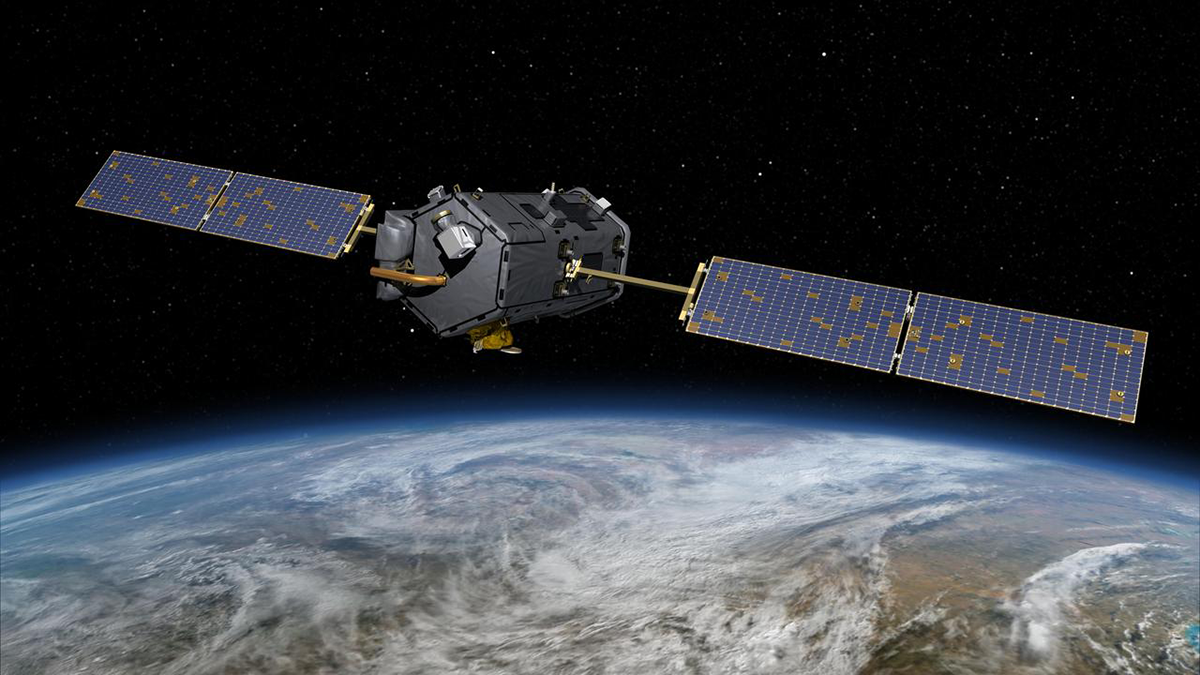
NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 satellite reveals an impressively dynamic picture of the Earth’s carbon cycle, yet it may be prematurely decommissioned and destroyed due to budget cuts.
COVID-19
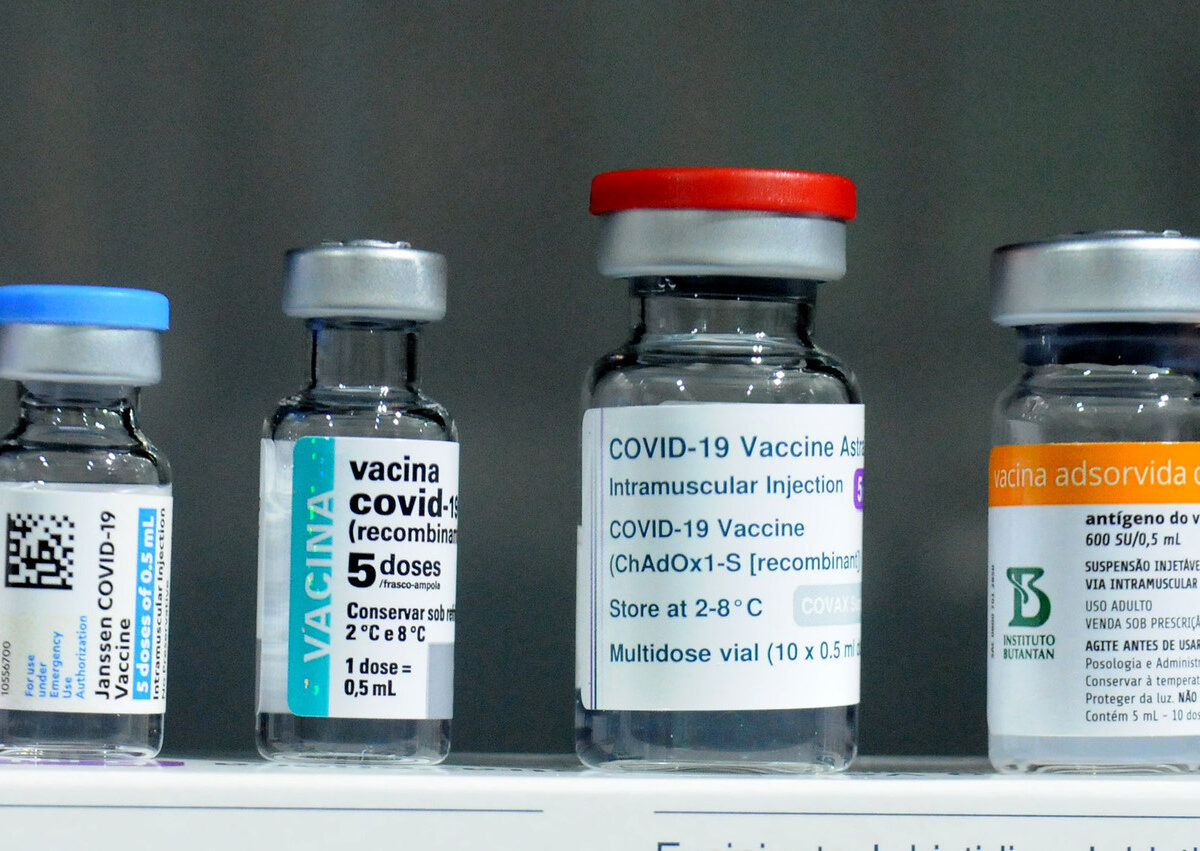
Government Will Reduce Access to COVID-19 Vaccine
Officials from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced on Tuesday that only adults older than 65 and people with specific medical conditions will be considered eligible for COVID-19 vaccinations this fall.
