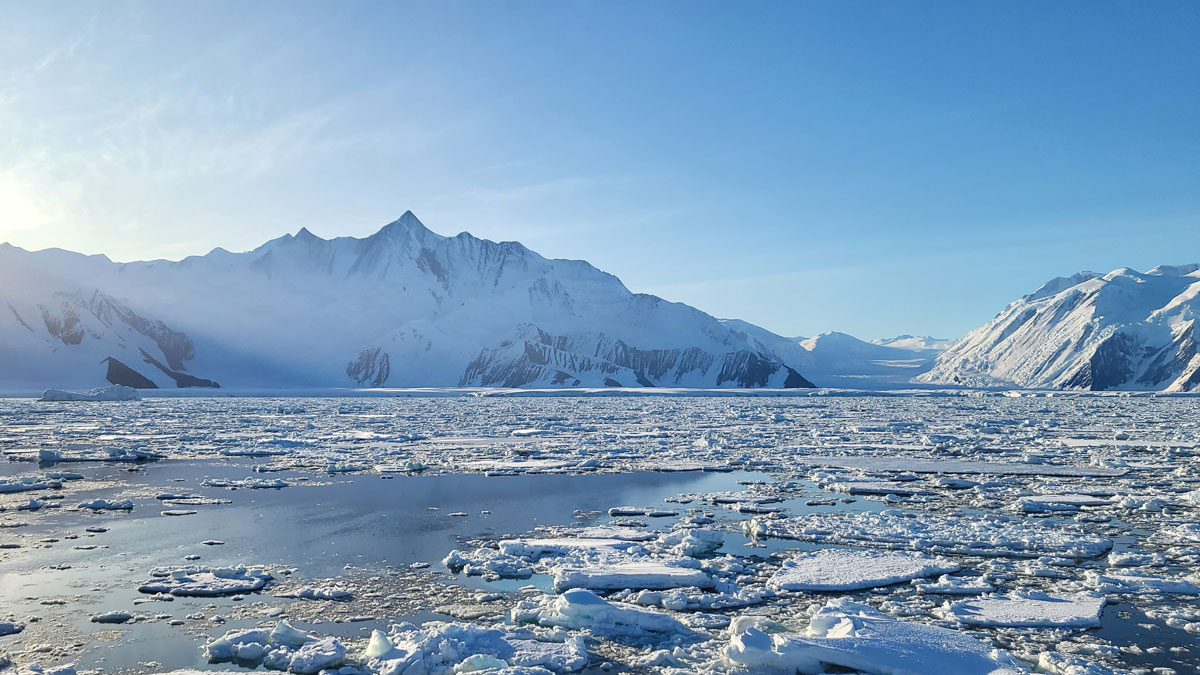
Scientists used sediments to create a millennia-long archive of Antarctic fast ice. Along the way, they discovered that the freezing and thawing of this enigmatic ice appear to be linked to solar cycles.
greenhouse gases
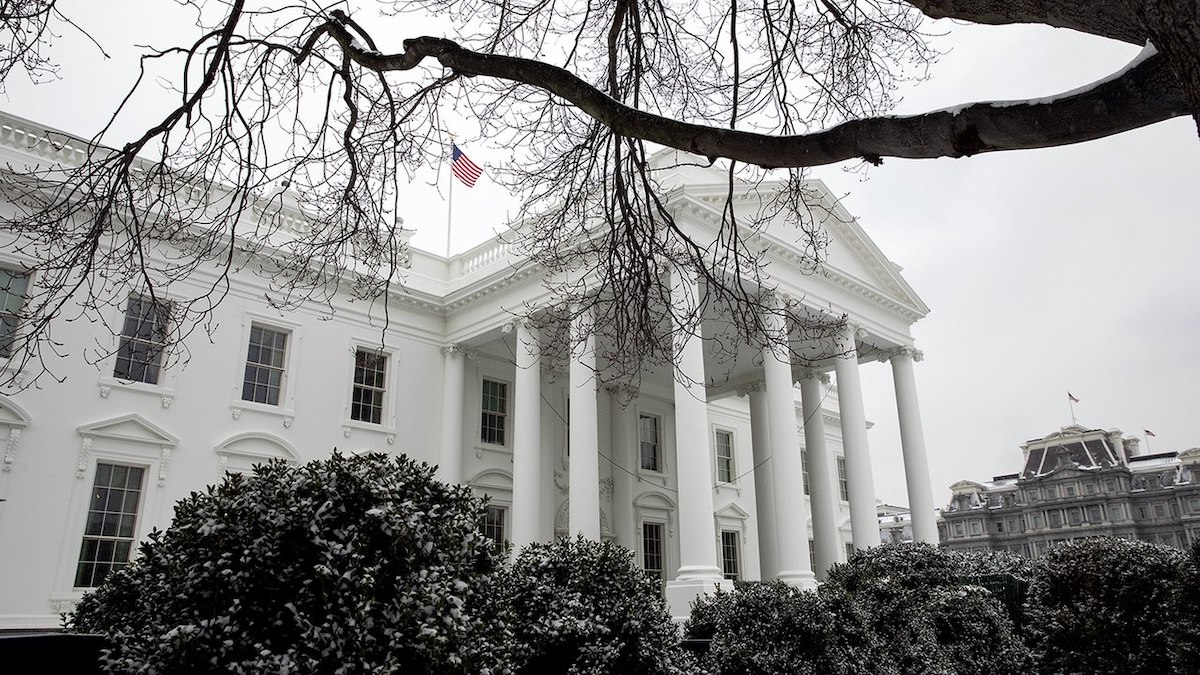
The Endangerment Finding is Lost
Tomorrow, the EPA will revoke the 2009 Endangerment Finding, finalizing a July