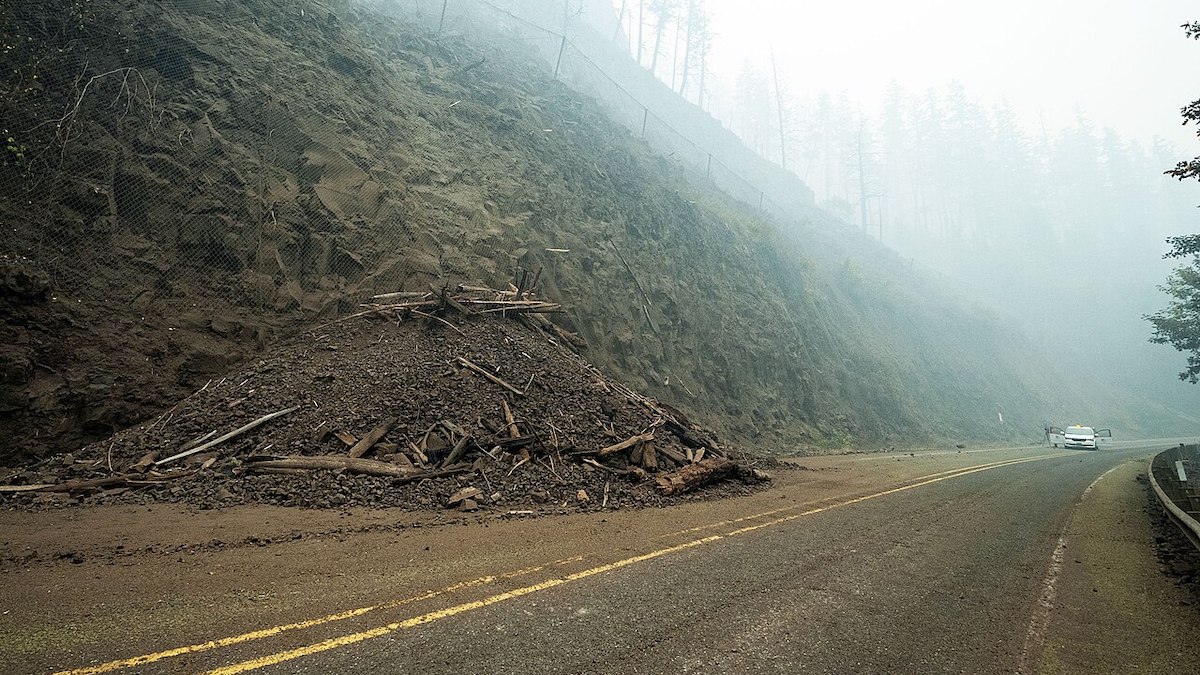
A new method provides highly accurate continental-scale landslide susceptibility maps that are being used in the aftermath of Hurricane Helene.
AGU Advances
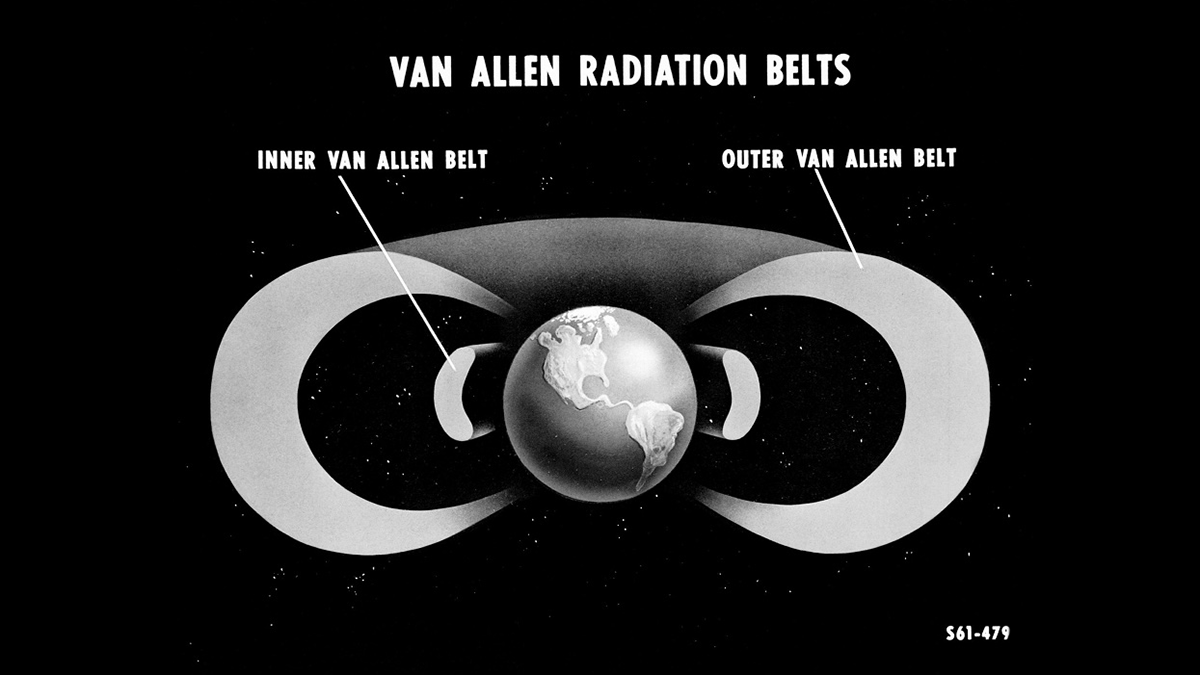
Audible Storm Waves Could Turbocharge Earth’s Radiation Belts
Electromagnetic chorus waves could generate more extreme radiation levels than previously thought, posing severe hazards for Earth-orbiting spacecraft.
