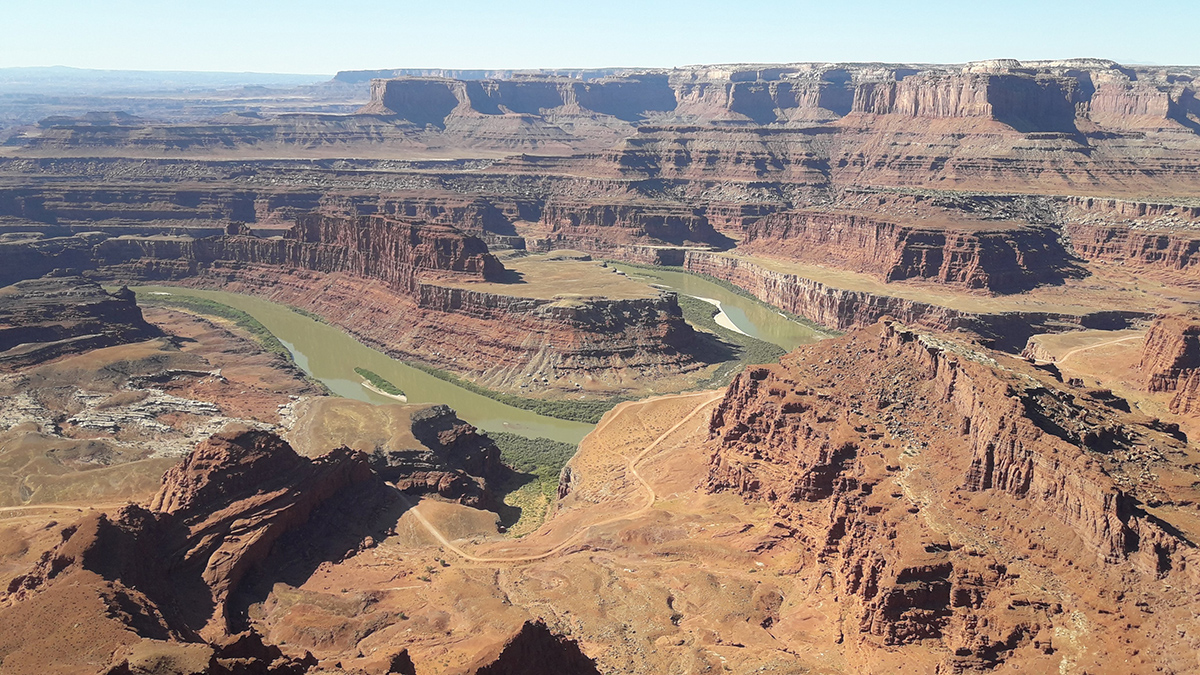
A new study offers insights into a puzzling piece of the geological history of the Grand Canyon and surrounding regions.
AGU Advances
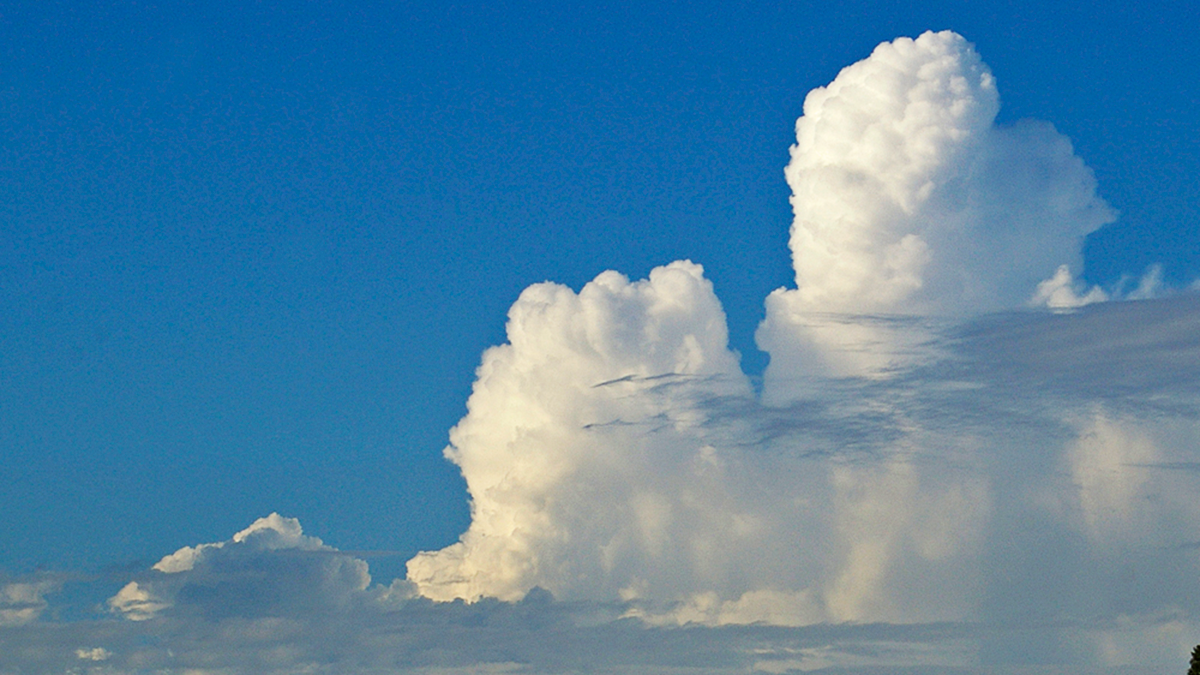
Tropical Congestus Clouds Explained by Water Vapor Spectroscopy
A new study demonstrates how the abundance of congestus clouds in the tropics can be explained by the water molecule’s discerning appetite for infrared radiation.
