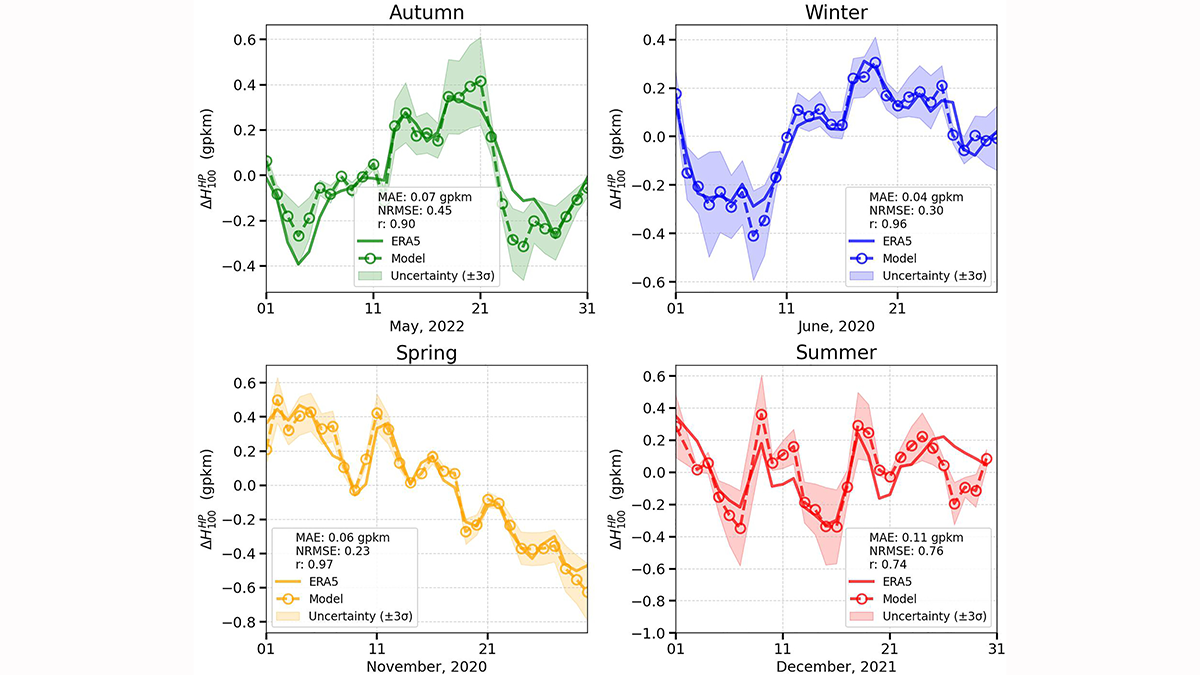
Water-Cherenkov cosmic-ray detectors can be used as a tool for monitoring and studying changes in the lower stratosphere over Antarctica.
Earth and Space Science
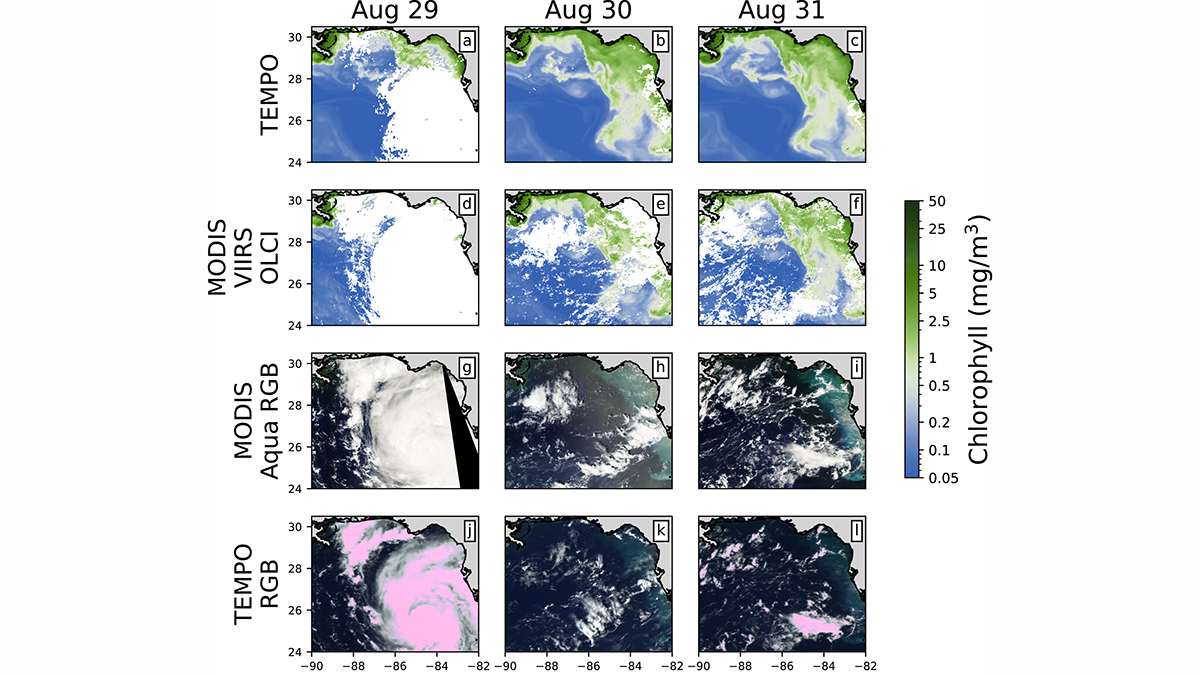
Monitoring Ocean Color From Deep Space: A TEMPO Study
Scientists apply machine learning to demonstrate that