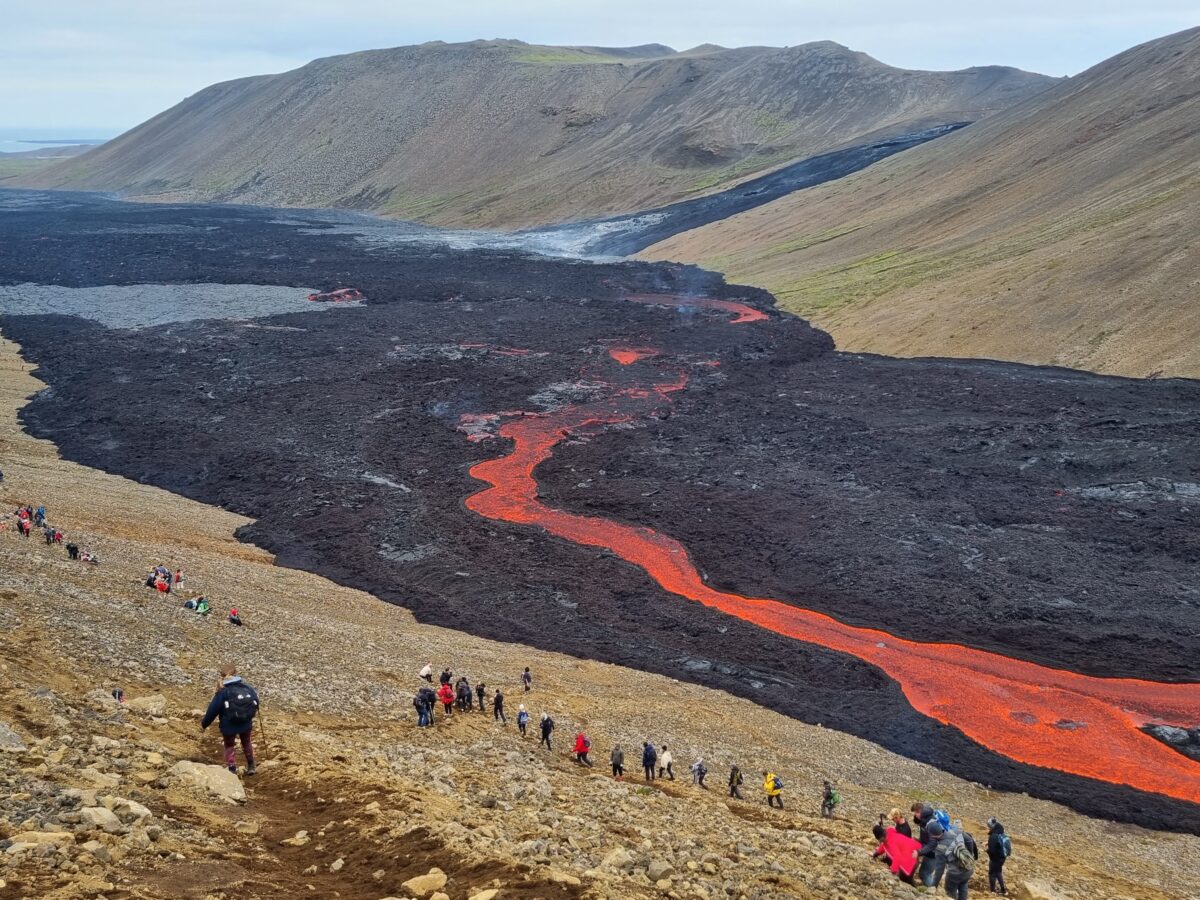
A set of lab experiments involving a laser, gelatin, and xanthan gum explored how varying flow patterns between dikes with similar speeds and shapes could affect eruption predictions.
