Faint magnetic properties in primitive asteroid fragments suggest an early magnetic field strong enough to shepherd the growth of the outer planets.
AGU Advances
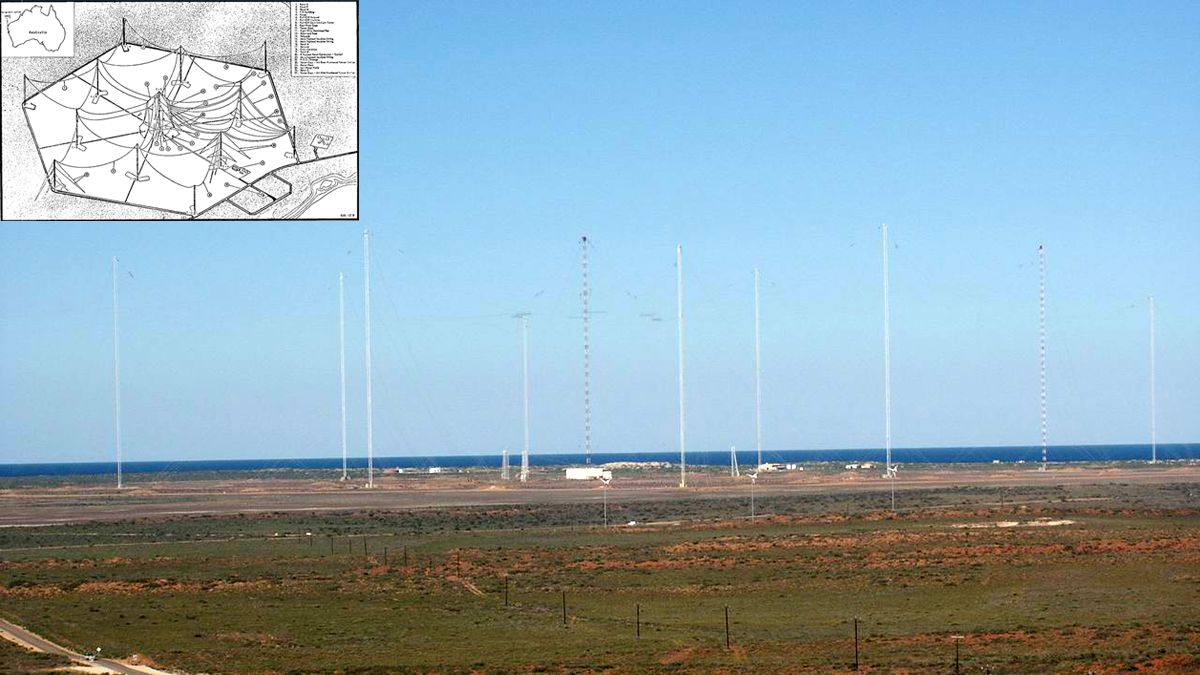
Ground-based Transmitters Cause Radiation Belt Electron Loss
A U.S. Navy transmitter in Australia produces wisps of electron loss as observed by the Colorado Inner Radiation Belt Experiment (CIRBE) CubeSat in Low Earth Orbit.
New Insight into Inland Water Carbon Dioxide Emissions
A process-based modeling technique reveals surprising information about carbon emissions from rivers, lakes, and reservoirs across the contiguous United States.
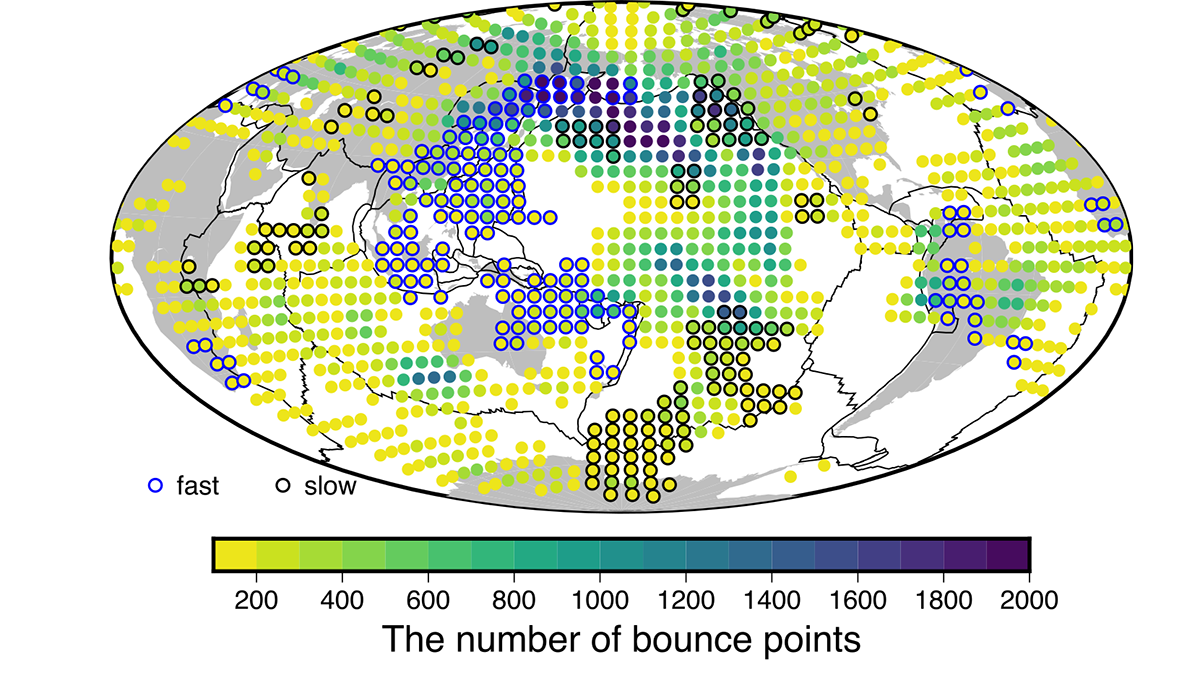
Compositional Anomalies Complicate Our Model of Mantle Convection
A new study expands on recent research which suggests that oceanic crust accumulates in the mid-mantle. The new seismological constraints advance our understanding of thermo-chemical planetary evolution.
