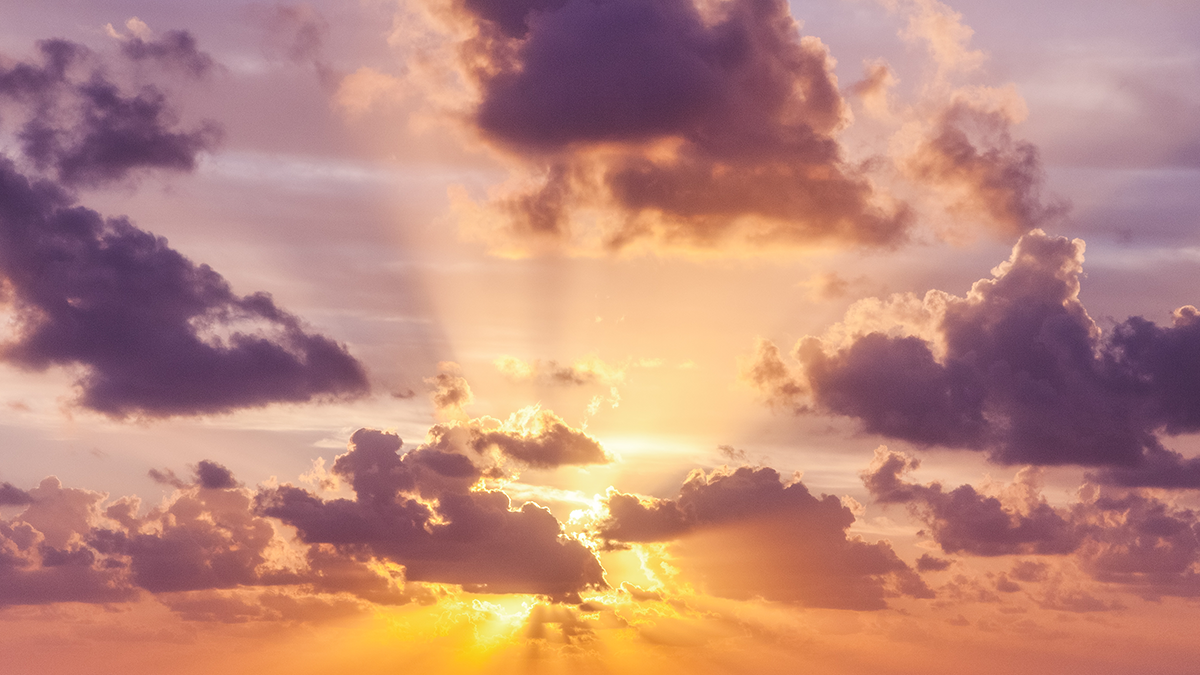
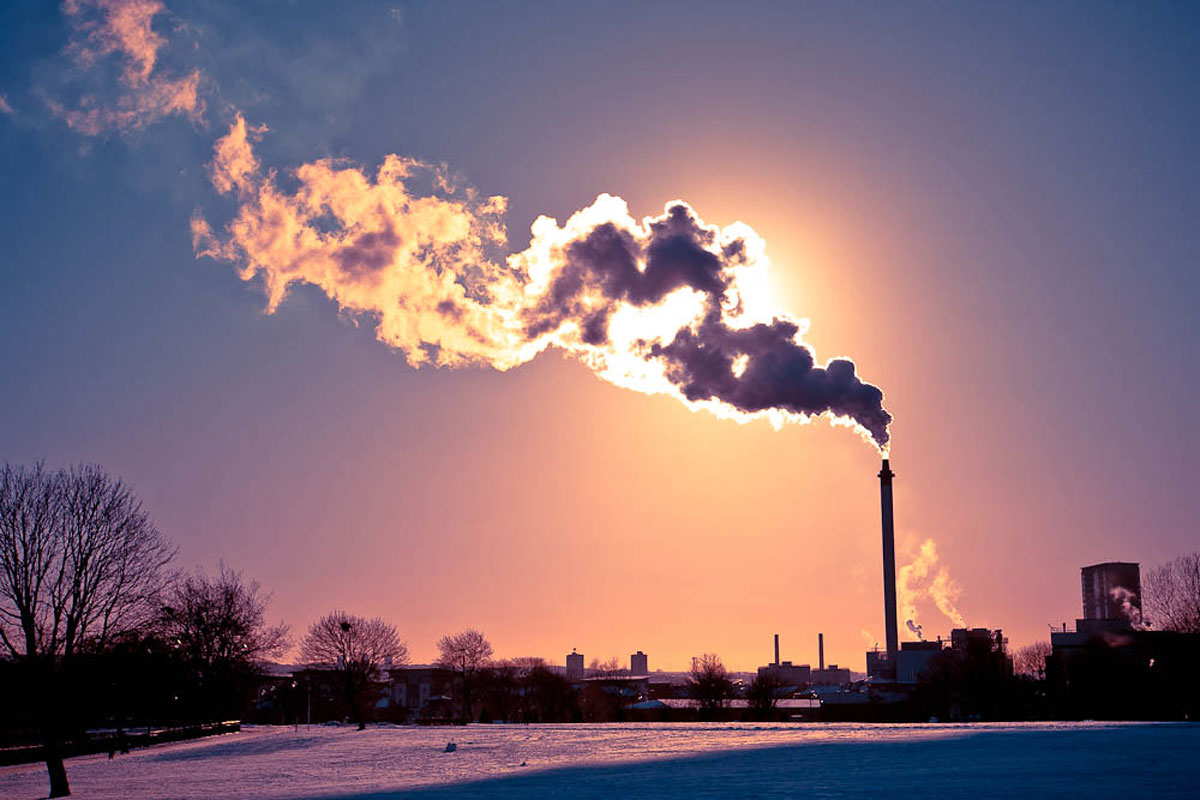
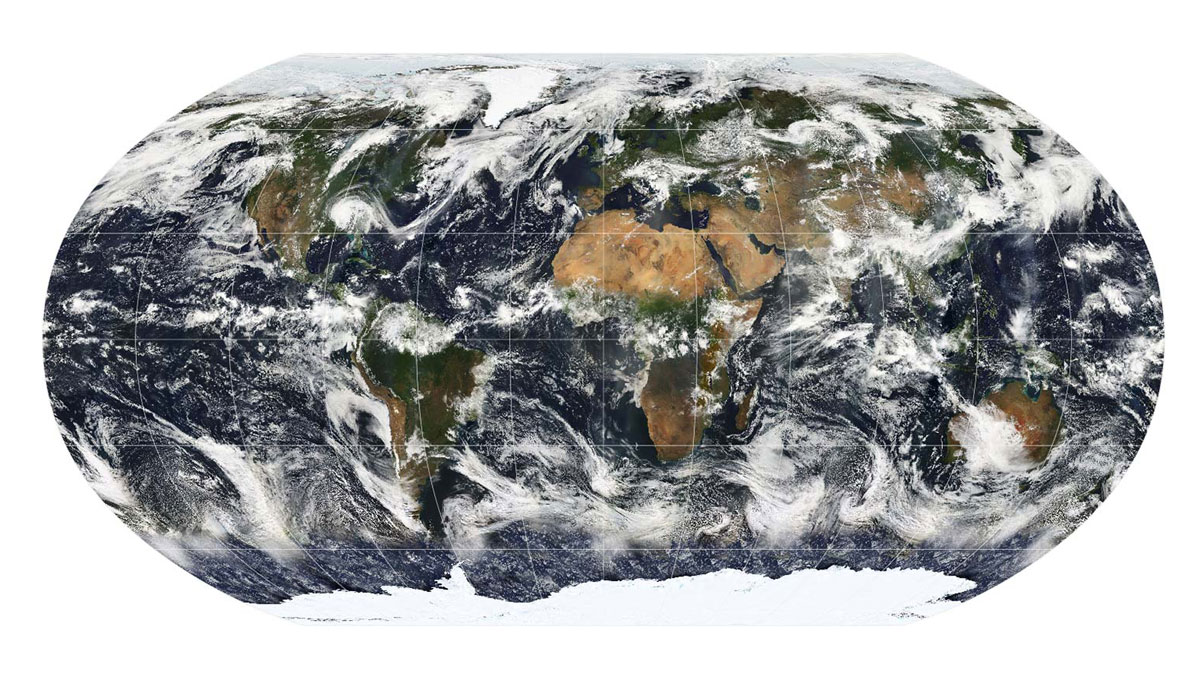
The area near clouds is often classified as ‘clear sky’, but a new study demonstrates the potential biases of misclassifying these transition zones and their significance for Earth’s energy budget.
