Subducting plates are stronger in certain directions than others, which may be a factor in how earthquakes occur and how seismic waves propagate.
anisotropy
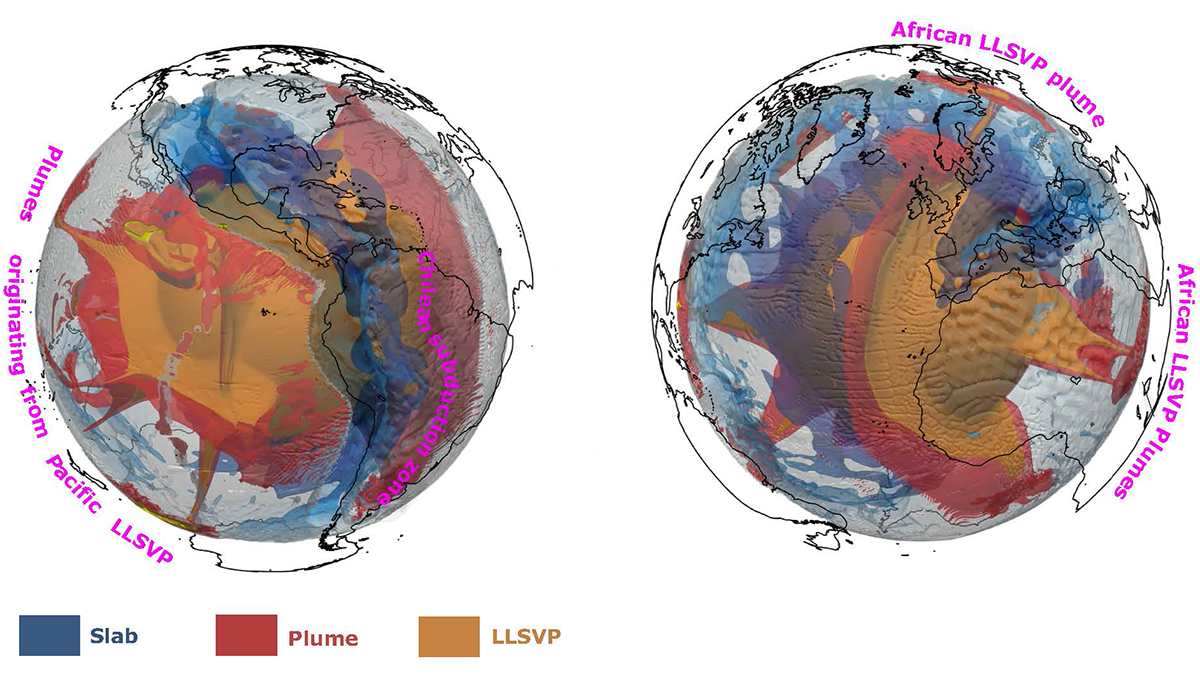
Seismic Anisotropy Reveals Deep-Mantle Dynamics
A new study offers insight into the viscous BLOBs at the base of Earth’s mantle.
