A roughly 70-million-year interval of anomalously weak magnetic field during the Ediacaran period could have triggered atmospheric changes that supported the rise of macroscopic life.
Ediacaran
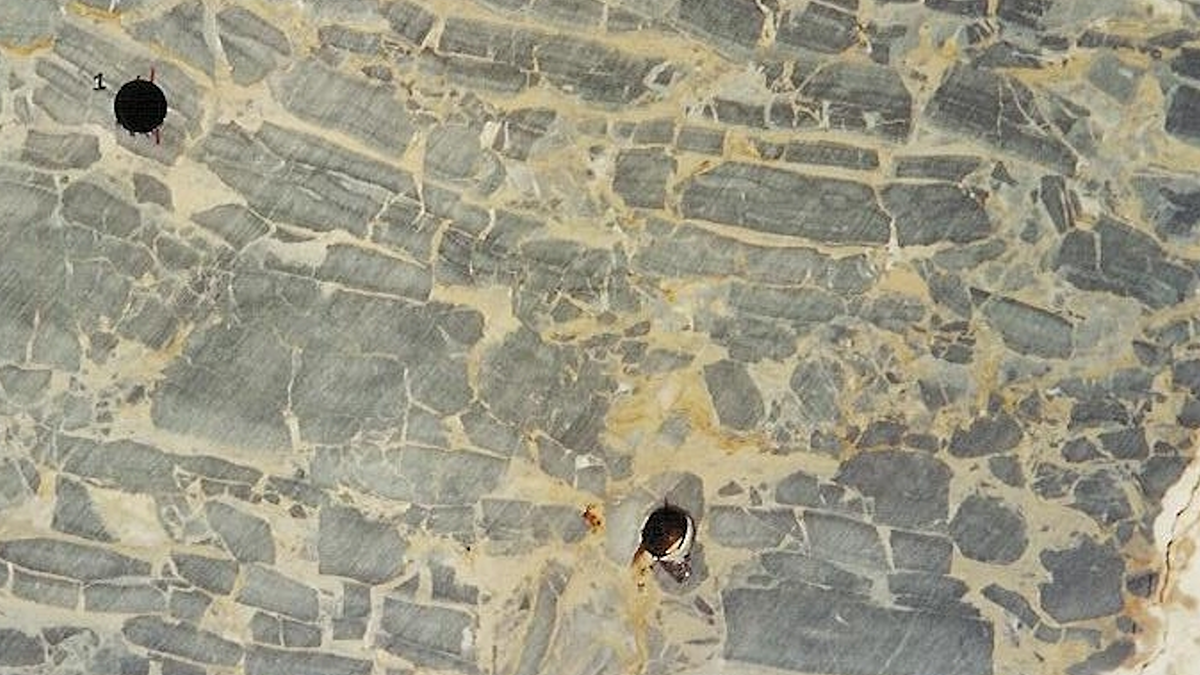
Remagnetization Illuminates Tectonic Consolidation of Megacontinents
New rock and paleomagnetic research give evidence for prolonged heating during the Cambrian-Ordovician tectonic consolidation of West Gondwanaland.
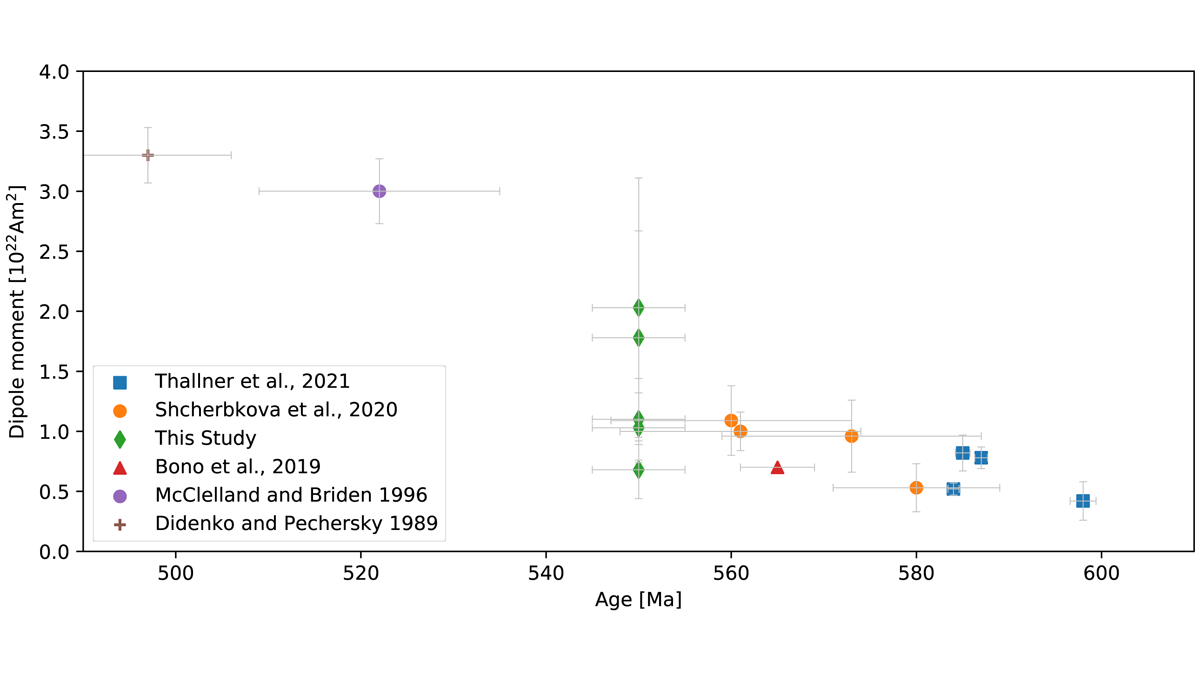
A Dipole Field from the Ediacaran-Cambrian Transition Onward?