The Delicate Balance of Permafrost in Arctic River Floodplains
To evaluate the vulnerability of permafrost in Arctic floodplain landscapes to warming, scientists explore dynamics of its loss and reformation.
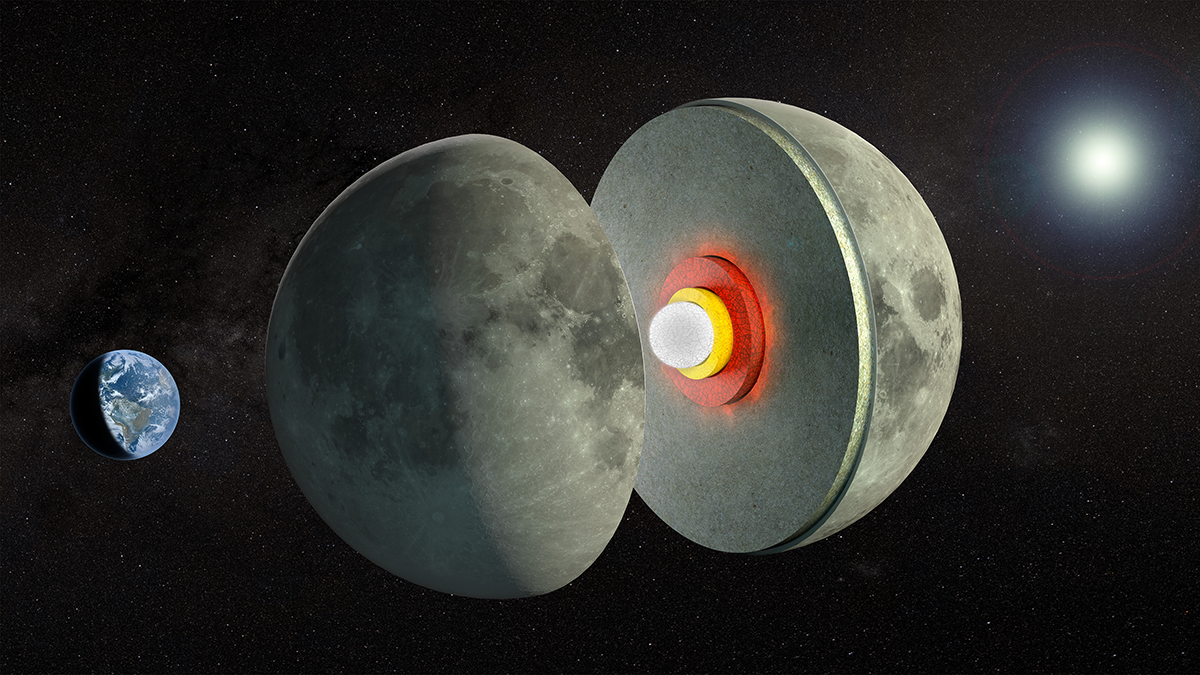
The Moon’s Tides Hint at a Melty Lunar Layer
New lunar gravity measurements support the idea that a partially molten mantle layer is sandwiched between the rest of the Moon’s mantle and its core.
