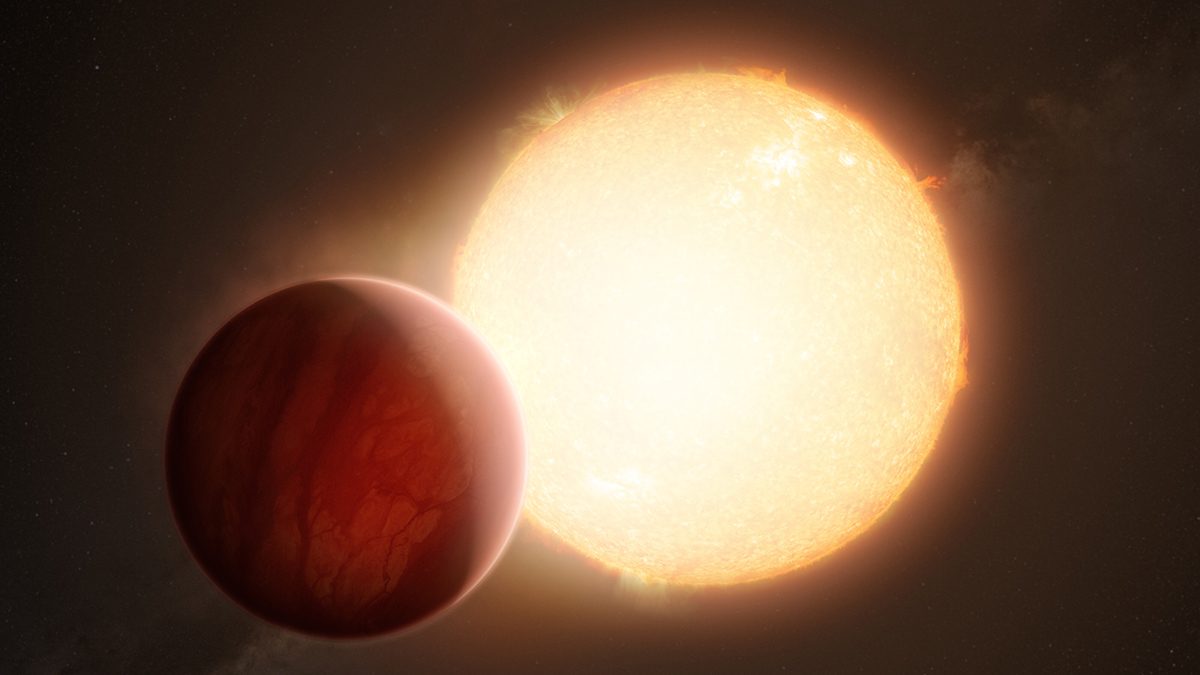
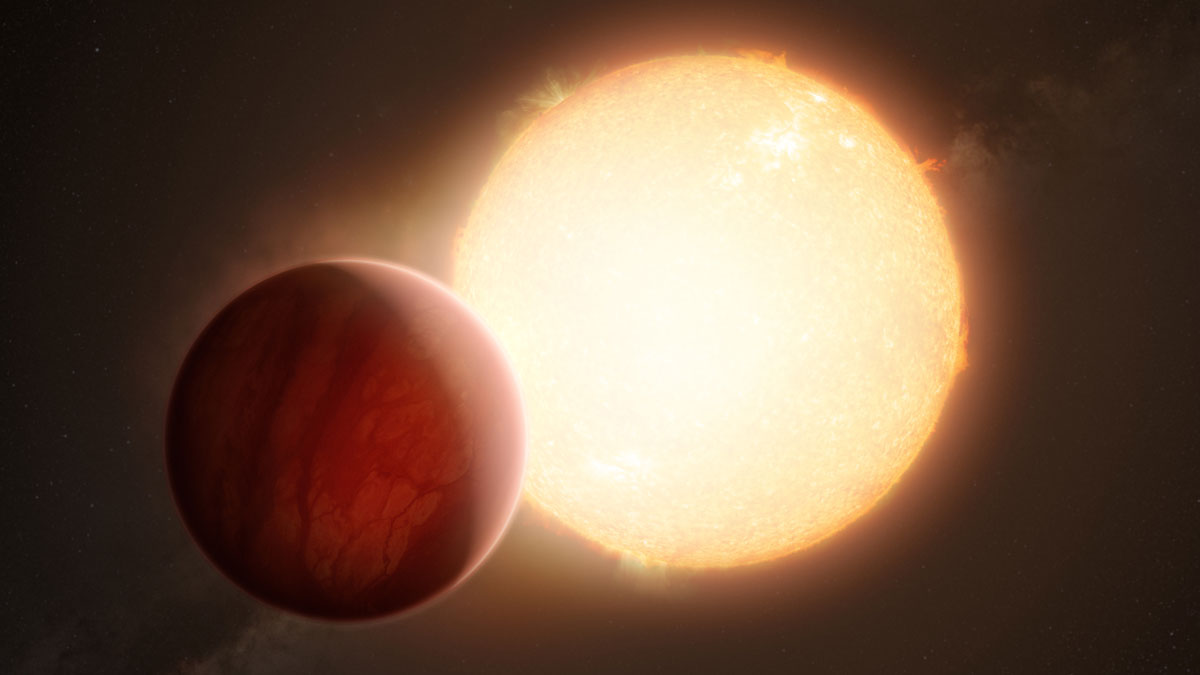
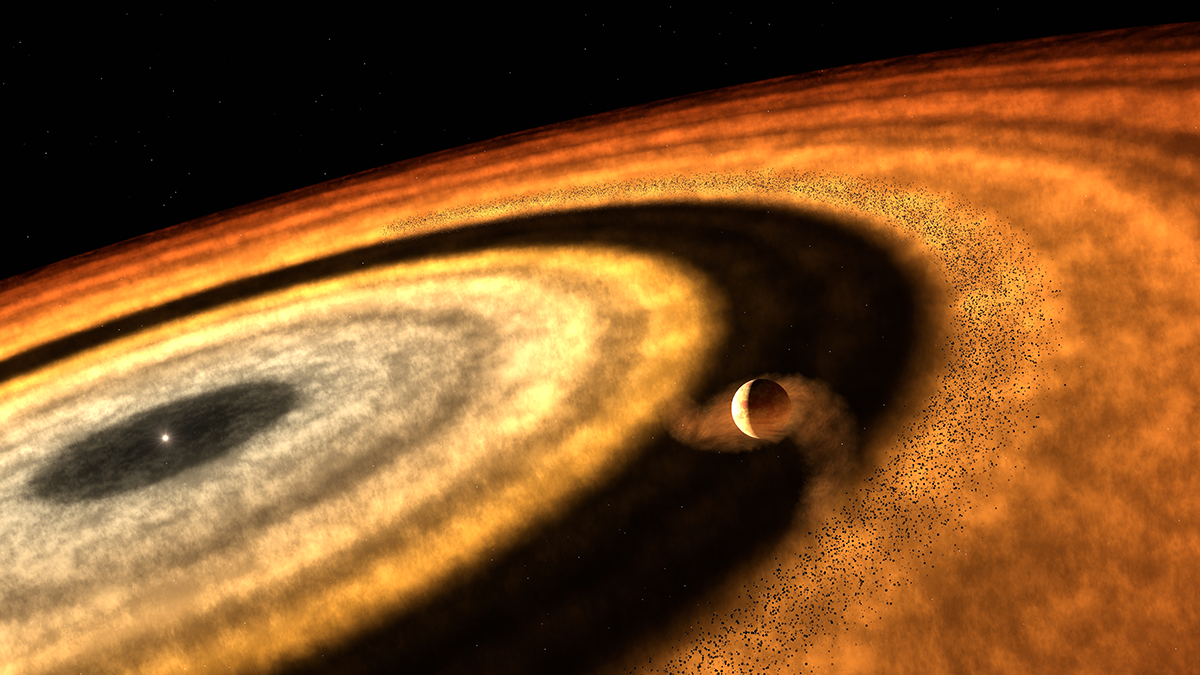
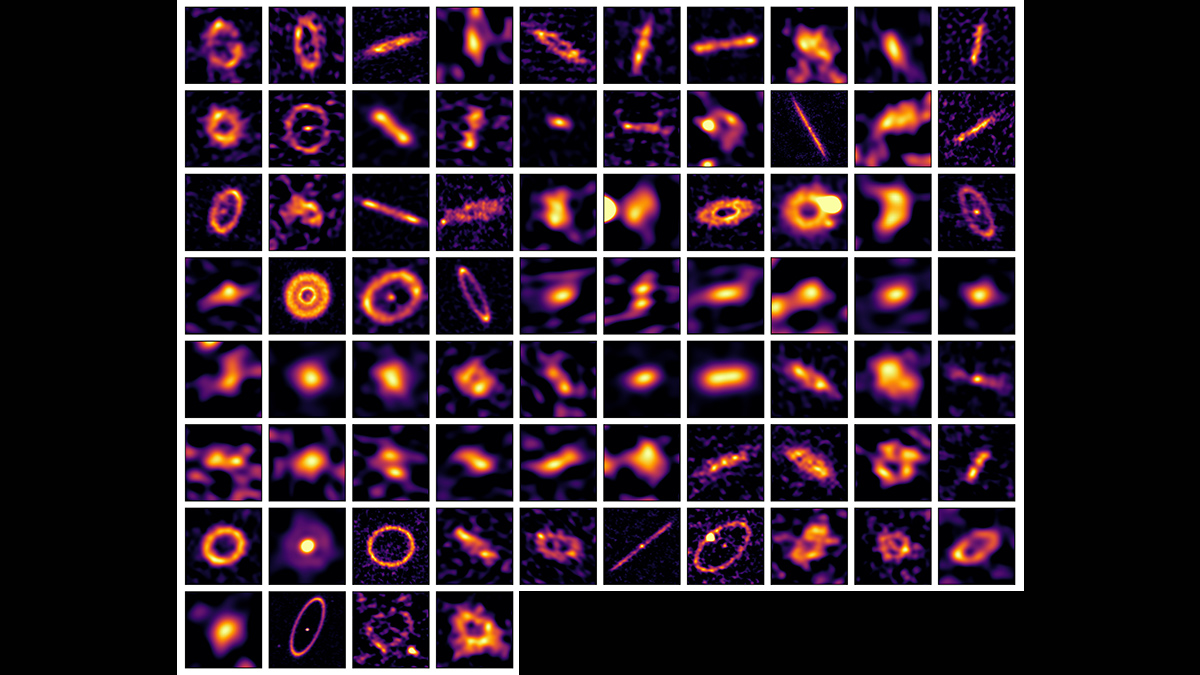
A new analysis shows that the way massive