Una técnica que mide la relación entre el dióxido de carbono producido y el oxígeno consumido podría mejorar las predicciones de la respuesta del suelo al cambio climático.
bacteria & microbes
Microscopic Hitchhikers Found on Deep-Sea Plastic
Are bacteria hailing a ride on plastic 2,000 meters deep?
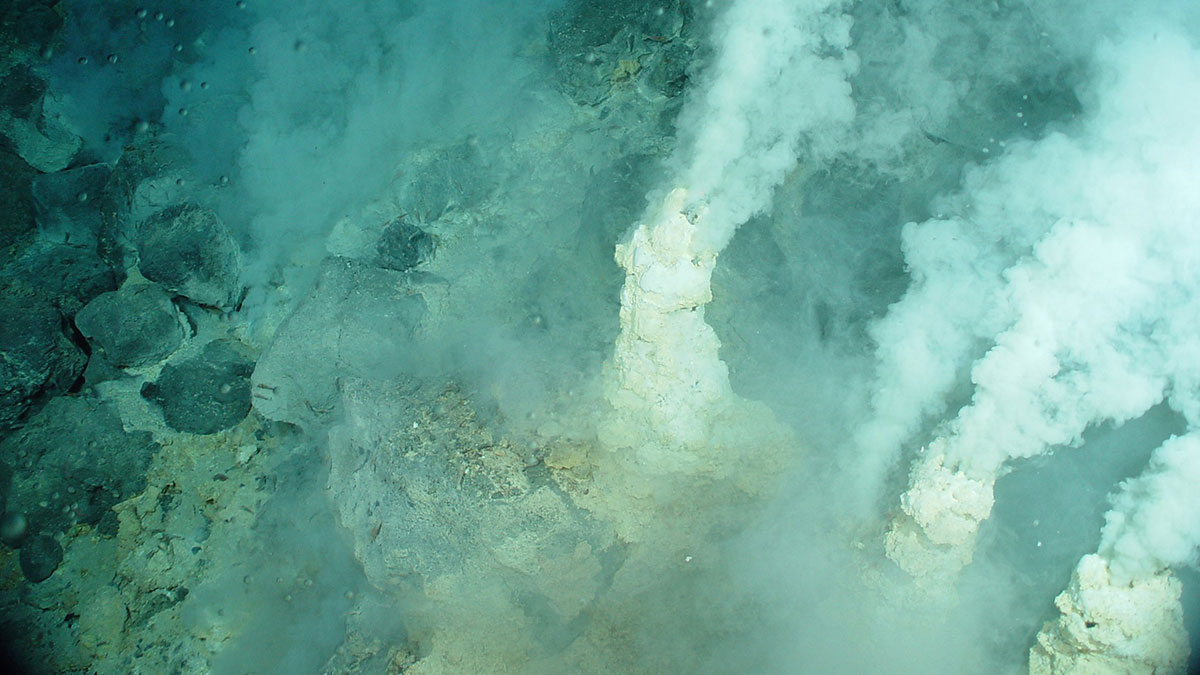
The Ocean Is Still Sucking Up Carbon—Maybe More Than We Think
Recent studies looking at carbon-sequestering microbes suggest we still have a lot to learn about the ocean’s biological carbon pump.
Paired Gas Measurements: A New Biogeochemical Tracer?
A technique that measures the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed could improve predictions of soil’s response to climate change.
Mortality of Seagrass Meadows May Not Kill Their Methane Release
New research indicates that seagrasses continue to release methane even after they die, complicating blue carbon initiatives.
Traditional Fertilizers Beat Out Industrial Chemicals in Soil Health Test
New research in western India found that fertilizer based on Traditional Ecological Knowledge made soil more fertile in a head-to-head test with industrial fertilizers.