AGU Advances
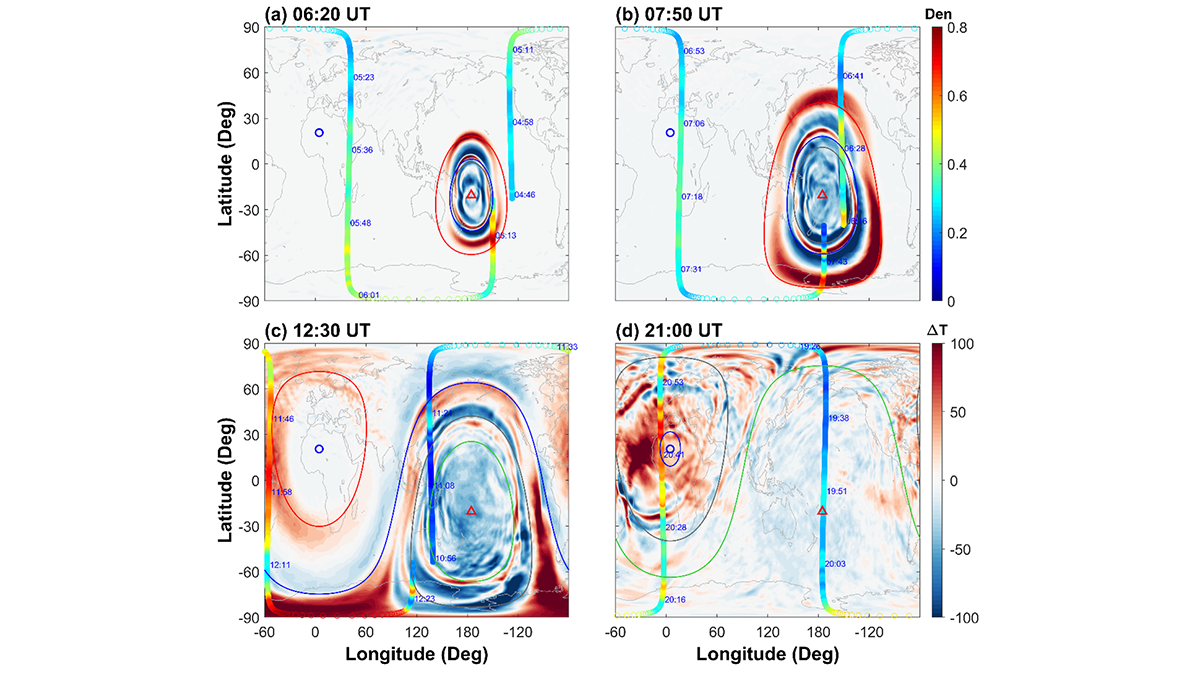
Tonga’s Volcanic Fury Ripples to the Netherworld
Secondary gravity waves emerge as the hidden architects of global-scale thermospheric upheaval following the Tonga eruption in 2022.
Compost and Biochar Could Boost Carbon Sequestration by Crushed Rock
Crushed rock additives may also help decrease soil emissions of other greenhouse gases, such as nitrous oxide and methane.
Modeling the Past, Present, and Future of Drought
A new study combines historical observations, climate modeling, and data from tree rings to create a fuller picture of historic as well as potential drought conditions.