planets migrate after their formation helps determine whether they have companion planets. The process hints at planetary formation in general.
exoplanets
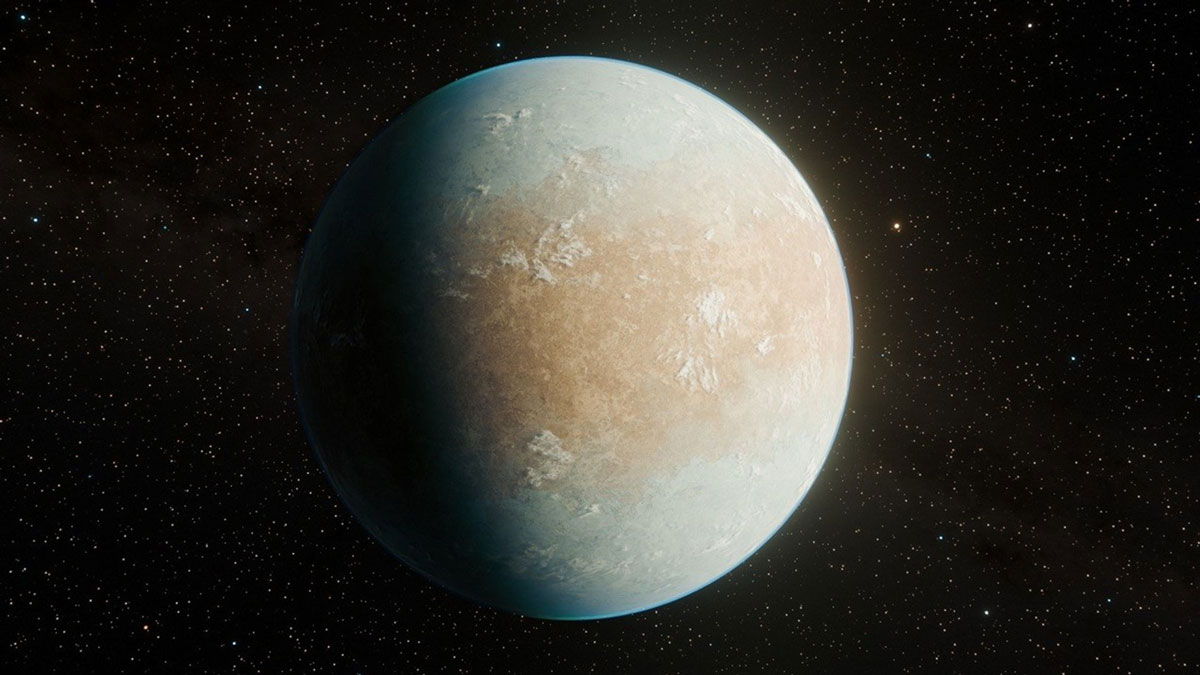