proposal to do so, Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt said in a 10 February announcement.
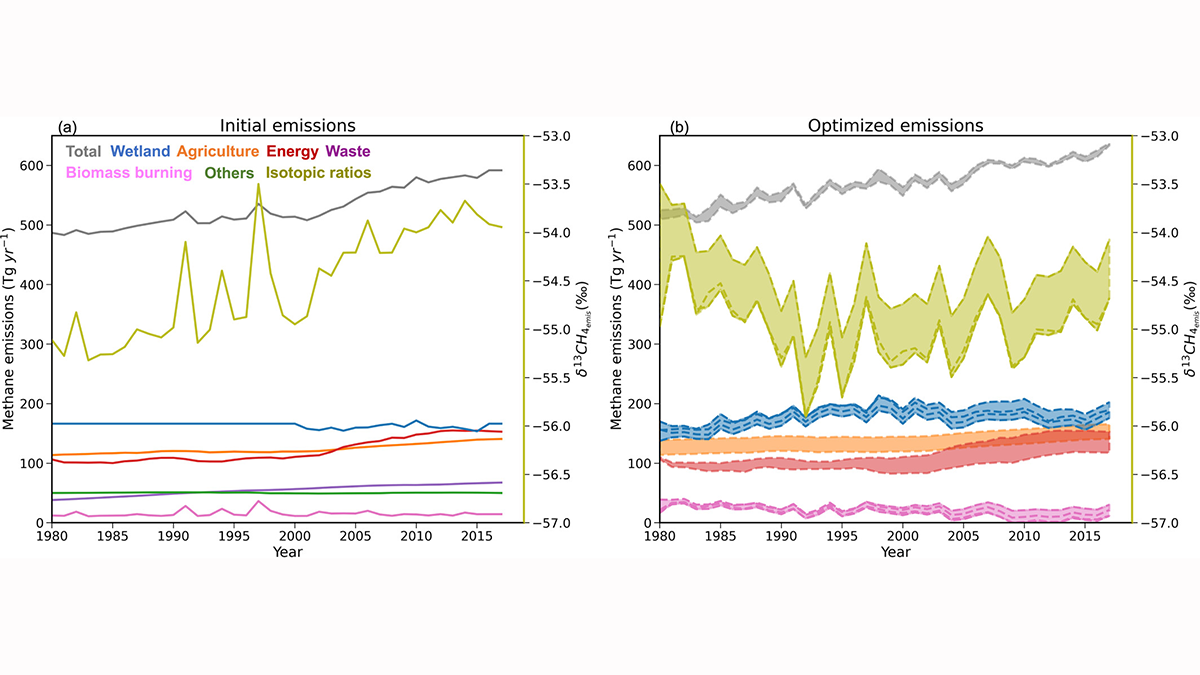
Cows, Coal, and Chemistry: The Role of Photochemistry in Methane Budget
Recent increases in atmospheric methane are a result of changing natural and manmade sources, climate, and other less-understood factors linked to its role in the atmosphere’s self-cleaning mechanisms.