Physics and Biology as Likely Stream Bedfellows
Streambeds are key sites for removal of nutrients and other contaminants through microbial processes, but are limited by diffusion, which can now be modeled from streambed physical properties.
Announcing New AGU Journal Editors-in-Chief Starting in 2025
AGU is excited to welcome new Editors-in-Chief for five of our journals in 2025.
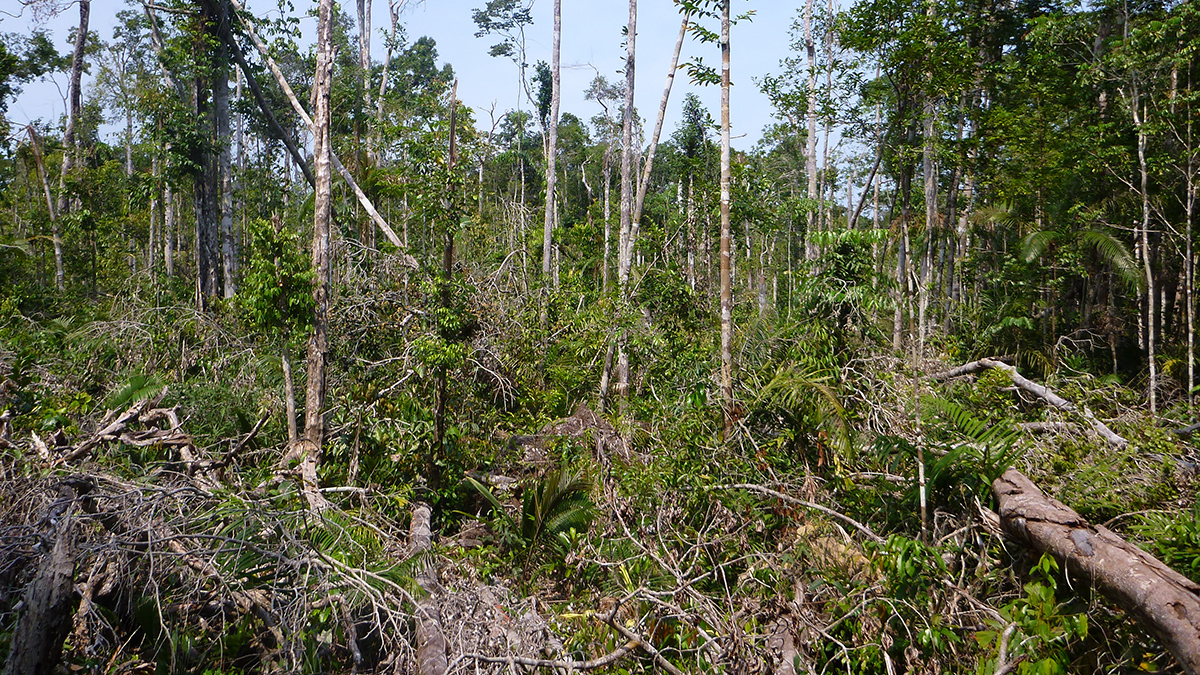
Storms Are Knocking Down More and More Trees in the Amazon
Windthrows have increased nearly fourfold in the region, likely because of stronger storms.
Clumped CO Isotopes – New Tracers for Atmospheric Chemistry
A new study reports the first measurements of 13C18O in atmospheric carbon monoxide (CO) and show their variations reflect chemical ‘aging’ consistent with predicted kinetic isotope effects.
Tracking a Disappearing Mantle Plume in Ancient Samoa
A thick portion of Earth’s crust may have capped the Samoan plume and suppressed volcanism for 30 million years, explaining a curious gap along the Samoan chain.