Global cooperation and knowledge sharing are essential to improve our understanding of cloud formation and evolution through aerosol-cloud interaction.
clouds
New Insights into the Foggy Role of Contrails Within Clouds
New research helps clarify how frequently contrails form within clouds and what that means for their effect on the climate.
Some Summer Storms Spit Sooty Particles into the Stratosphere
Earth’s typically pristine stratosphere is filling with particles from wildfires and additional moisture due to strong convective storms.
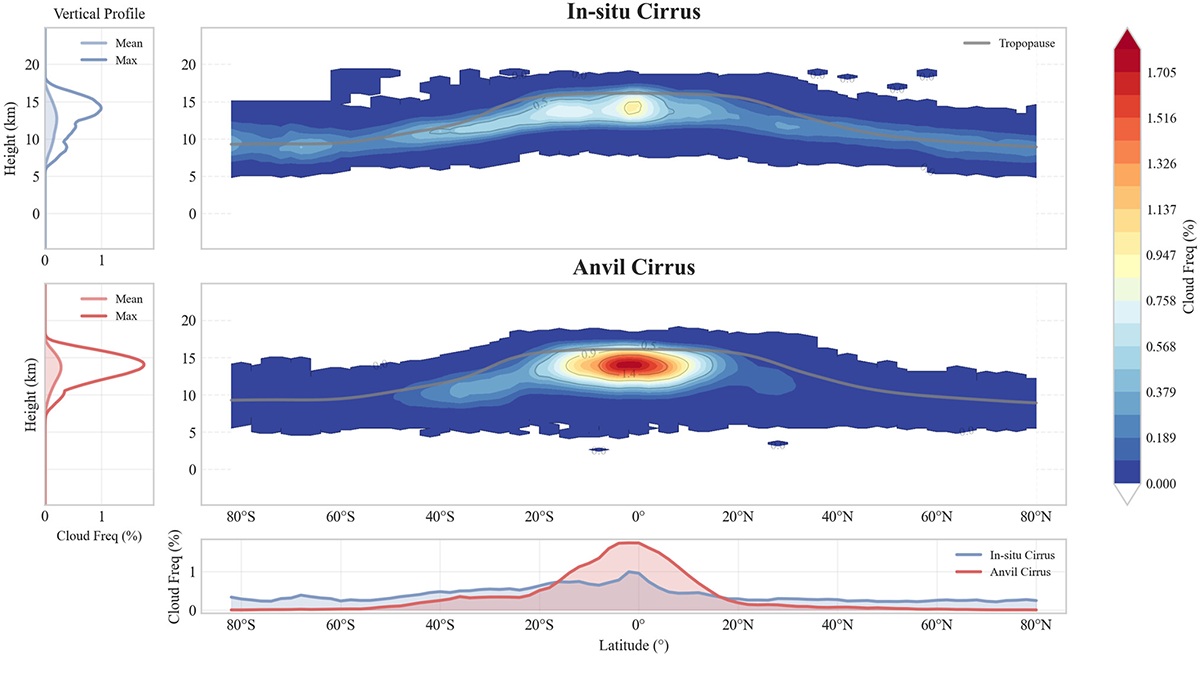
Understanding Relative Atmospheric Roles of Anvil and In-situ Cirrus Clouds
New framework for separating anvil and in-situ cirrus clouds provides a pathway for modeling cirrus and how regional shifts in convection could reshape global cirrus distributions and their radiative impact.
Understanding Cloud Droplets Could Improve Climate Modeling
The microphysical structure of cloud droplets affects behavior like precipitation. Current models may be underestimating how much these structures can vary within a single cloud.
New Satellite Data Reveal a Shift in Earth’s Once-Balanced Energy System
The Northern Hemisphere is absorbing more sunlight than the Southern Hemisphere, and clouds can no longer keep the balance.
Dust Is the Sky’s Ice Maker
New analysis links desert dust to cloud freezing, with big implications for weather and climate models.