Managing Carbon Stocks Requires an Integrated View of the Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle community calls for an integrated carbon observing system leveraging near-surface partial-column data to better resolve finer spatial scales where key processes and decisions occur.
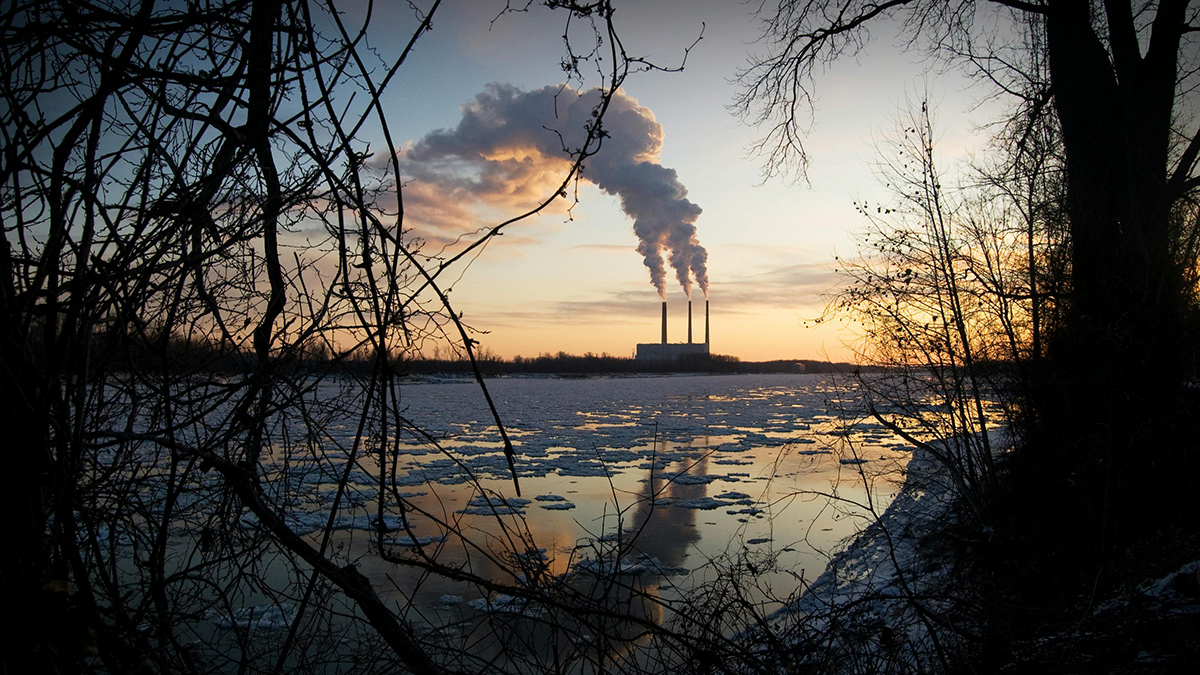
Trump Proposes Weakening Fuel Economy Rules for Vehicles
At the White House today, President Donald Trump announced his administration would “reset” vehicle fuel economy standards. Trump said the administration plans to revoke tightened standards, also known as Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, set by President Joe Biden in 2024.
