A new study suggests that spillover of tropospheric ozone is affecting measurements of stratospheric ozone recovery more than previously realized.
AGU Advances
Are the Geosciences Failing Their Qualifying Exam Goals?
Scientists favor data-driven reasoning but administer graduate student qualifying exams with surprisingly little guiding data. Re-examining these exams may advance educational equity and quality.
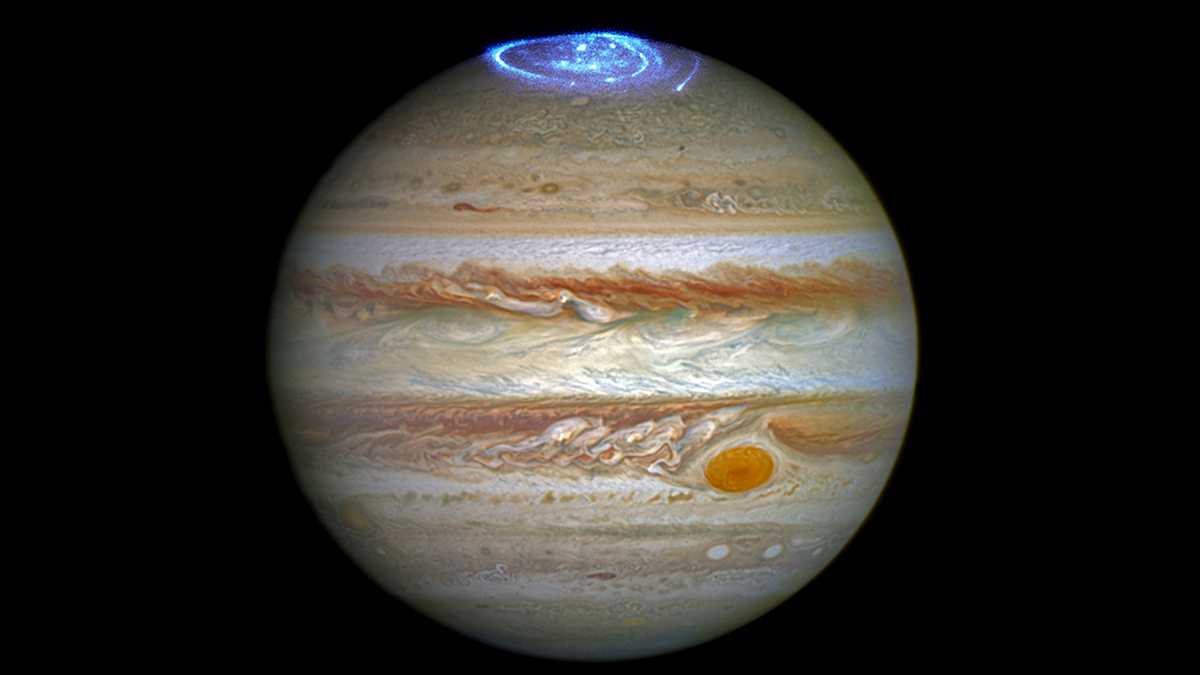
Jupiter’s Magnetosphere Has a Semi-Open Relationship with the Solar Wind
Computer simulations and data from NASA’s Juno mission reveal information about the relationship between solar wind and Jupiter’s massive magnetosphere.
Tiny Satellites Can Provide Significant Information About Space
Students and faculty at the University of Colorado Boulder use CubeSats to learn more about the near-Earth environment.
Discounting Carbon Gain to Prevent Water Loss Today
A new study introduces a timescale for optimizing tradeoffs between carbon gain and water loss to improve estimates of photosynthesis during prolonged dry spells.
When Extreme Drought Becomes Commonplace
As drought becomes a more regular occurrence, a new study looks at the U.S. Drought Monitor, the nation’s preeminent drought classifier, to see how it has reflected climate change since 2000.
Fault Maturity or Orientation: Which Matters More for Quakes?
Close examination of a 2021 earthquake on the Tibetan Plateau provides hints that, counter to prior assumptions, the influence of fault orientation can sometimes trump that of maturity.