geosynchronous satellites can be used to assess the health of oceans from deep space.
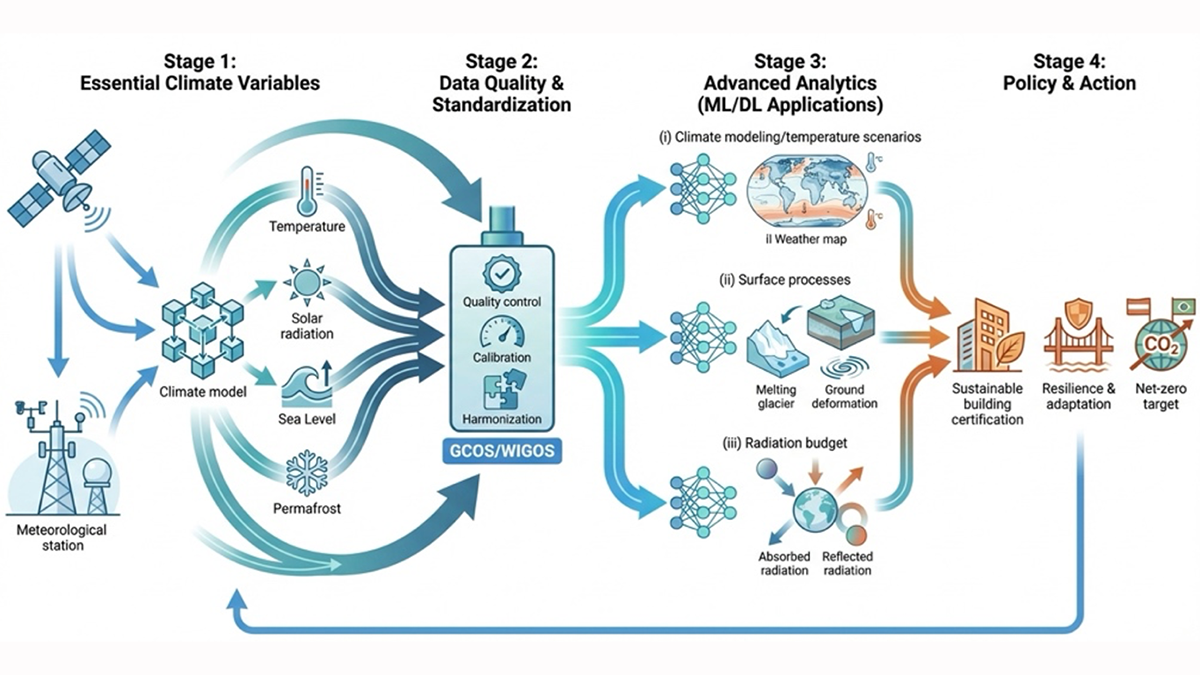
Bridging the Gap: Transforming Reliable Climate Data into Climate Policy
A new special collection welcomes research that bridges the gap between rigorous Essential Climate Variable (ECV) monitoring, AI analytics, and climate policy.
