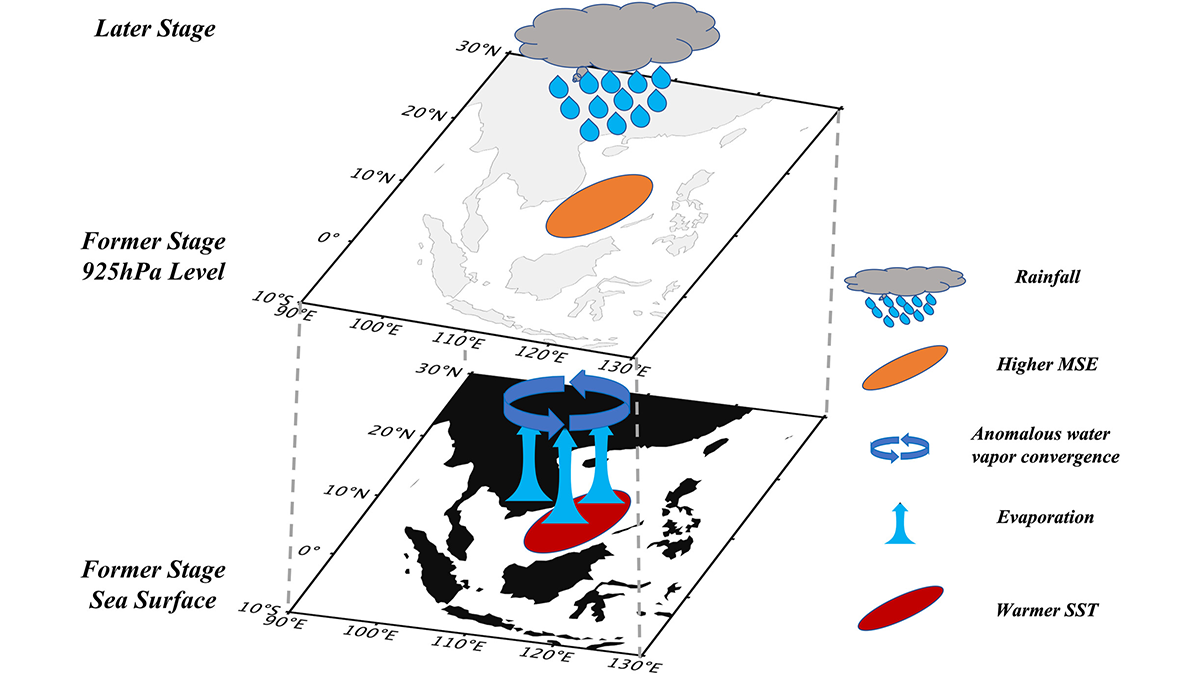
Most marine heatwaves experience reduced precipitation throughout their lifetime, but warmer events in the early stage can trigger increased precipitation after reaching peak intensity, causing faster decay.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
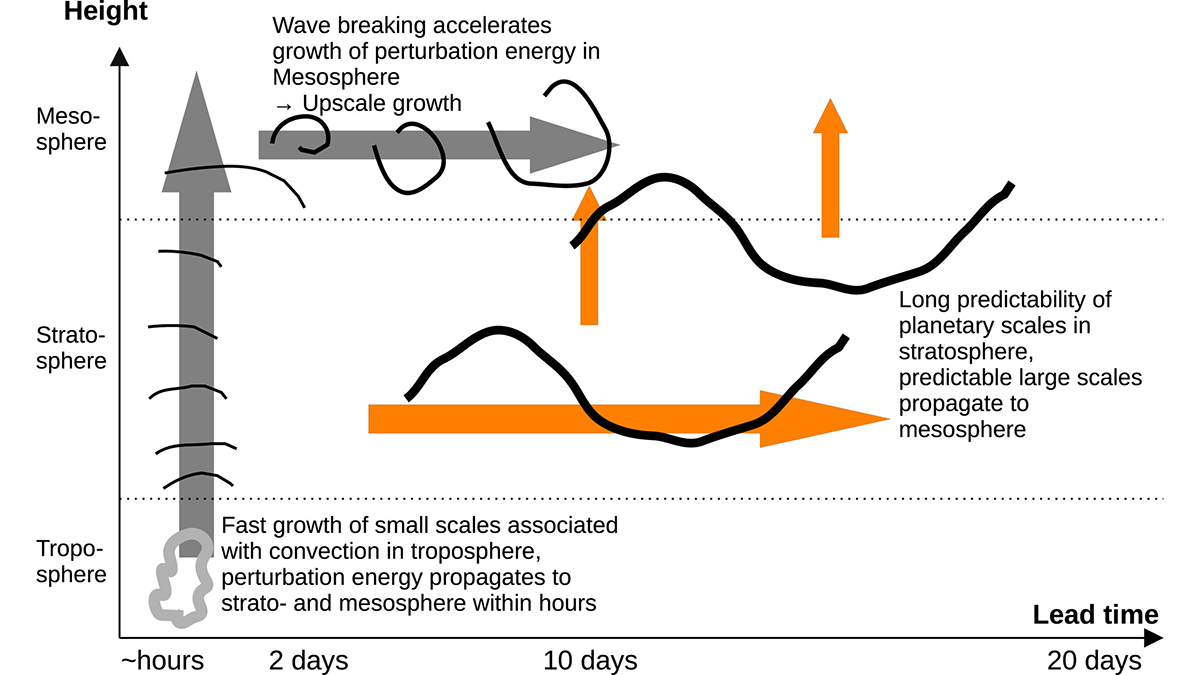
Quantifying Predictability of the Middle Atmosphere
A new high-resolution global model is used to study predictability of atmospheric circulation from the surface to 120 kilometers.
ARMing SCREAM with Observations to Expose Cloud Errors
Modern ARM observations expose persistent process-level errors in a global cloud-permitting model, guiding future developments and improvements.
Bringing Storms into Focus
A new study evaluates the performance of kilometer-scale models in predicting large tropical storms, which are key drivers of extreme rainfall and severe weather.