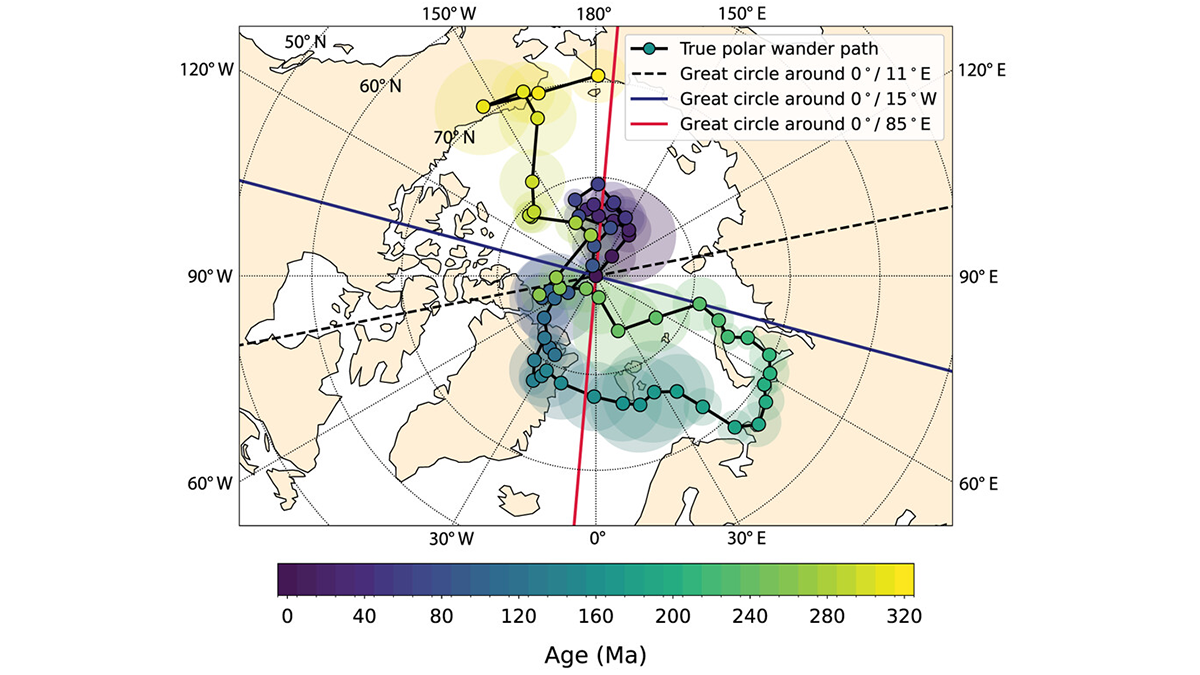
300 Million Years of Polar Wander: Slowly but Surely
A reanalysis of paleomagnetic poles provides tighter bounds on the style and rate of motions of our whole planet with respect to its rotation axis.
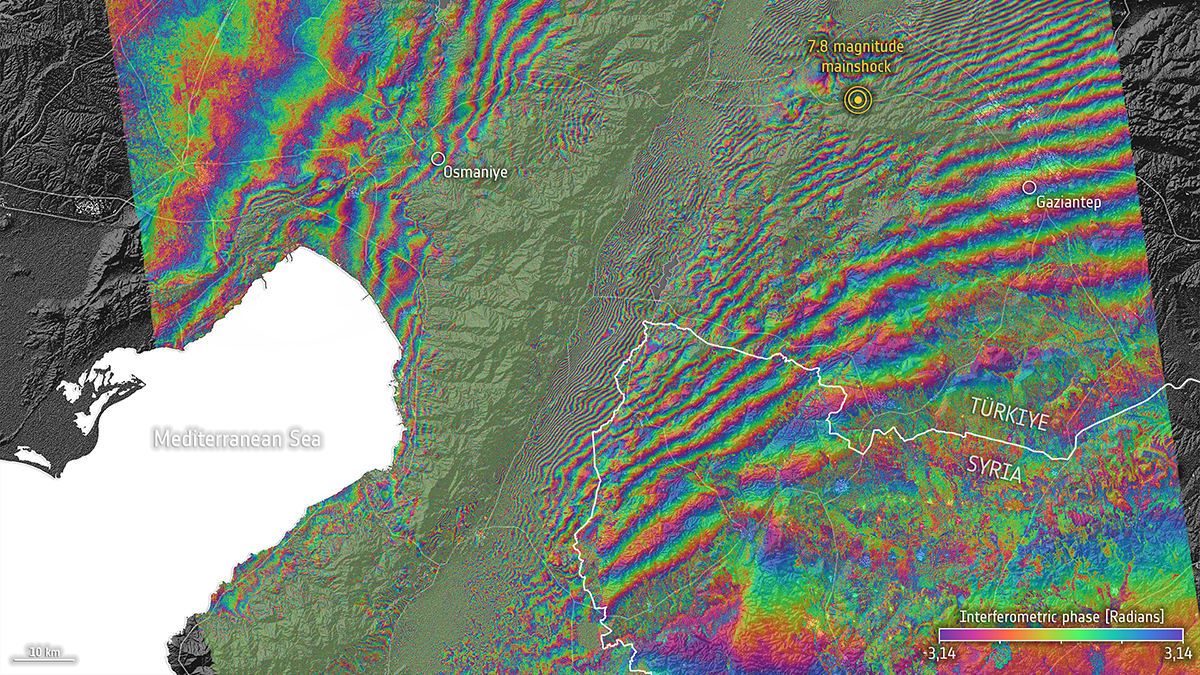
Türkiye-Syria Temblors Reveal Missing Piece in Earthquake Physics
Newly discovered aseismic events triggered by the 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquake may represent a mode of fault slip between earthquakes and slow-slip events that researchers have long been seeking.