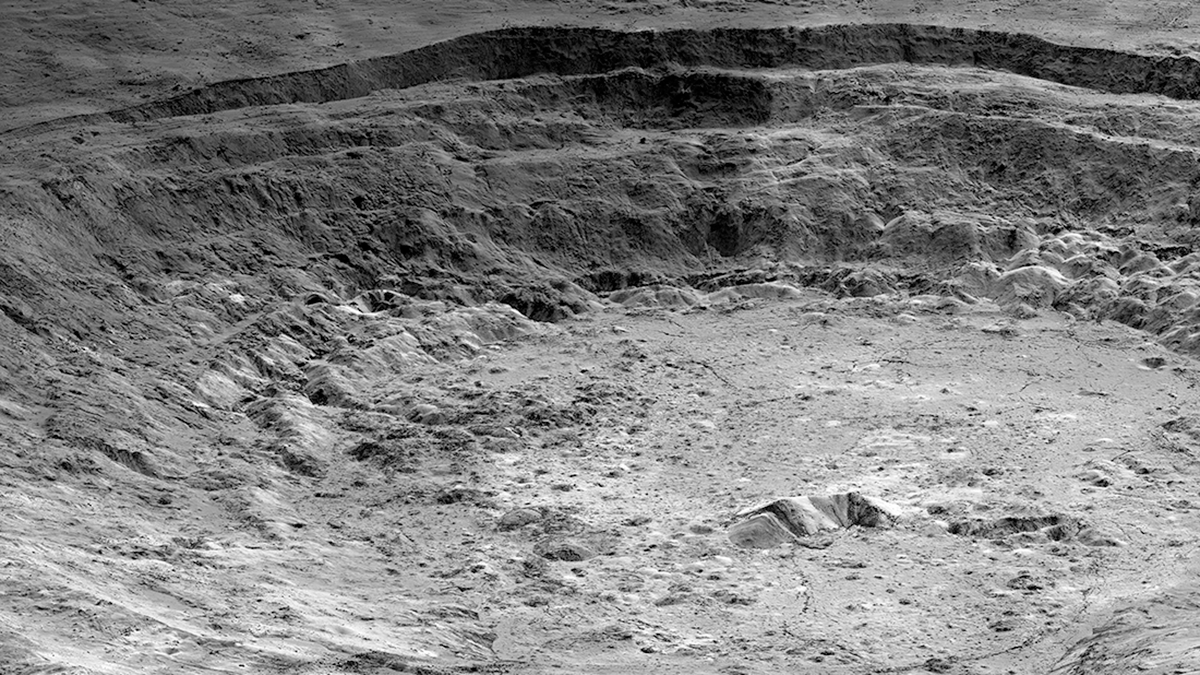
Gravity with an “Edge”: What Lies Beneath Aristarchus Crater
A method combining three different approaches to the processing and analysis of GRAIL data from the Moon defines areas of sharply contrasting densities beneath Aristarchus Crater.
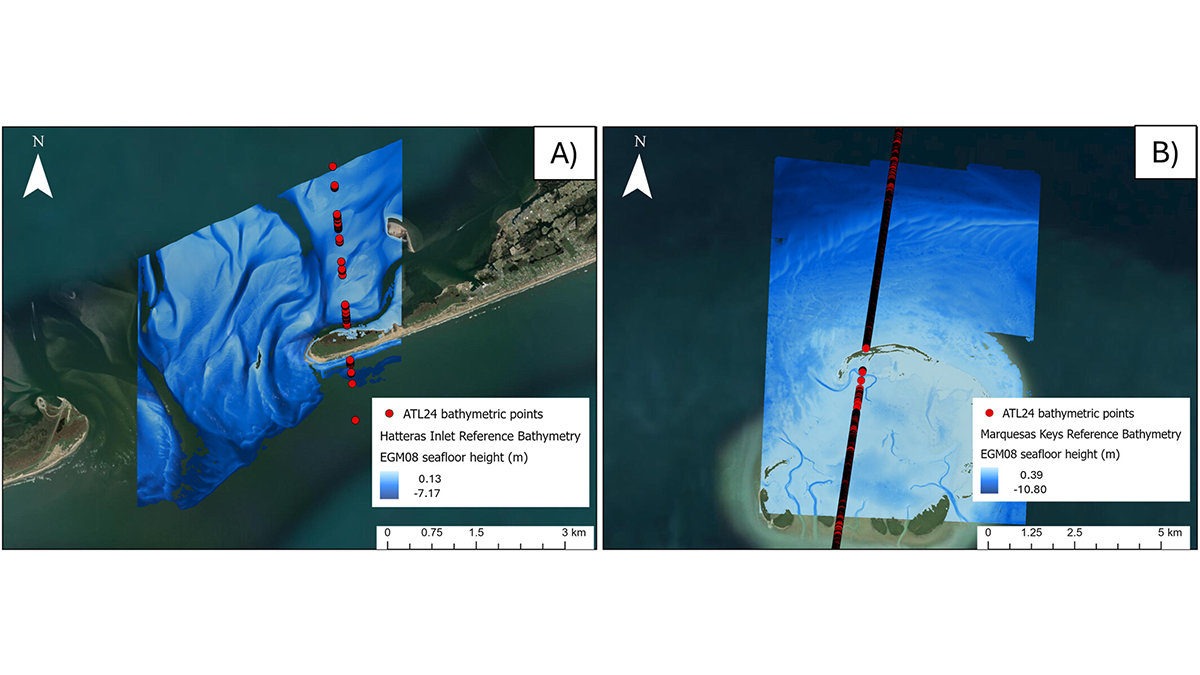
NASA Mission Creates a New Global Coastal Bathymetry Product
NASA’s Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite 2 (ICESat-2) mission