This Potential Exoplanet Is Earth Sized but May Be Colder Than Mars
A new analysis of old mission data may have revealed a possible Earth-sized planet orbiting the K-dwarf star HD 137010.
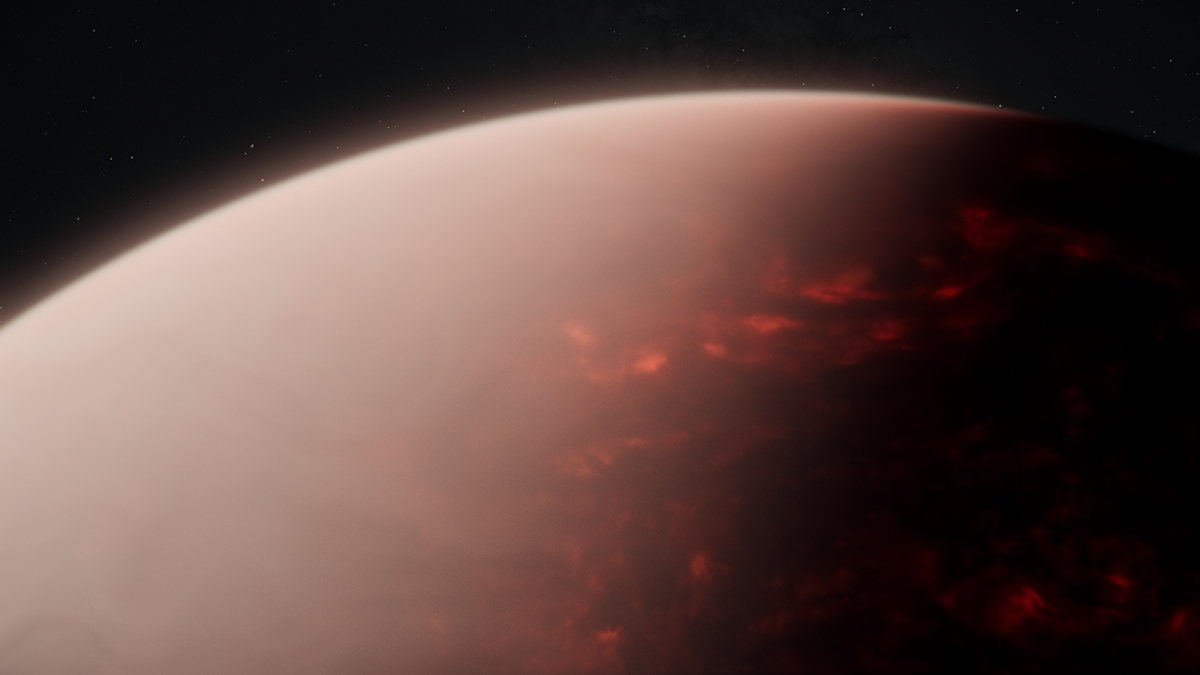
A “Lava World” Unexpectedly Hosts an Atmosphere
TOI-561 b, an exoplanet roughly 275 light-years away, seems to have a thick atmosphere despite being wildly irradiated by its host star.