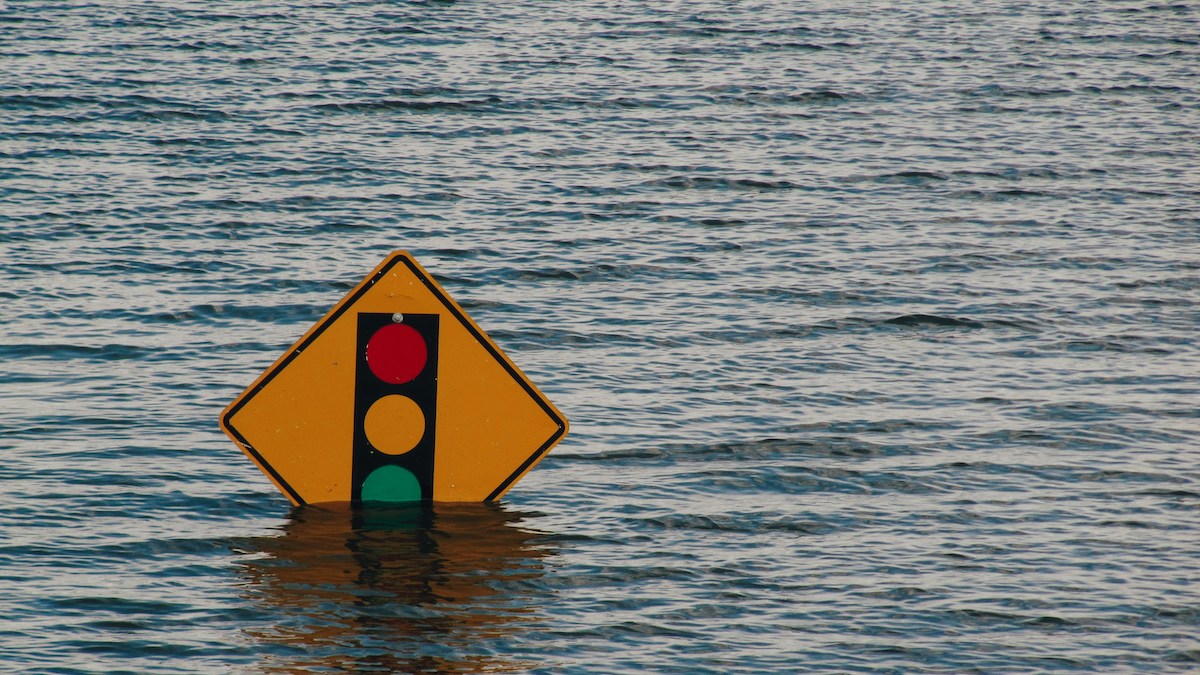
5,500 Toxic Sites in the U.S. at Risk of Flooding as Seas Rise
Rising sea levels have put thousands of facilities containing hazardous materials at risk of flooding this century, according to a new study published in Nature Communications.
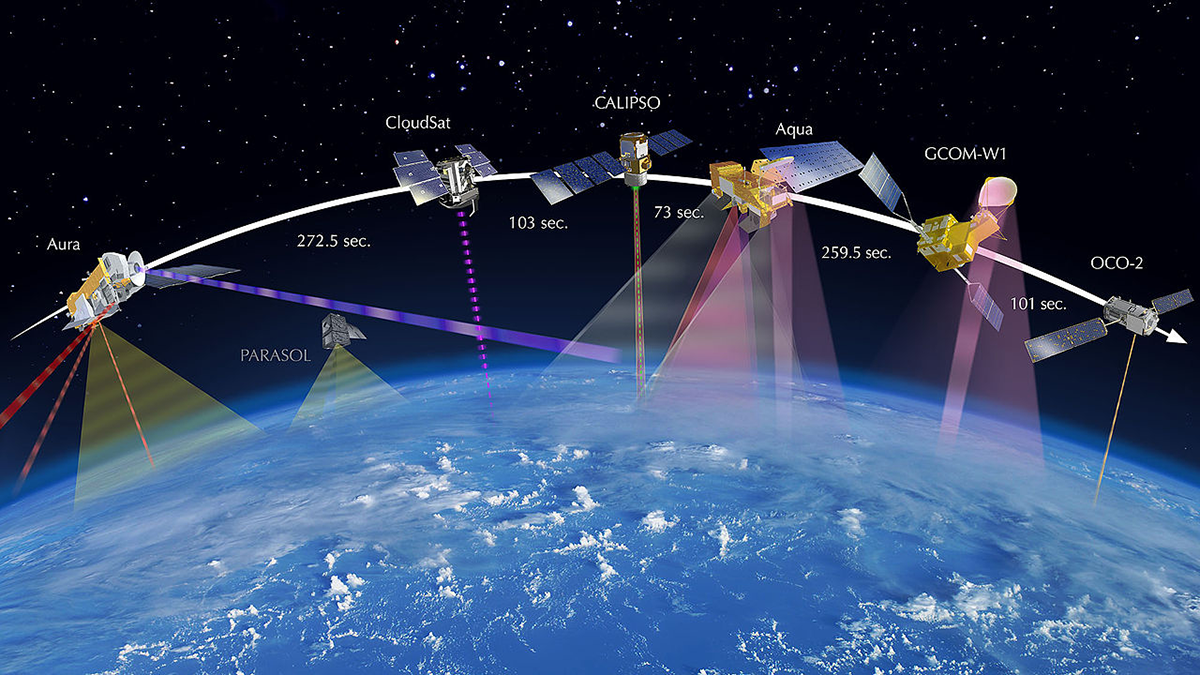
A Better Way to Monitor Greenhouse Gases
A unified, global observing system could more effectively monitor progress in reducing emissions and accelerate climate action through improved data and decision support.