recently released a new shallow water bathymetry product, which has already delivered data for 13.7 million kilometers of coastal waters.
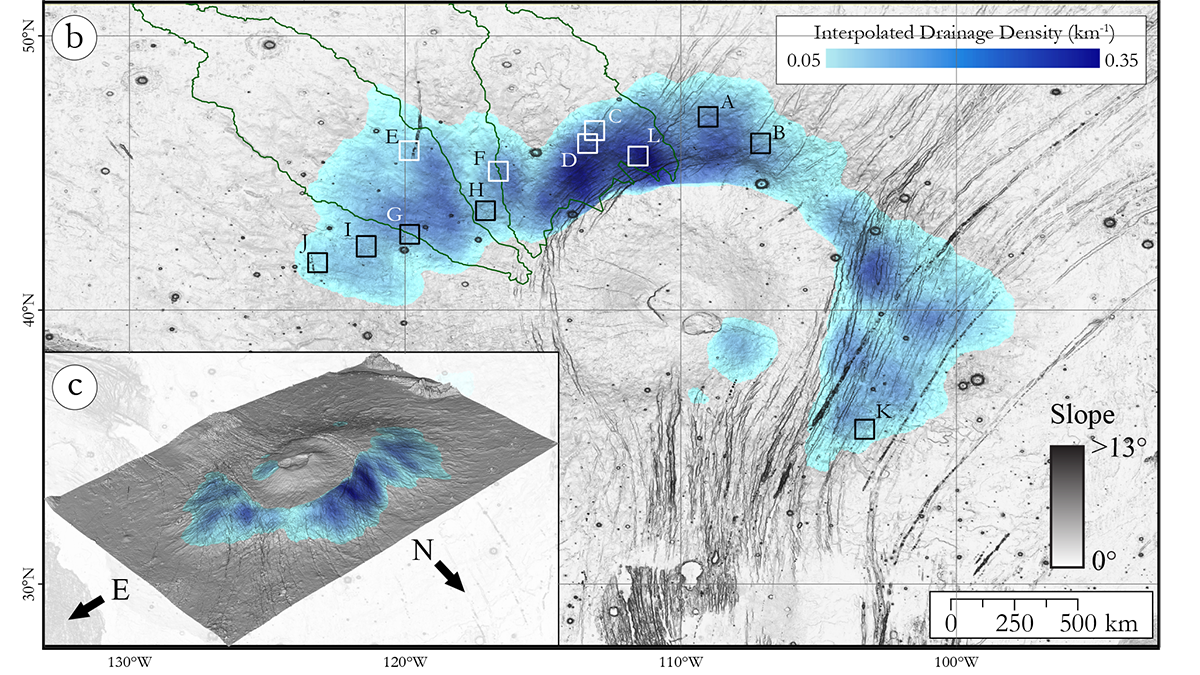
Young Rivers on a Martian Volcano Reveal Insights into the Amazonian Climate
A comprehensive inventory of rivers on Alba Mons on Mars reveals a prolonged history of erosion and development into mature drainage networks during the Amazonian, with contributions of rainfall and snow melt.