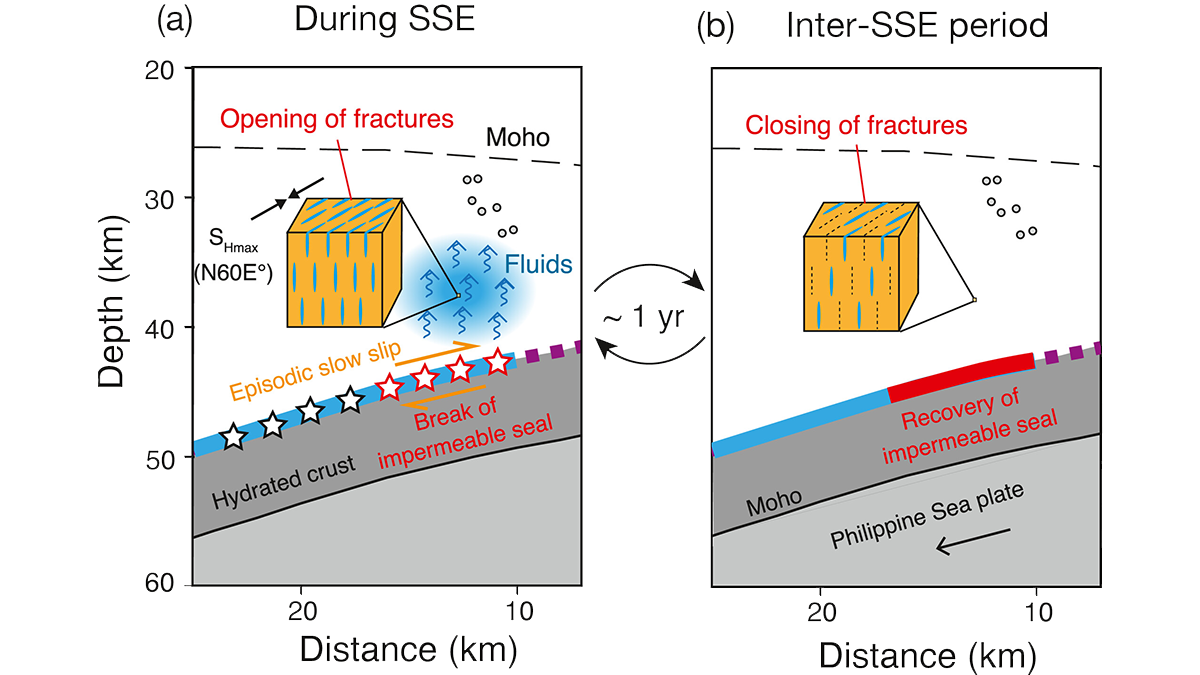
Cyclic Opening of Deep Fractures Regulates Plate Boundary Slip
Seismic anisotropy changes through time suggest that cyclical opening of fluid-filled fractures is synchronized with subduction zone slow slip events.
Seismology Helps Us Understand How Material Flows in Earth’s Deepest Mantle
Recent progress in the analysis of seismic waves enables us to determine where, and sometimes how, the base of the mantle deforms.
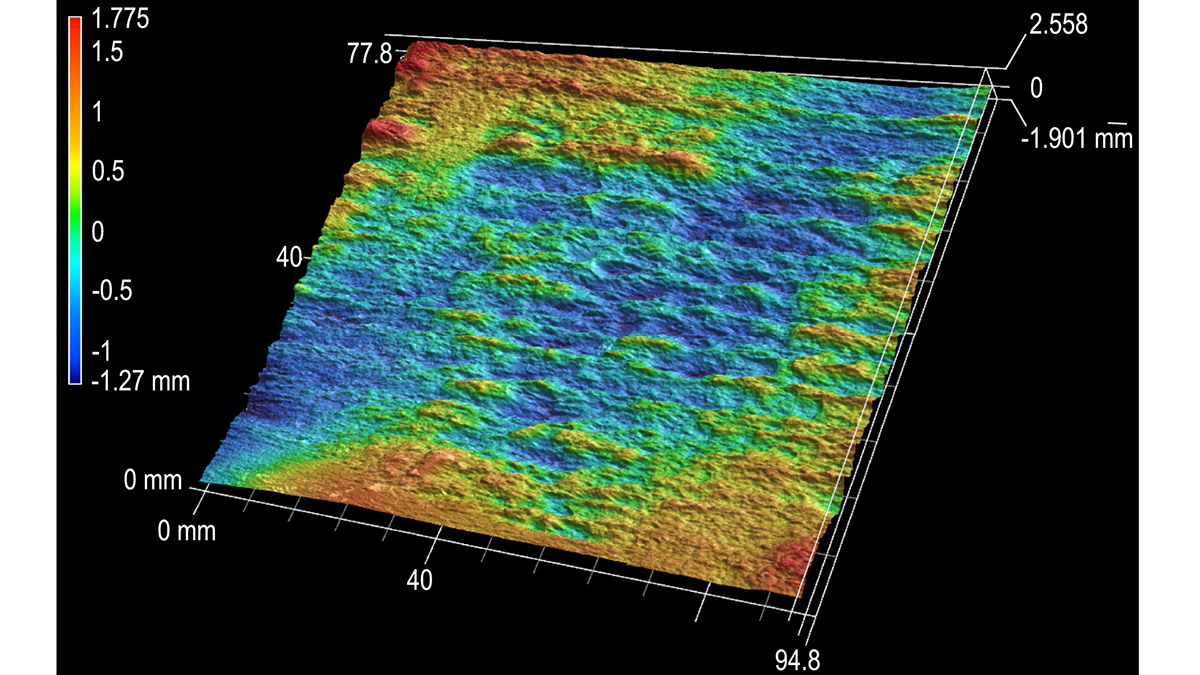
Hydraulic Fractures Are Lazy
The layering of rock masses can help constrain and focus the growth of hydraulic fractures.