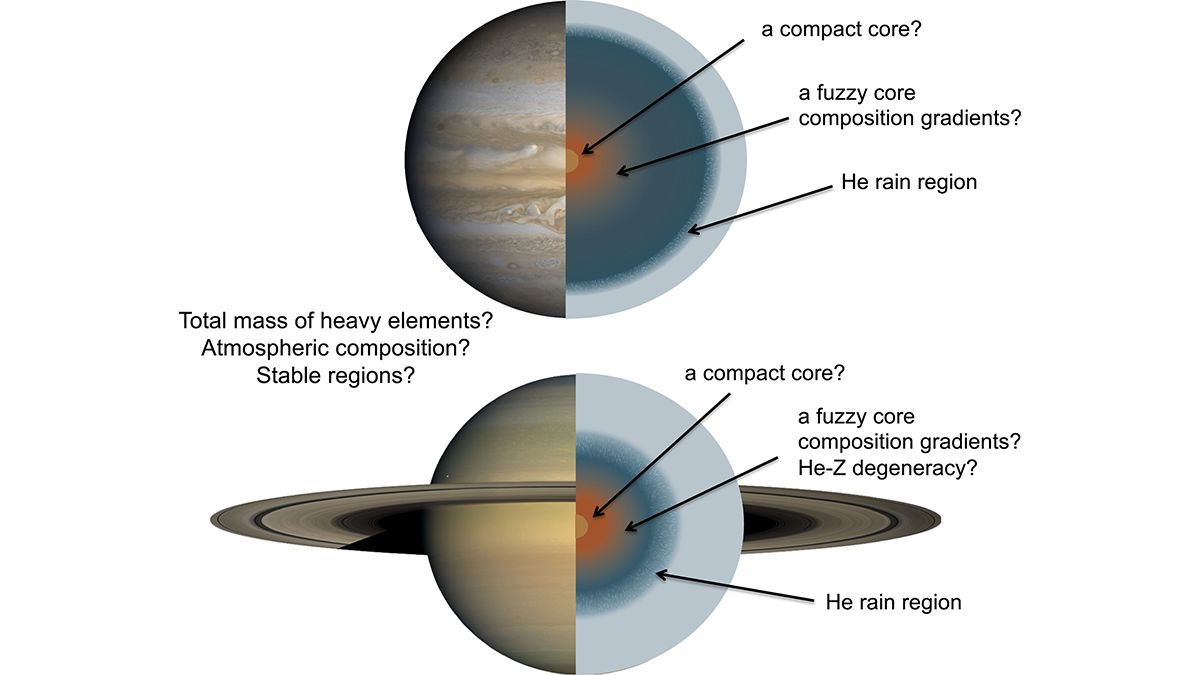
Gas Giants with Fuzzy Cores
New measurements of Jupiter and Saturn show that both planets have dense cores that are gradational (fuzzy) and large, rather than small and compact.
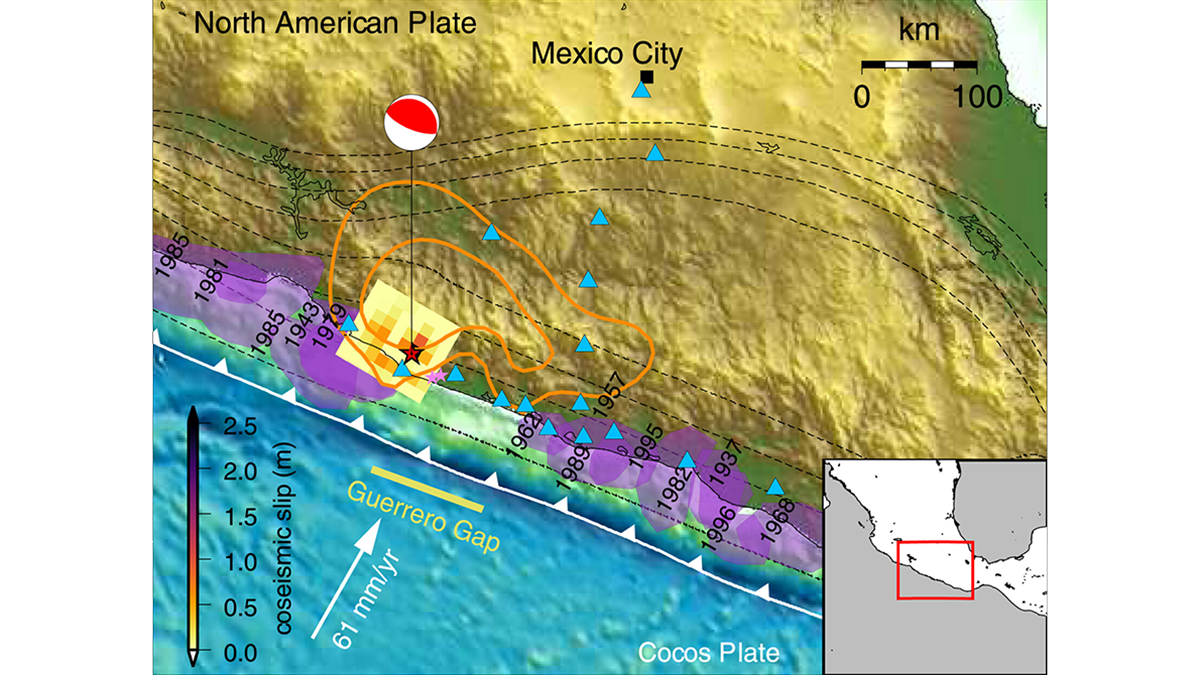
Forecasting Earthquake Ruptures from Slow Slip Evolution
A new generation of physics-based models that integrate temporal slip evolution over