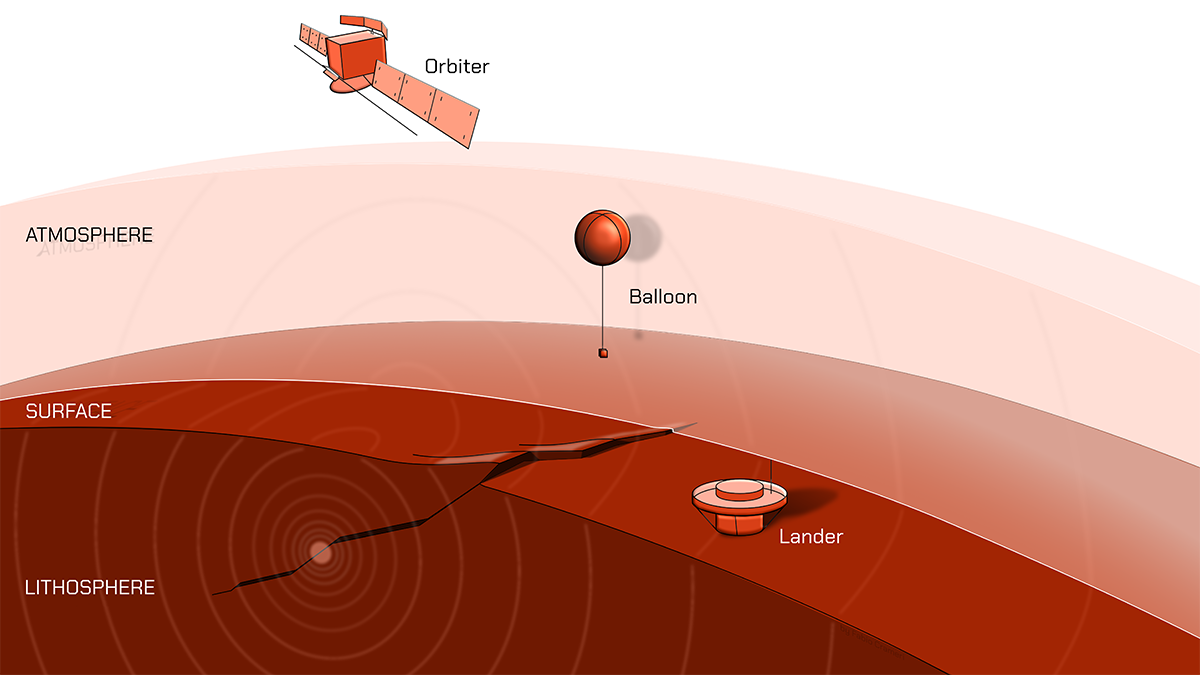
Three Ways to Track Venusquakes, from Balloons to Satellites
The planet’s harsh conditions make studying seismicity challenging, but it is likely possible.
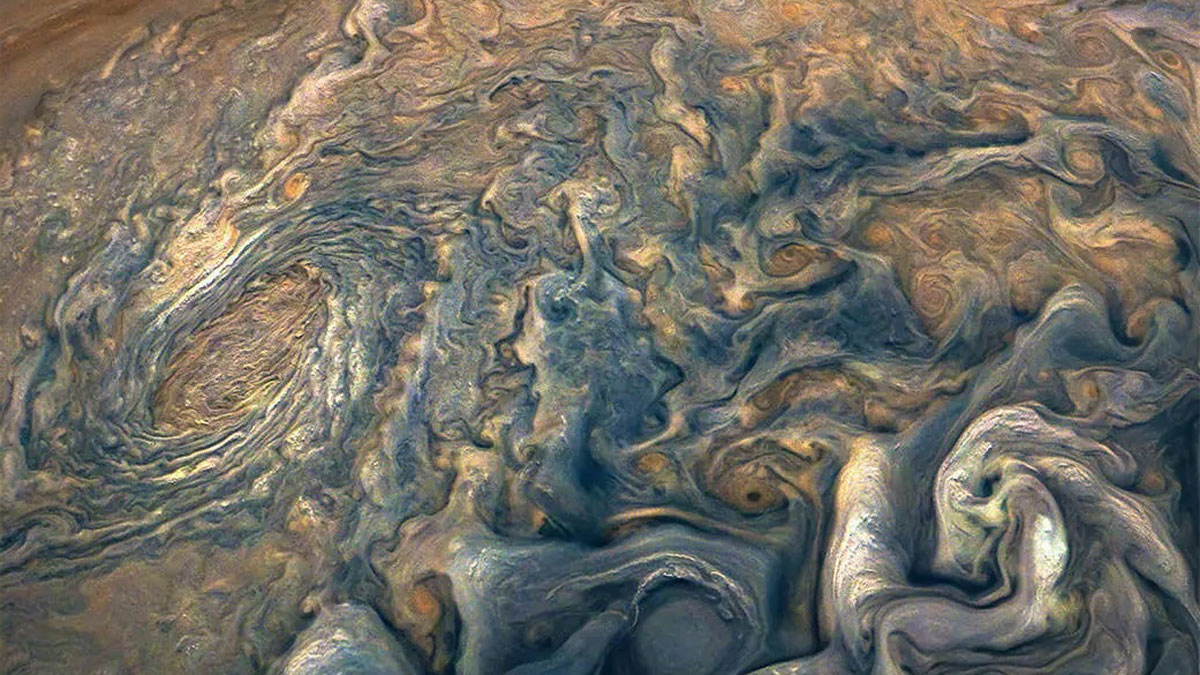
All Eyes on Jupiter
Astronomers hope amateur enthusiasts will help them monitor Jovian weather.
