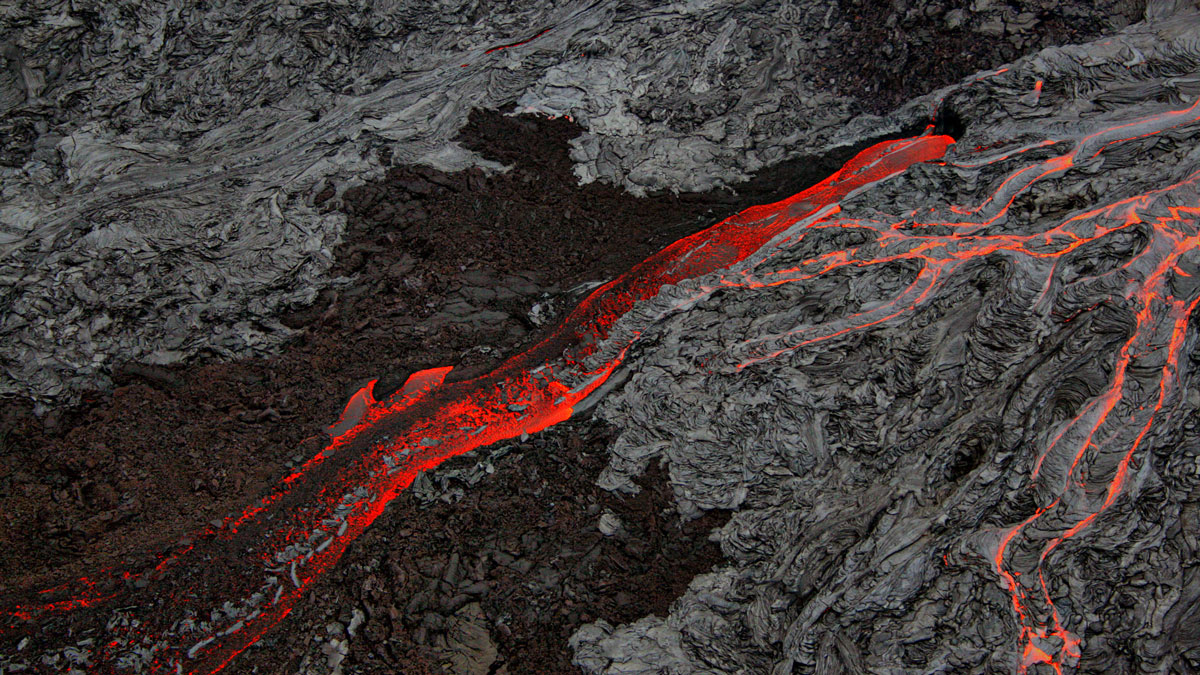
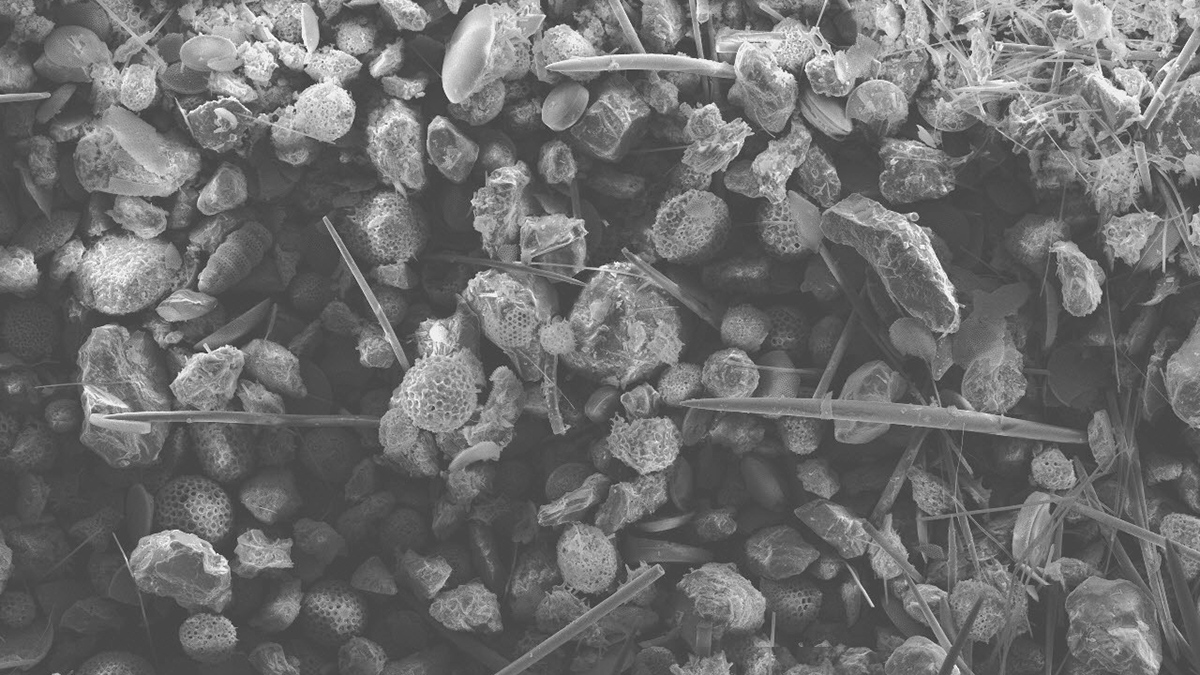
Dissolved carbon dioxide may have bubbled up from magma far below the surface, contributing to prolonged warming.