The All-In-One Cyclone Identification Framework
Researchers present a new framework for global detection and classification of all low-pressure systems.
Rapid Thunderstorm Charging Produces Strong Gamma‐Ray Glows
A new study explains how thunderstorm electric fields produce strong gamma‐ray glows with oscillating gamma‐ray rates, and that these oscillations develop into intense pulse trains that closely resemble terrestrial gamma-ray flashes.
Impacts of Urban Heat and Friction on a Tropical Cyclone
A new computer modeling-based study demonstrates dual mechanisms that reduce pre- and post-landfall tropical cyclone intensity.
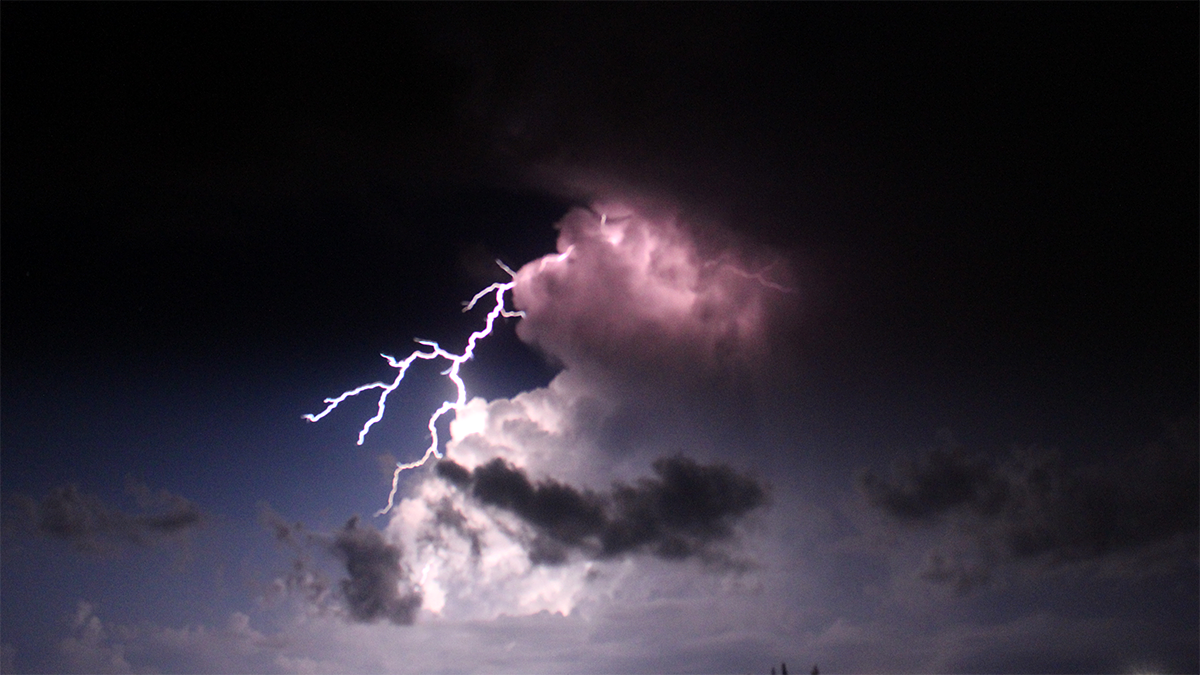
Lightning Initiating at High Altitudes May Develop Continuously
Recent radio observations reveal a new mode of initial lightning development in the form of continuous initial breakdown burst of several kilometers in length at high altitudes within thunderstorms.