The Ediacaran features an instable magnetic field complicating paleogeographic reconstructions; a new paleointensity study on late Ediacaran rocks indicates a weak but stable dipolar field.
Habitability and the Evolution of Life Under Our Magnetic Shield
Earth’s global magnetic field likely dates back billions of years and is a barrier against cosmic radiation. What roles has it played in the planet’s biosphere?
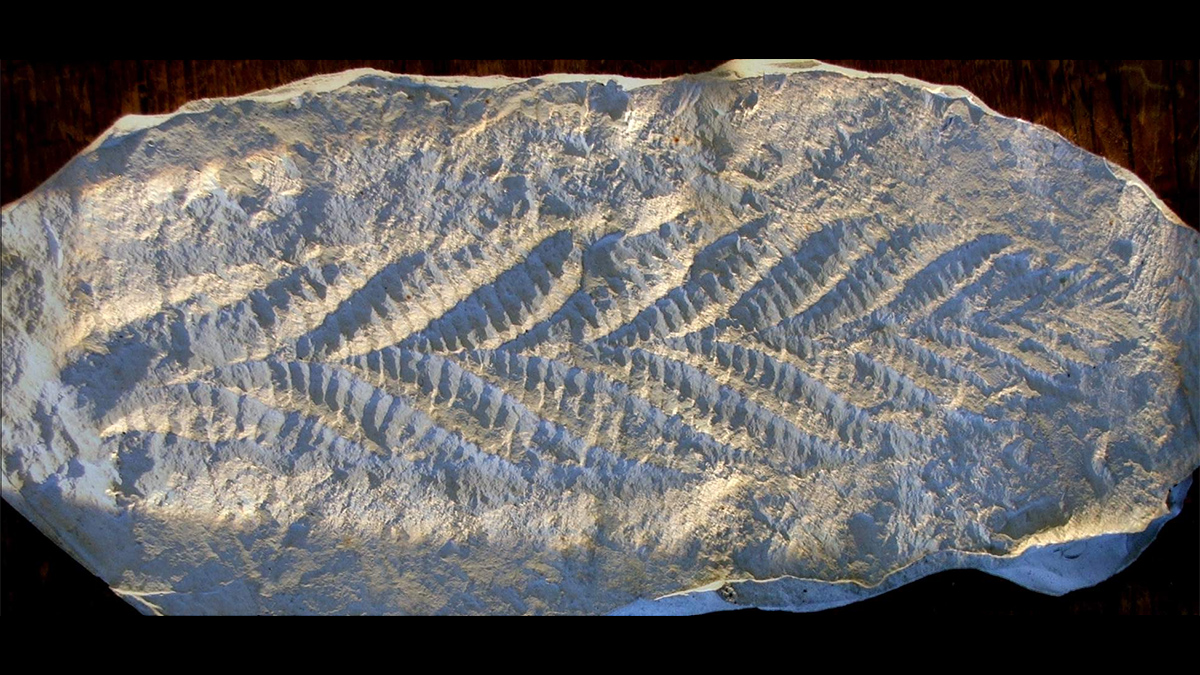
Hunting Rare Fossils of the Ediacaran
The search for fossil imprints and casts of squishy organisms takes time, perseverance, and sometimes a sprinkle of luck.
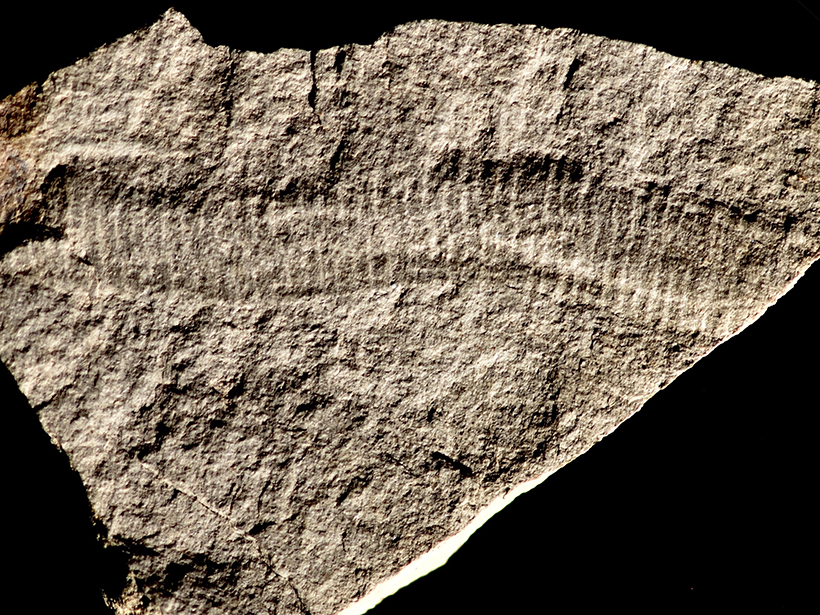
How Did Fragile Early Microbes Become Fossils?
During the Ediacaran period more than a half billion years ago, clay mineral coats likely shielded delicate remains, helping them become exquisitely preserved in rock, recent experiments suggest.