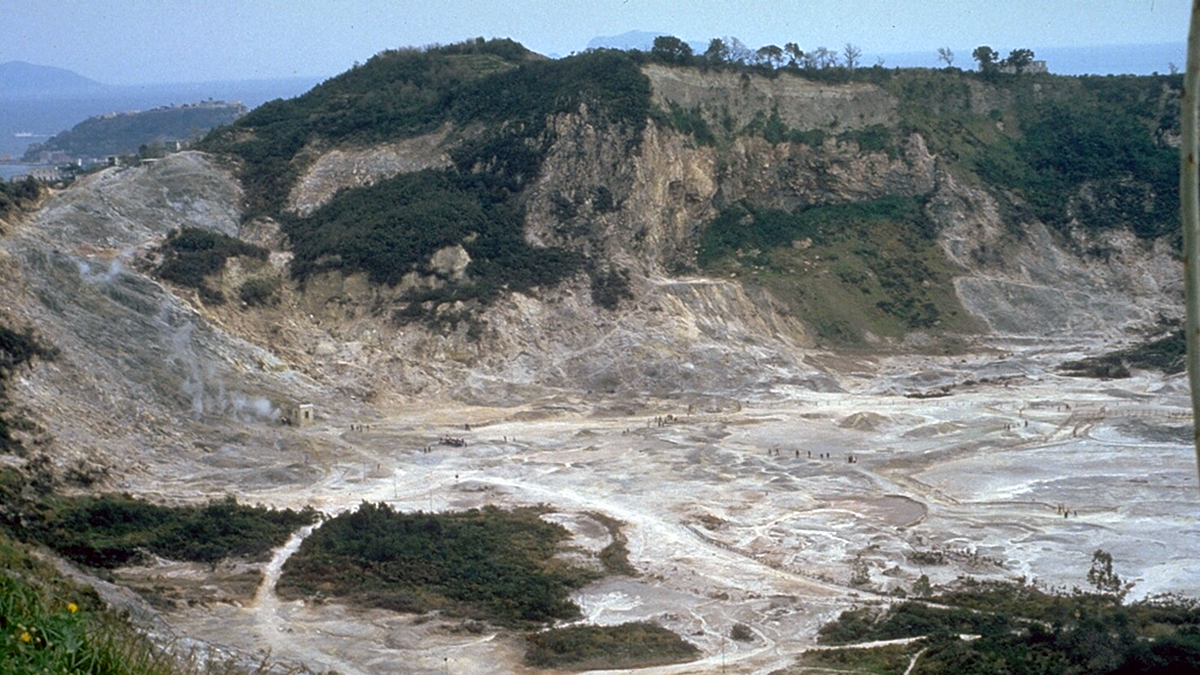
Deflected Dikes Perturb the Plumbing System
A multidisciplinary synthesis of the Campi Flegrei, Italy volcanic setting highlights the importance of sub-caldera layering for magma dynamics.
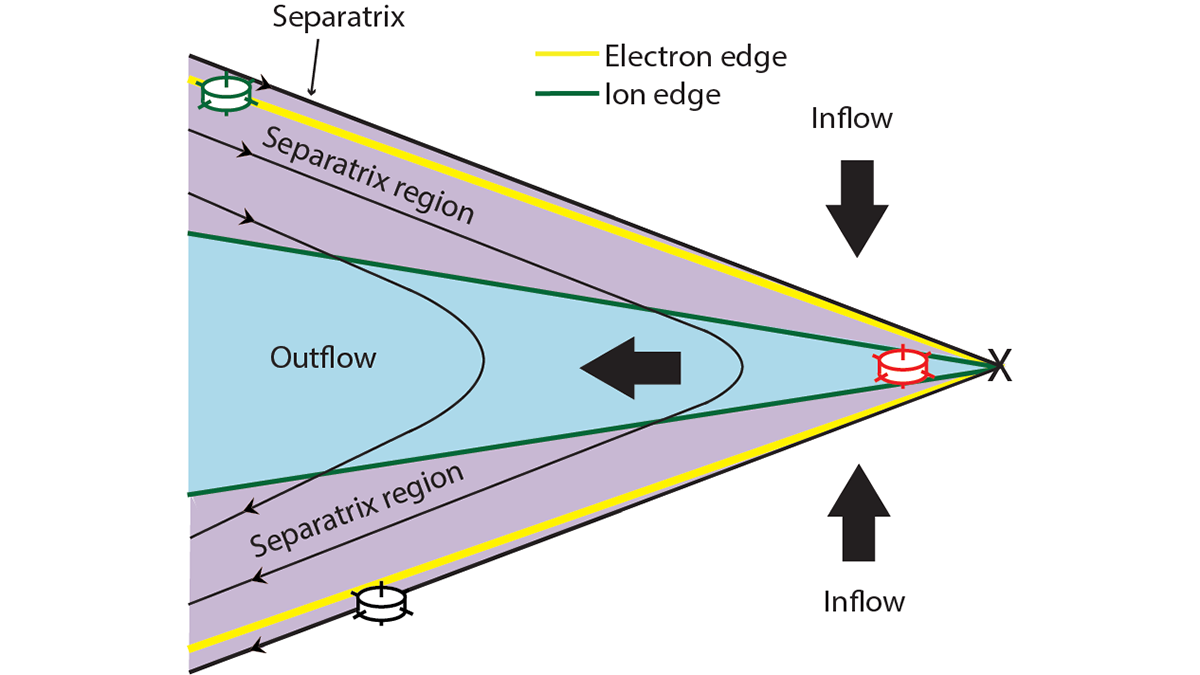