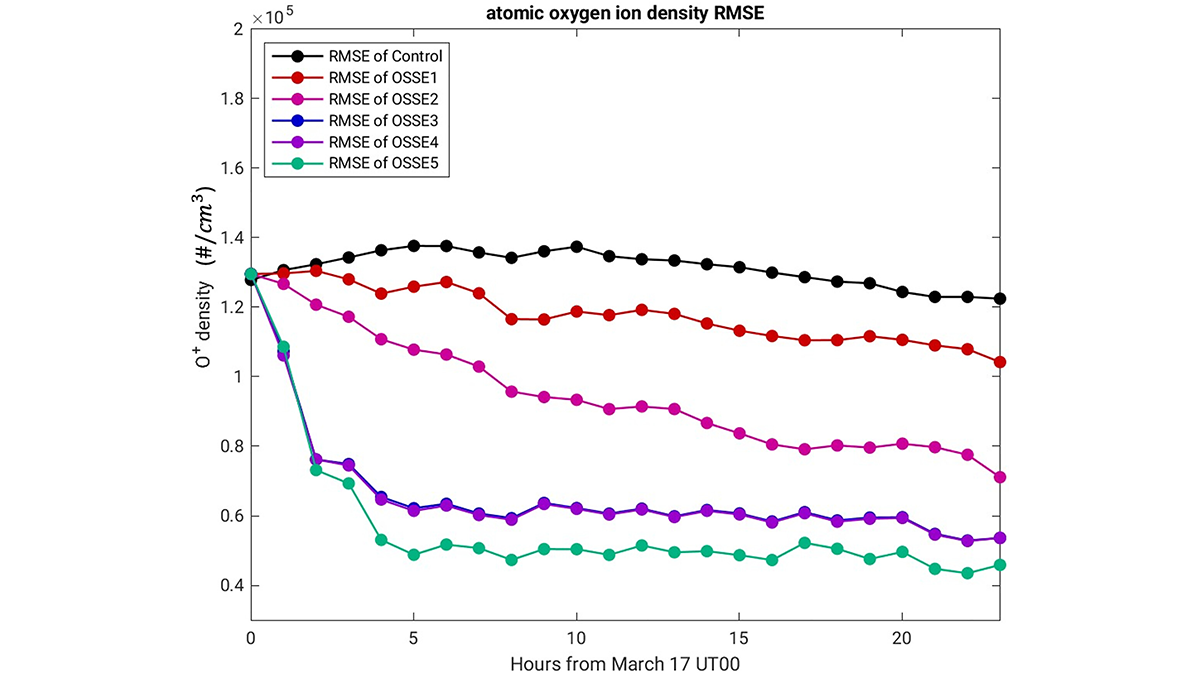
Impact of NASA’s GDC Measurements on Predicting Earth’s Upper Atmosphere
A new study finds that assimilating observations of the ionosphere and thermosphere reduces the error in model predictions more than modeling either one individually.