AGU Advances
Ancient Climate Reconstruction Links Past and Future
A new map of climate conditions during the Pliocene epoch—the last time Earth’s carbon dioxide concentrations hit 400 parts per million—could offer clues about possible climatic changes in store for the 21st century.
How Southern Ocean Currents Modulate Global Biogeochemical Cycles
Swirling currents called mesoscale eddies occupy about 22% of the ice-free Southern Ocean. Using data from drifting floats and satellites, scientists report the impact these eddies have on biogeochemical cycles.
Mars and Earth: A Tale of Two Energy Budgets
The first view of Mars’ latitudinal radiant energy budget reveals stark contrast with Earth’s energy distribution, offering new insights into each planet’s unique energy dynamics.
Wave-Modulated Electron Loss Affects GPS Location Determination
Earth’s magnetosphere controls ionospheric total electron content modulation via plasma wave-induced electron loss impacting GPS spatial location determination.
Bringing Climate Change’s Effects on Atmospheric Circulation to Light
A lengthening observational record is being used to test predictions and improve understanding of the mechanisms behind changing circulation.
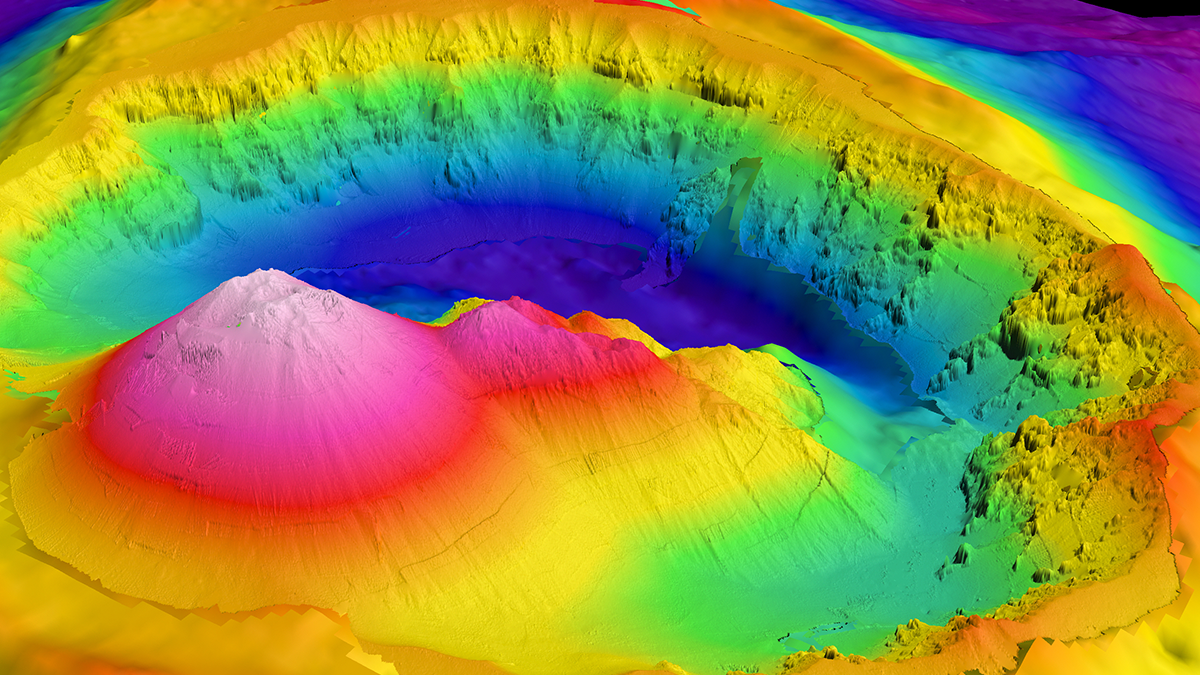
Imaging Magma from Afar
Reservoirs of magma and fluids in the crust create gravity anomalies detectable by altimetry, which can help find submarine volcanoes and provide key insights into their depth, shape and volume.