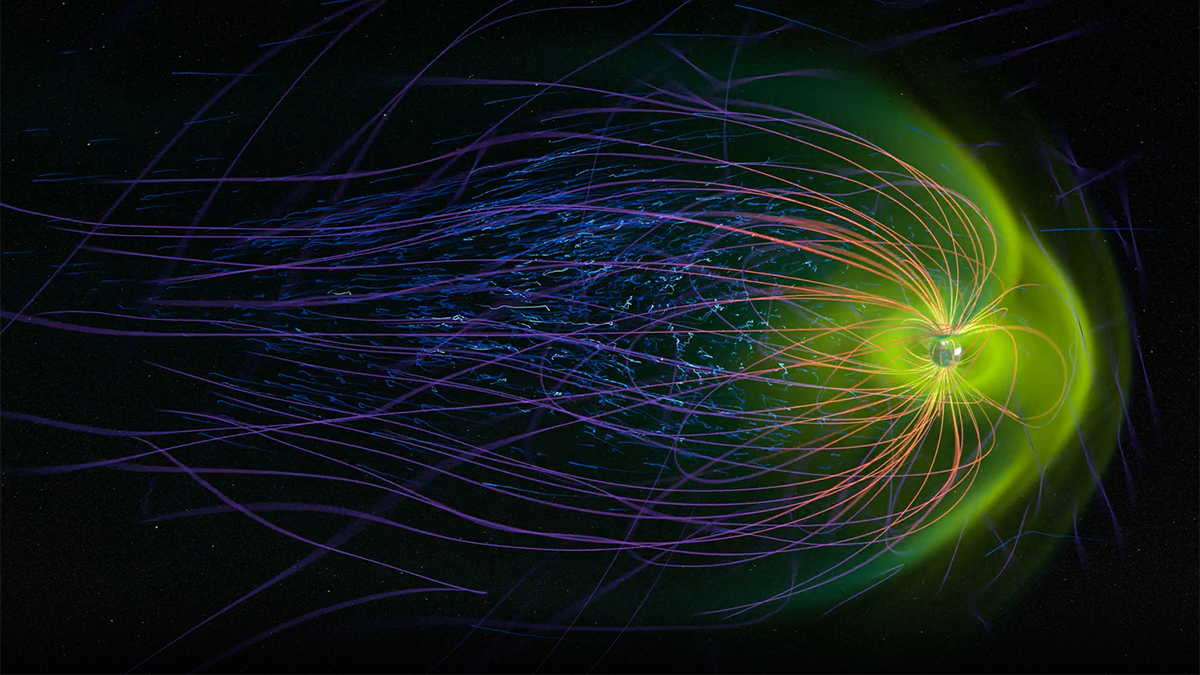
Fast Flows in Earth’s Magnetotail Surveyed by NASA Satellites
A survey of high-speed electron flow observed by NASA satellites in the Earth’s magnetotail is presented and related to the process of magnetic field line reconnection and particle acceleration.