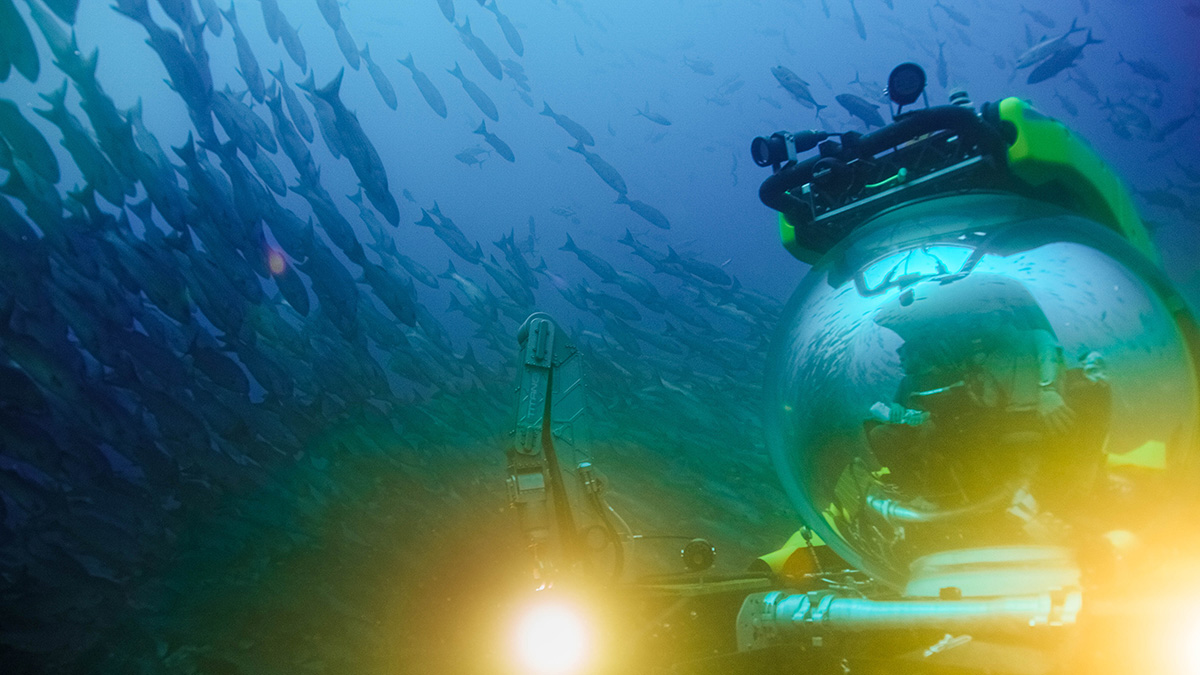
Deep-Sea Exploration Could Help Us Fight the Next Pandemic
Deep-ocean-dwelling microbes may hold keys to improved medical diagnostics and new drugs for fighting diseases. But we must search Earth’s most extreme habitats to find them.
Biological Crusts Affected by Drought Can Still Stabilize Soils
Results of in situ experiments on natural microbial communities suggest that biological crusts can protect soils from erosion, but their protective role could be compromised under predicted future climate scenarios.
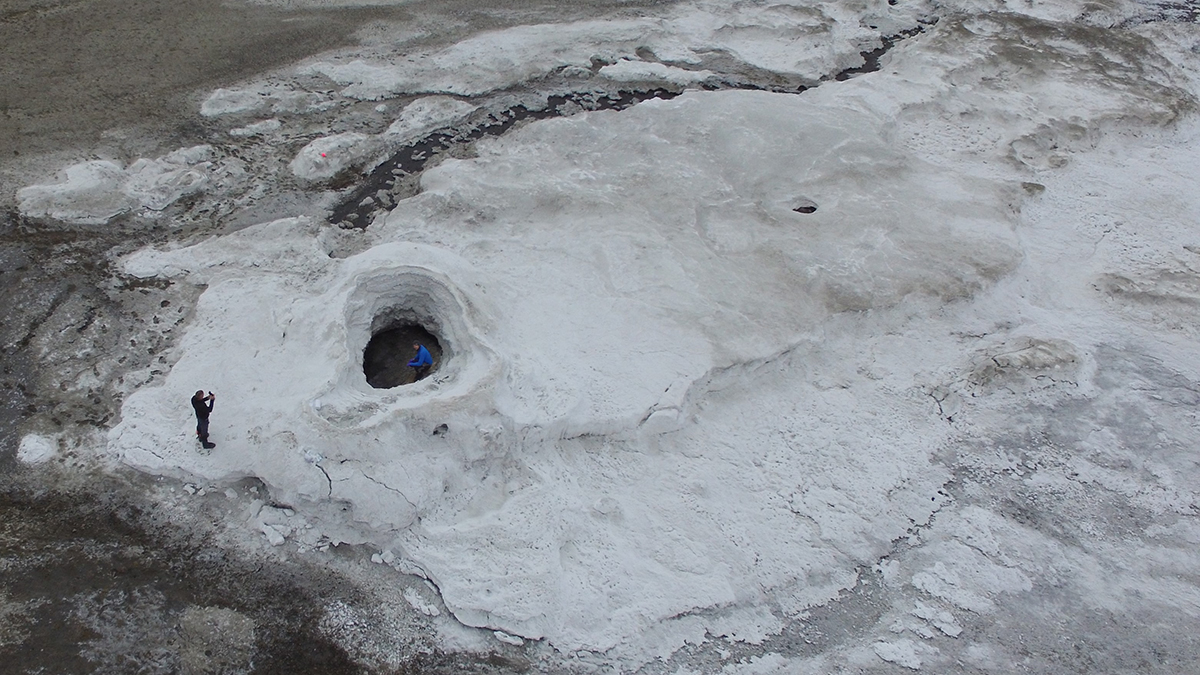
Lipids from Europa’s Ocean Could Be Detectable on the Surface
A super salty spring in the Canadian Arctic provides insights key to detecting life on a distant ocean world.