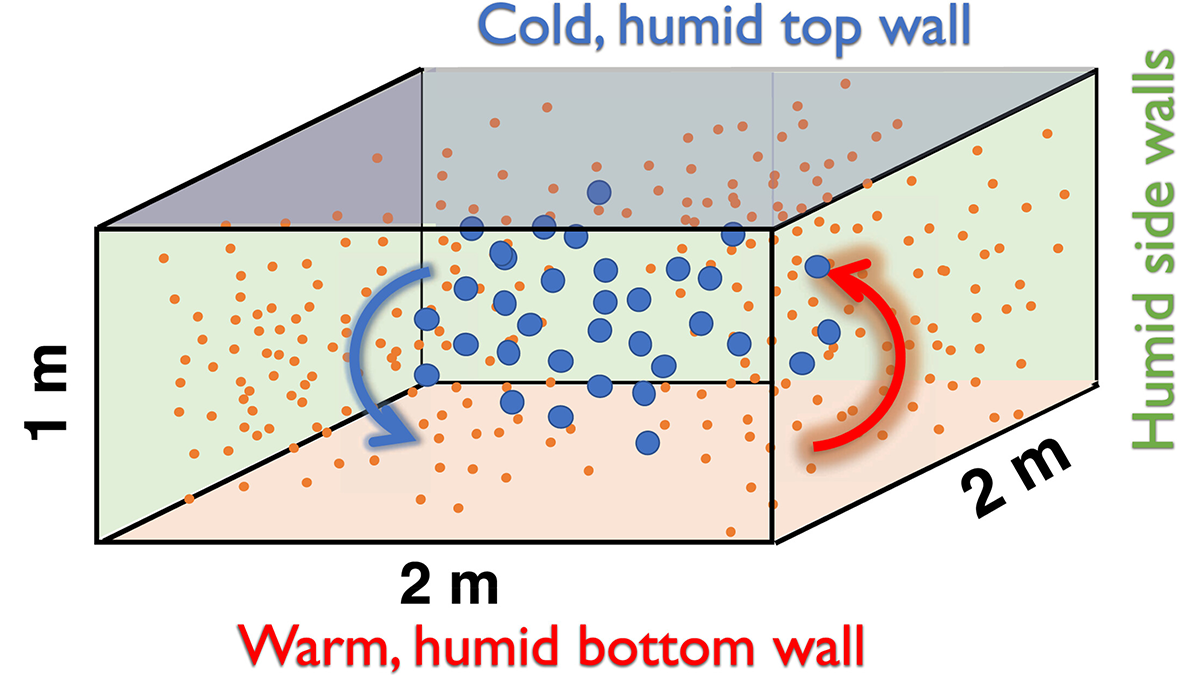
From Aerosols to Clouds: Testing Models with a Convection Cloud Chamber
Researchers benchmark seven cloud models against cloud chamber measurements to reveal how well models capture aerosol-cloud-turbulence interactions and where models still diverge.
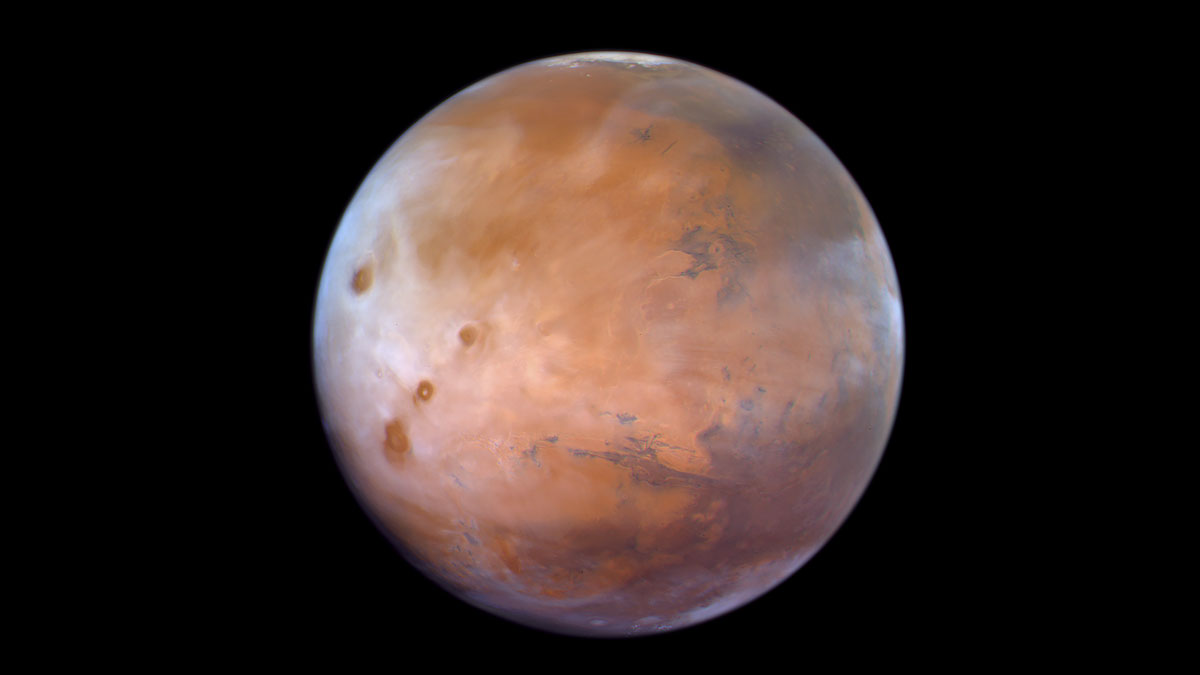
First Complete Picture of Nighttime Clouds on Mars
Data captured by the Emirates Mars Mission reveal that clouds are typically thicker during Martian nighttime than daytime.
ARMing SCREAM with Observations to Expose Cloud Errors
Modern ARM observations expose persistent process-level errors in a global cloud-permitting model, guiding future developments and improvements.