A Warming Climate Is Shifting Eurasian Drought Conditions
Researchers use tree ring records to help reconstruct hydroclimate patterns and isolate drivers of drought.
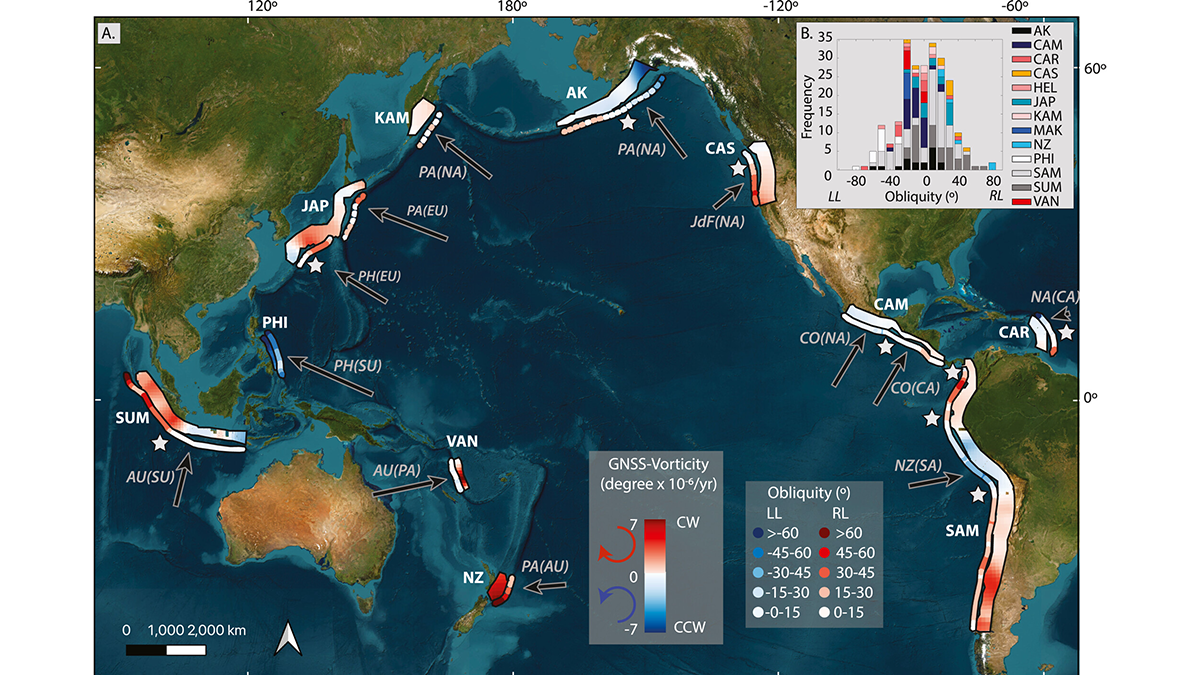
Skewed Subduction Shear Zones
A global reanalysis of both short- and long-term deformation clarifies how obliquity affects strain partitioning in convergent plate boundaries.