NIH Cancels Climate and Health Research Grants
The Trump administration’s intentions toward addressing climate change are clear: Federal agencies purged mentions of the climate crisis from their websites and slashed funding for mitigation tools such as the Future Risk Index. Now, those intentions are extending to health research: The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has begun to cancel funding for investigations into the health effects of climate change, and will not financially support new research on the subject, according to ProPublica and Nature.
Particulate Pollution and its Climate Impacts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The impacts of COVID-19 on short-lived pollutants highlight the predominant influence of the transportation sector and the resulting changes in regional climates and ecosystems.
Oil, Gas, and COVID-19
Early in the pandemic, people living near oil and gas wells experienced higher rates of COVID-19 and related mortality compared with those with no exposure to well pollution.
National Science Board Reports a Need for More Support of STEM Talent
U.S. National Science Board members called for more robust funding for science and engineering.
Reflecting on 4 Years at the helm of JGR: Solid Earth
The outgoing Editor-in-Chief of JGR: Solid Earth reflects on their tenure and expresses appreciation to all those who contributed to the success of the journal over recent years.
The Importance of Archiving the Seafloor
Marine geological sample repositories are vital for ocean science, climate change studies, and more. The value of their collections is growing amid efforts to meet rising demand for their services.
Air Pollution Increases COVID-19 Risks
A crop of new studies shows that exposure to air pollution adds days to hospital stays and increases the likelihood of death from COVID-19.
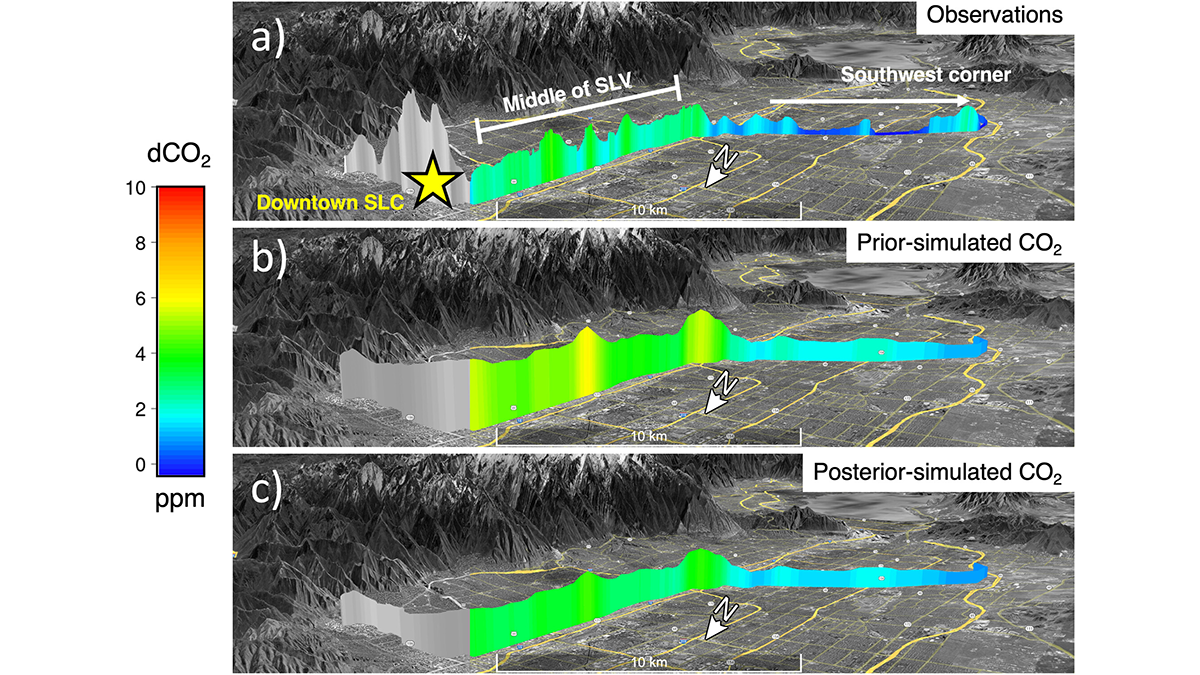
Tracking Human CO2 Emissions from Medium-Sized Cities
Atmospheric inverse models, combined with observations, successfully tracked modest CO2 emission reductions in Salt Lake City during the first COVID-19 lockdown in 2020.