Planet-Eating Stars Hint at Earth’s Ultimate Fate
A sampling of aging Sun-like stars demonstrates that they likely eat their closest planets.
Tilted Planet System? Maybe It Was Born That Way
New observations could shed light on the degree to which misalignment in a planet-forming disk contributes to skewed planetary orbits.
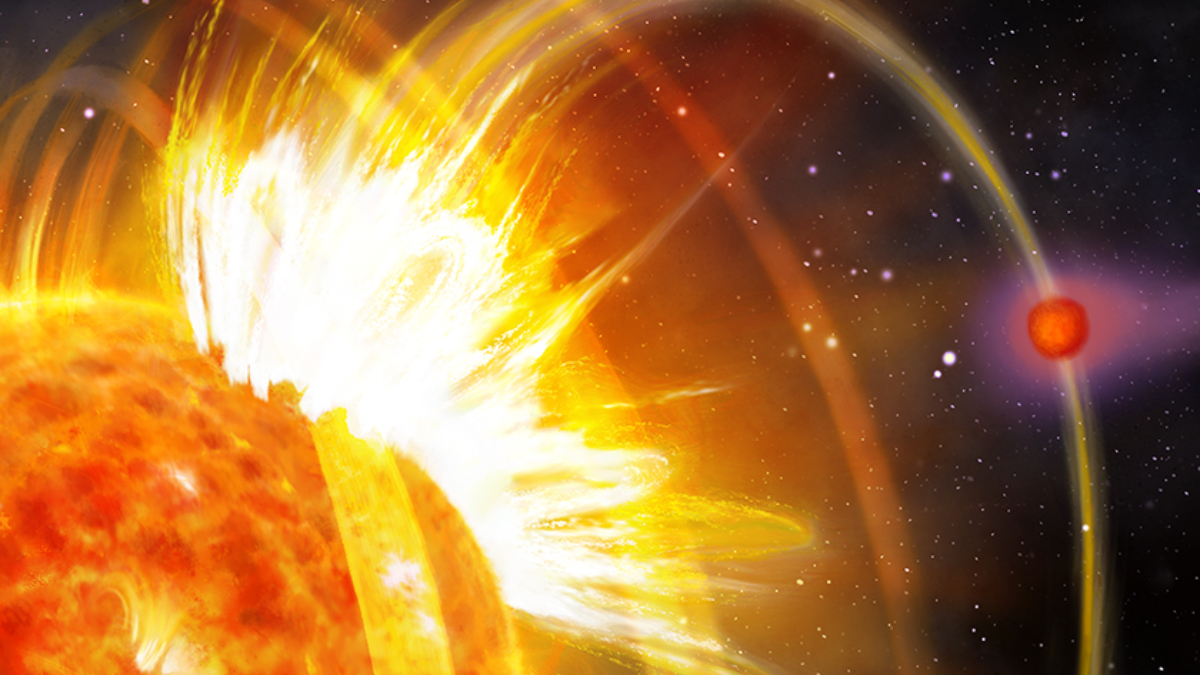
Exoplanet Triggers Stellar Flares and Hastens Its Demise
HIP 67522 b can’t stop blasting itself in the face with stellar flares, a type of magnetic interaction that scientists have spent decades looking for.
This Exoplanet May Have Grown Stranger as It Journeyed Starward
WASP-121b, an already unusual planet, might have a remote origin that explains some of its peculiar properties—from iron rain to the unexpected presence of methane.
A New Exoplanet Resets the Scale
TOI-6894 b, the largest exoplanet relative to its host star yet seen, doesn’t fit the most widely accepted formation model for giant worlds.
Cinturones polvorientos ofrecen una visión más clara de la formación de exoplanetas
Las observaciones en longitudes de onda milimétricas de polvo y guijarros en 74 sistemas estelares sugieren que las migraciones planetarias podrían ser más comunes de lo que pensábamos.
First 3D Map of Exoplanet Weather Reveals Superfast Jet
New observations also answer a long-standing question about where this ultrahot planet keeps its titanium.