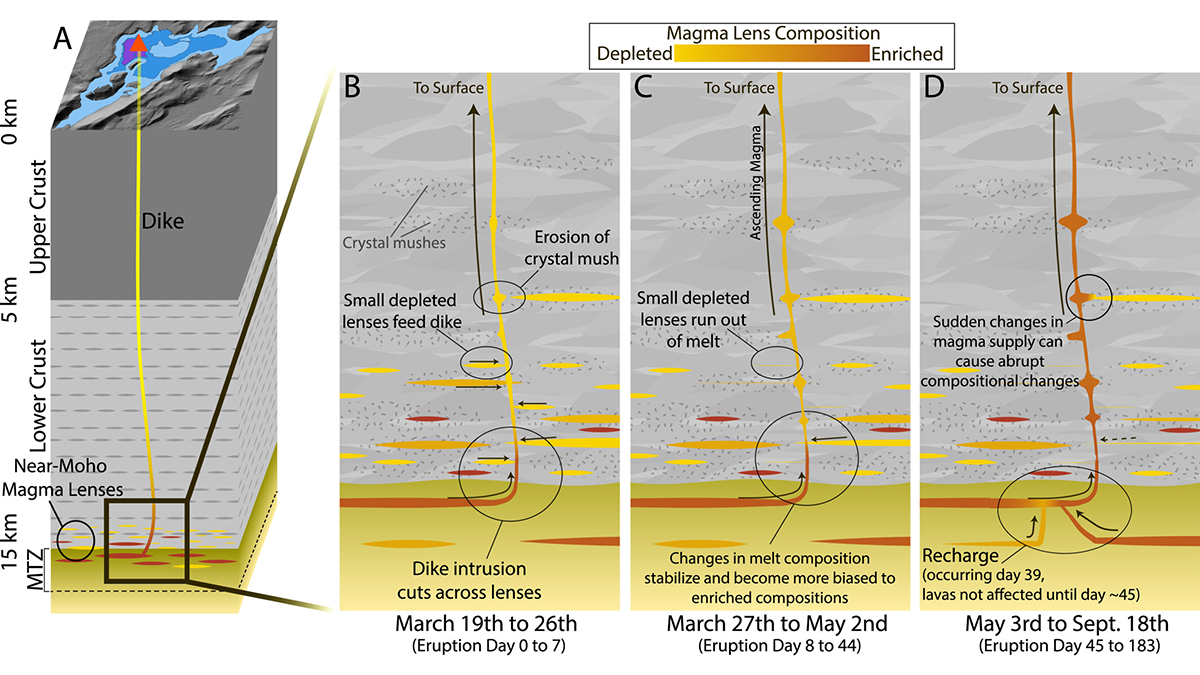
Magma Diversity in Iceland
Iceland’s recent basalt eruptions originated at the crust-mantle boundary and show chemical variability over remarkably short timescales of weeks, suggesting exchanges between diverse magma sources.
Aerosols Could Be Weakening Summertime Circulation
Anthropogenic aerosol emissions may be a culprit behind weakening jet streams and weather systems in the Northern Hemisphere.
Las tormentas están tirando cada vez más árboles
La cantidad de árboles derribados por el viento ha incrementado casi cuatro veces en la región, probablemente por tormentas más fuertes.