extinctions
Mega El Niño May Have Led to Major Mass Extinction 252 Million Years Ago
The extreme climate conditions wrought by a decades-long ENSO pattern could be the culprit in the Great Dying, which wiped out nearly 90% of life on Earth.
Clays May Have Slowed Earth’s Recovery After the Great Dying
Without tiny marine organisms using silica for shells, Earth’s oceans generated more clay, released more carbon dioxide, and kept Earth warmer for longer.
Future Supercontinent Will Be Inhospitable for Mammals
Pangea returns in 250 million years, and it’s not looking good for us.
UV Radiation Contributed to Earth’s Biggest Mass Extinction
To find the first direct evidence of heightened UV radiation during the end-Permian mass extinction, researchers turned to chemical evidence preserved in pollen grains.
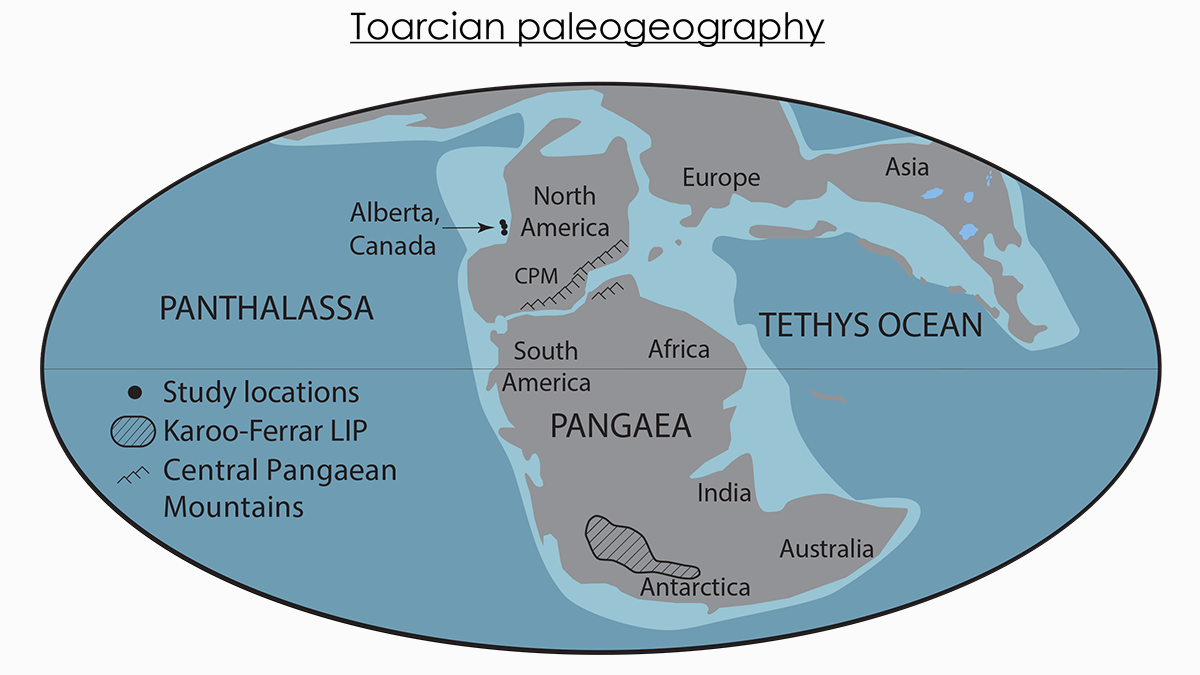
Marine Molybdenum Loss During the Toarcian Ocean Anoxic Event
The reconstructed loss of molybdenum during the Toarcian ocean anoxic event suggests deeply anoxic conditions during this time period allowing massive amounts of organic carbon being buried.
Impact Crater off the African Coast May Be Linked to Chicxulub
The underwater crater, spotted serendipitously in commercial observations of seafloor sediments, is believed to have formed at roughly the same time as the famous Cretaceous-Paleogene impact event.
A Post-Impact Deep Freeze for Dinosaurs
New research supports the hypothesis that dinosaurs were done in by climate change after an asteroid impact kicked up a massive plume of sulfur gases that circled the globe for several decades.
Volcanic Winters Ushered in the Jurassic Reign of the Dinosaurs
Sediment cores from northwestern China reveal freezing conditions during the Late Triassic killed off many forms of life—but not dinosaurs.