Illuminating the Complex Structural Fabric Beneath the European Alps
A new study investigates the dynamics of the complex continental collision that formed the European Alps and reveals how structural alignments change with depth.
Small-Scale Convection Shuffles the Oceanic Lithosphere
Seafloor spreading organized lithospheric minerals into a lattice, but small-scale convection jumbled up the innermost layer.
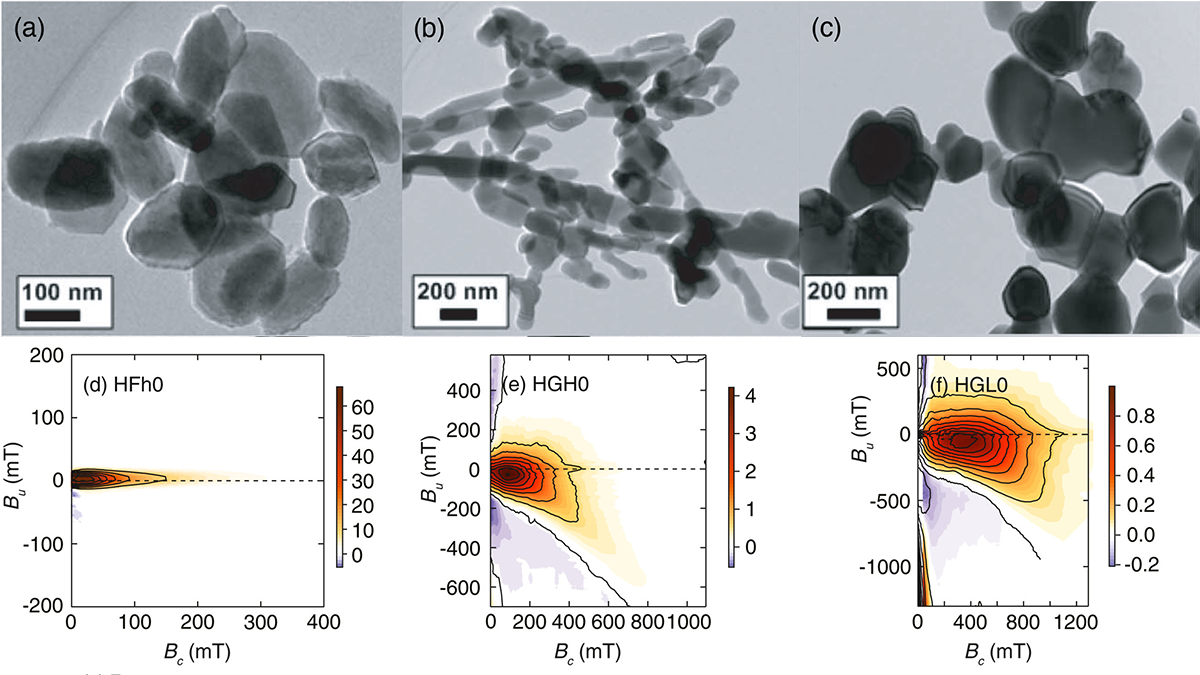
A Step Towards Understanding the Magnetic Properties in Hematite
Scientists present the most comprehensive available magnetic domain state and anisotropy study for synthetic and natural hematite from first-order reversal curve diagrams.
Observation of Shear Wave Anisotropy in the Earth’s Inner Core
Coda-correlation wavefields reveal direction-dependent inner-core shear-wave speed, ~5 s faster in directions oblique to the Earth’s rotation axis than directions parallel to the equatorial plane.
Improving Weather Simulations Through Increased Generality
By adding support for spatially variable velocity fields and anisotropy, the CoSMoS simulation package can more accurately reproduce physical phenomena.





![Figure 2 from Wang and Tkalčić [2021]](https://eos.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2021GL094784-Figure-2-sized-1200x675-1.png)