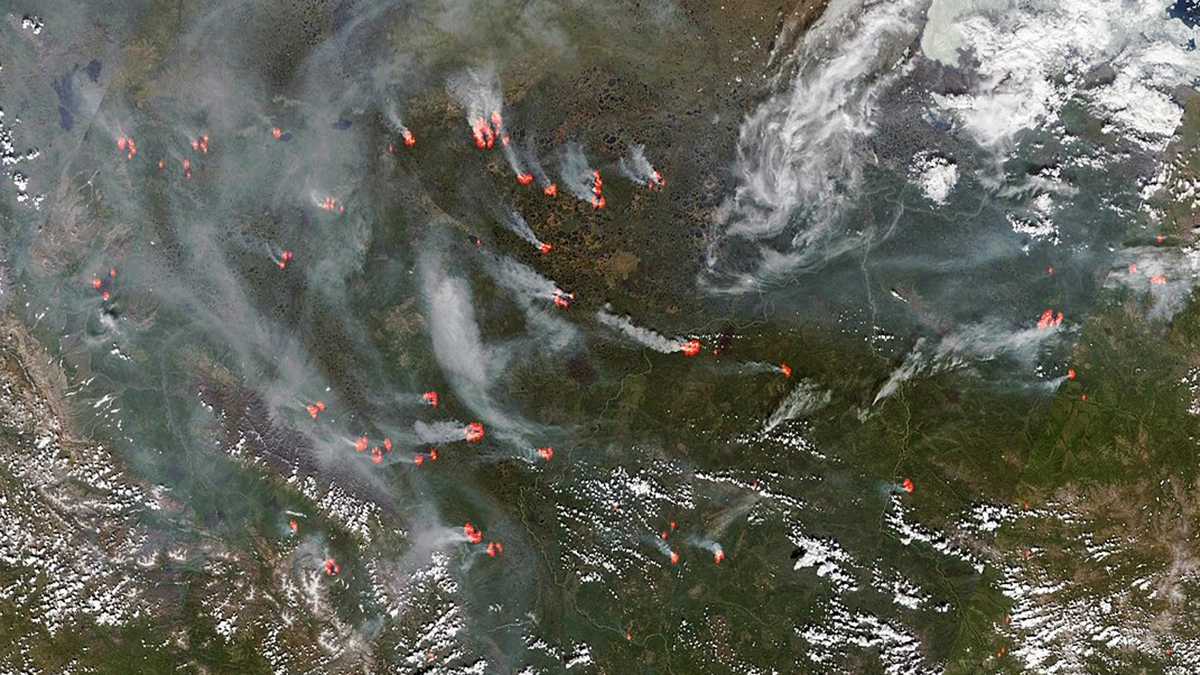
Arctic Warming Is Driving Siberian Wildfires
Increased temperatures and drought are leading to more wildfires. And wildfire smoke aerosols can suppress precipitation, drying out soils and further increasing fire risk.
Shallow Waters Make the Best Carbon Sinks
Oxygen content and microbial prevalence may not be as influential on carbon sedimentation as previously thought.
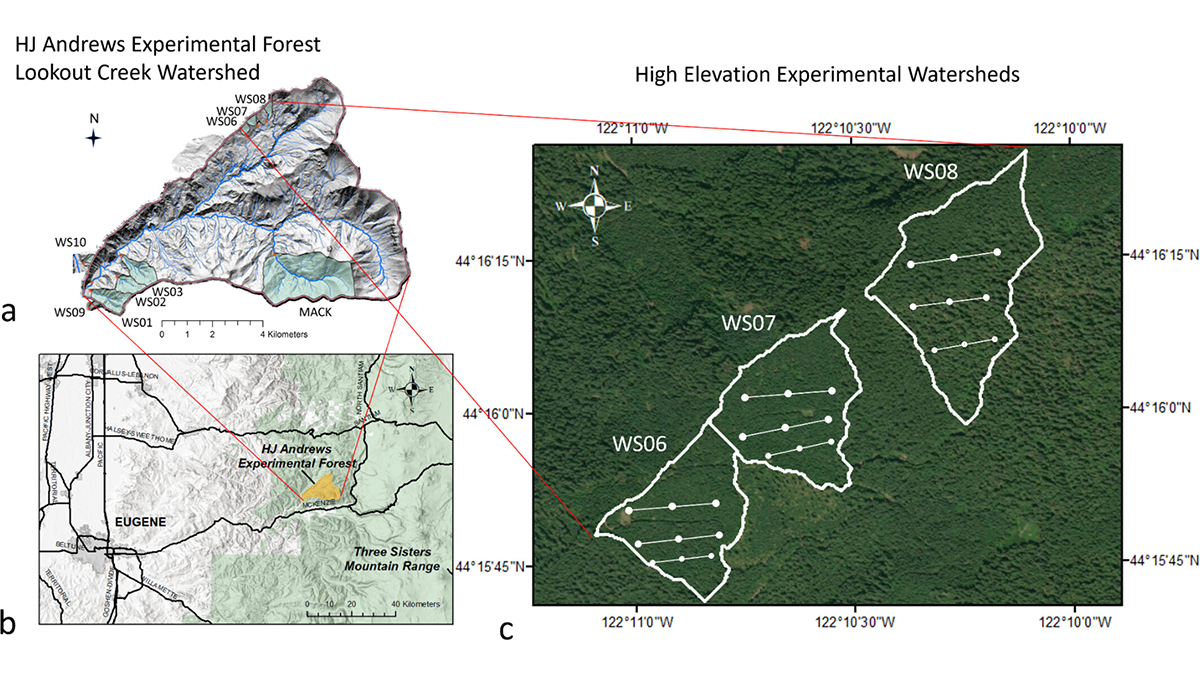
Understanding Carbon-Water Tradeoffs in Pacific Northwest Forests
A new study documents how spruce forests differing in management and age structure influence individual tree growth, carbon stocks, and landscape-water balance in the Pacific Northwest.
Fixing Pollution from Space Needs Global Coordination
Remote sensing is a tool of choice for monitoring regions for air pollution, but the scale of the problem requires extending geostationary soundings globally.
Ocean Spray Is Relatively Lifeless
Organic contributions from ocean organisms are sparse in sea spray, helping to clarify predictions of its impact on the climate.
Using Satellite Data to Estimate Atmospheric CO2 Growth Rates
A new method improves growth rate estimates of carbon dioxide increase in the atmosphere by combining the standard NOAA approach with satellite data.