decades to seconds opens new possibilities for understanding how large subduction zone earthquakes occur.
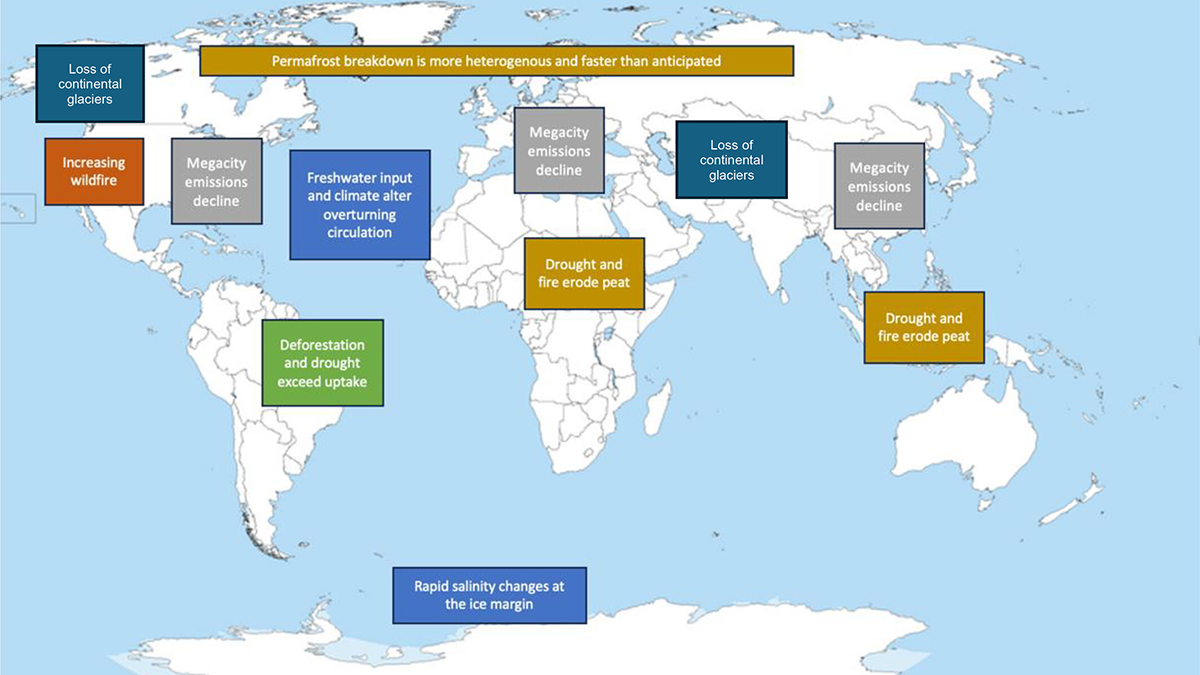
Framing the Next Decadal Survey for a Warming World
The next decadal survey (DS28) will be framed by a rapidly changing world, and will be critical to consider observational needs of the 2030s-2040s, a world increasingly dominated by climate extremes.