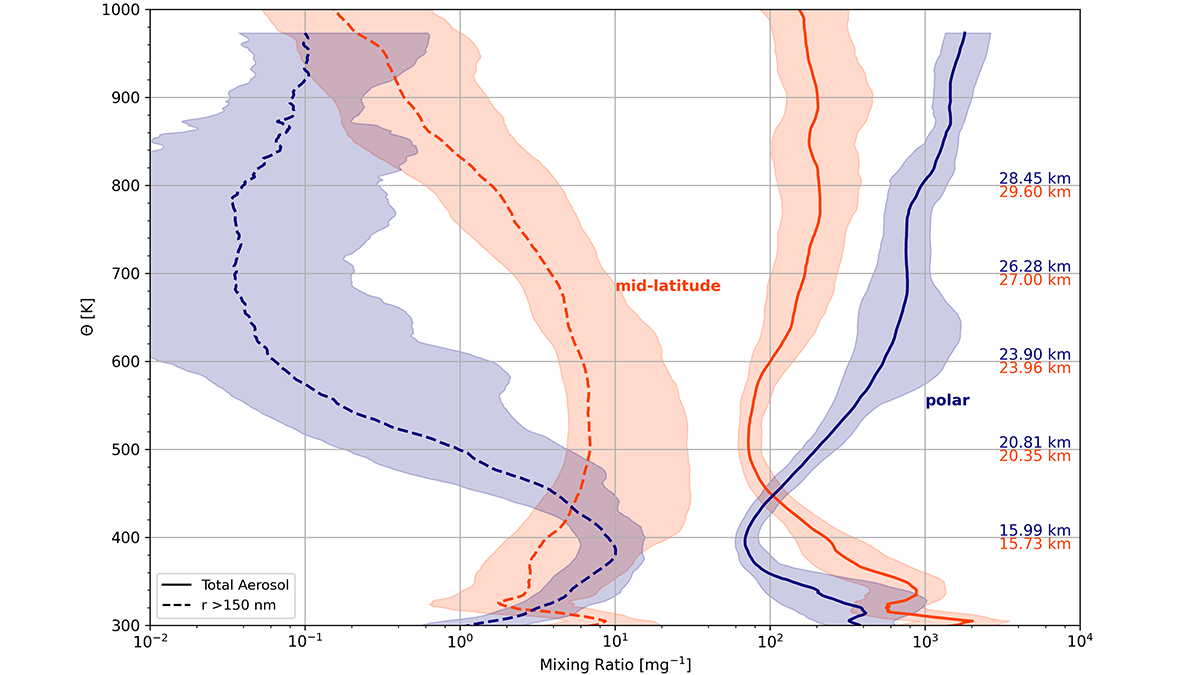
Five Decades of Stratospheric Aerosols from Balloon Measurements
Long-term global measurements of stratospheric aerosols reveal climatological structures and processes controlling new particle formation.
Air-Ice-Ocean Coupling Observed in an Arctic Cyclone Event
New observations show detailed features of the ice-ocean response to a strong Arctic cyclone in the winter of 2019-2020.