EPA Proposes That Major Polluters No Longer Report Their Emissions
The EPA proposed today that approximately 8,000 polluting facilities, including oil refineries, power plants, and steel mills, should no longer be required to report their greenhouse gas emissions.
Public Speaks Out Against EPA Plan to Rescind Endangerment Finding
Advocates, scientists, doctors, members of Congress, kids, parents, and other individuals spoke out in a series of hearings last week to let the Environmental Protection Agency know how they feel about a potential sea change in climate and environmental policy: the proposed repeal of the 2009 Endangerment Finding.
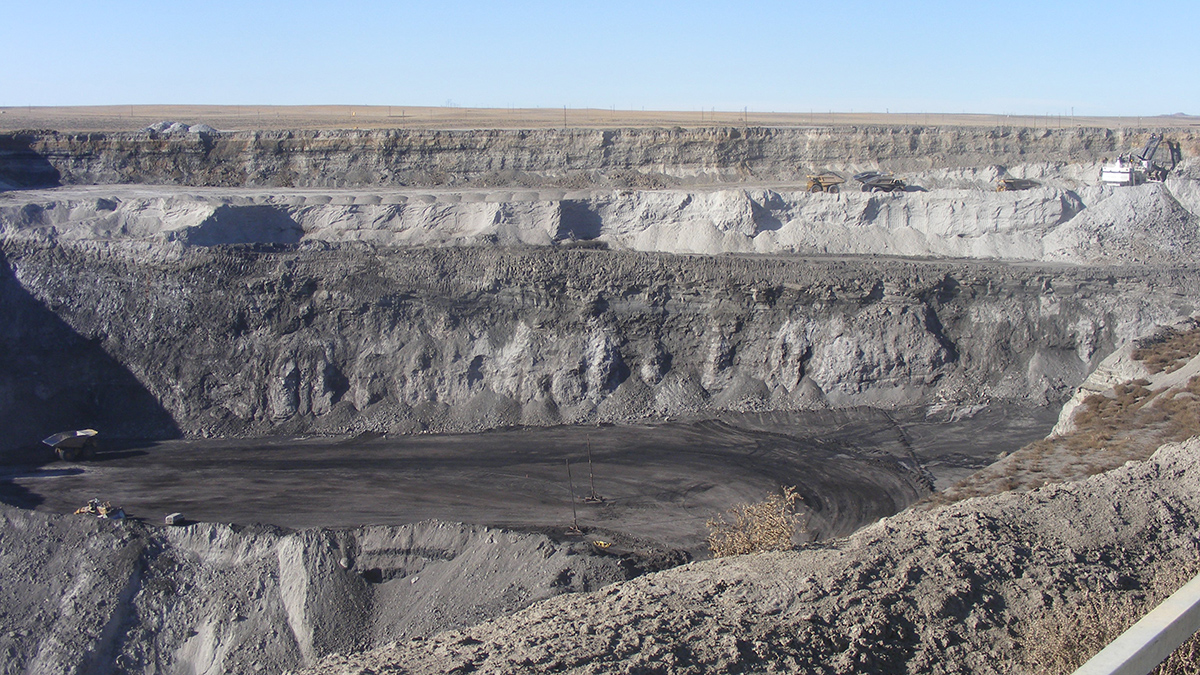
By 2051, Emissions from Coal Mining on Federal Lands Could Drop by 86%
Researchers predict that if early 2024 policies hold, emissions related to coal’s extraction, transportation, and combustion will drop over the next 25 years.