Jupiter’s Moon Callisto Is Very Likely an Ocean World
A closer look at previously disregarded observations reveals stronger evidence that a deep ocean lies beneath Callisto’s icy surface.
Using Satellite Data for More Effective Disaster Response
Satellite data play a crucial role in disaster assessment and response. Meeting expanding demand requires not only accelerated data processing but increased collaboration with responders.
Trees Can Cool Cities, But Only with a Little Help
To get the benefits of trees, city managers must give greenery what it needs to thrive, says new research.
Editorial Handover at AGU Advances
The outgoing and incoming Editors-in-Chief of AGU Advances reflect on recent years of growth and expansion in the journal while they plan for the challenges ahead.
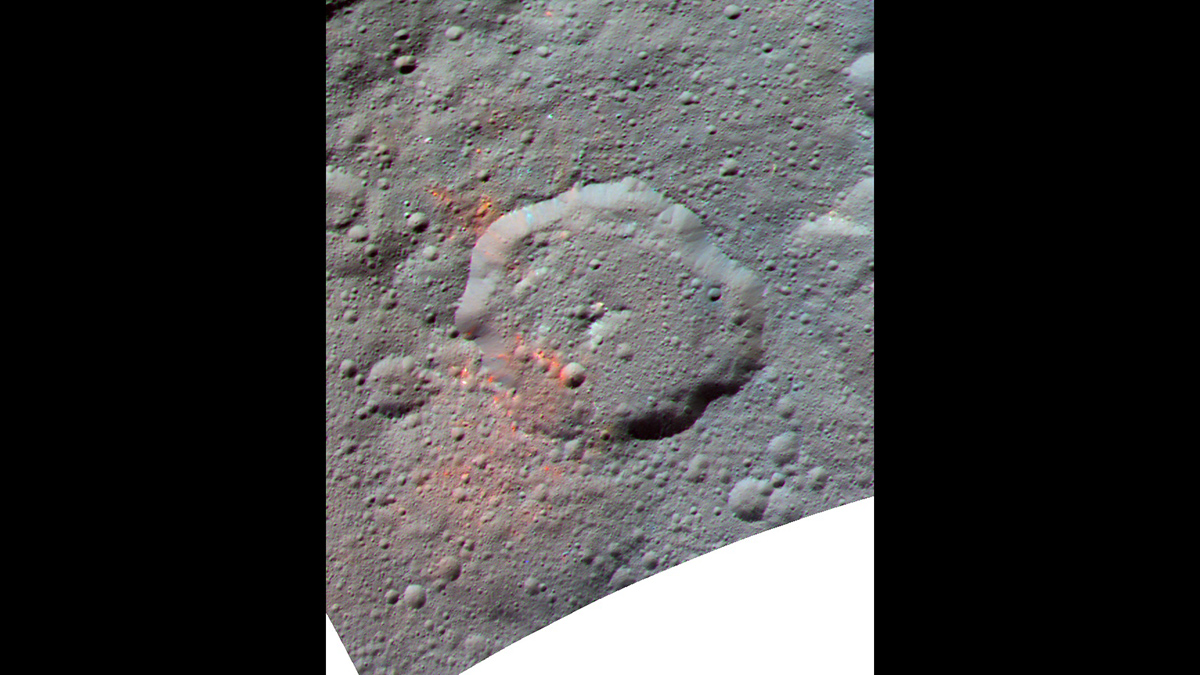
Ceres’s Organics Might Not Be Homegrown After All
Scientists have been unable to determine whether the dwarf planet’s organics were produced by its own chemical processes or delivered by asteroids. New evidence implicates asteroids.