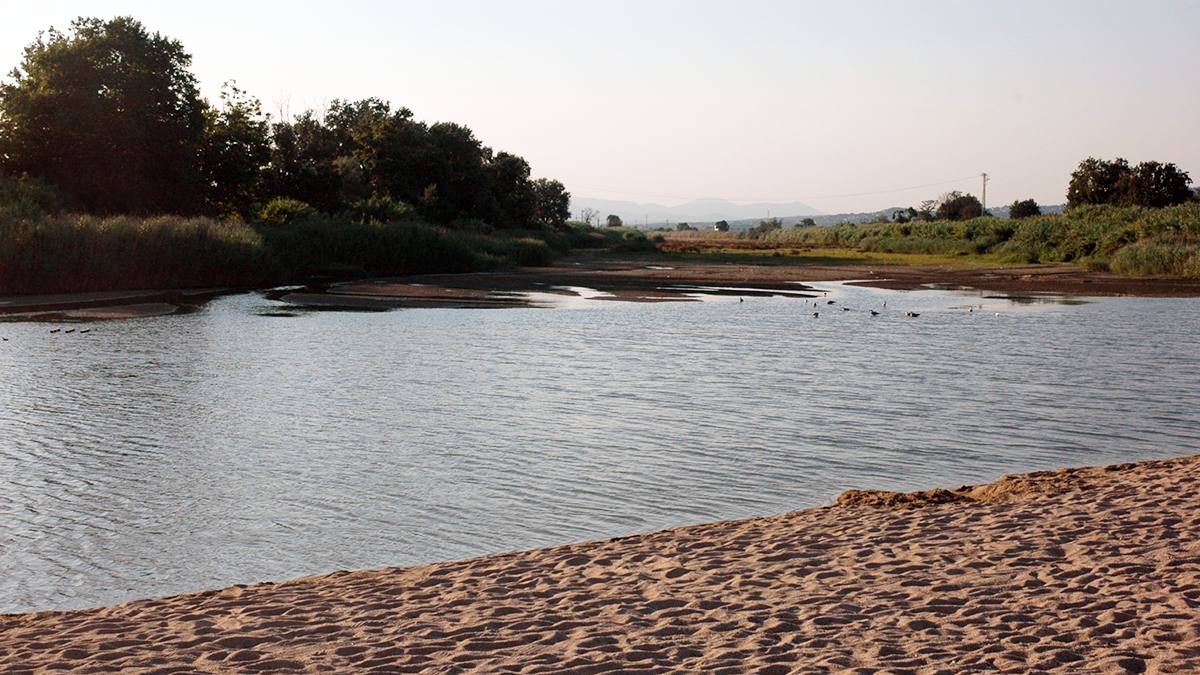
The type of organic matter, and ratio of nutrients to carbon, impact the ability of heterotrophic bacteria to effectively remove certain forms of nitrogen pollution (nitrate) from streams.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences
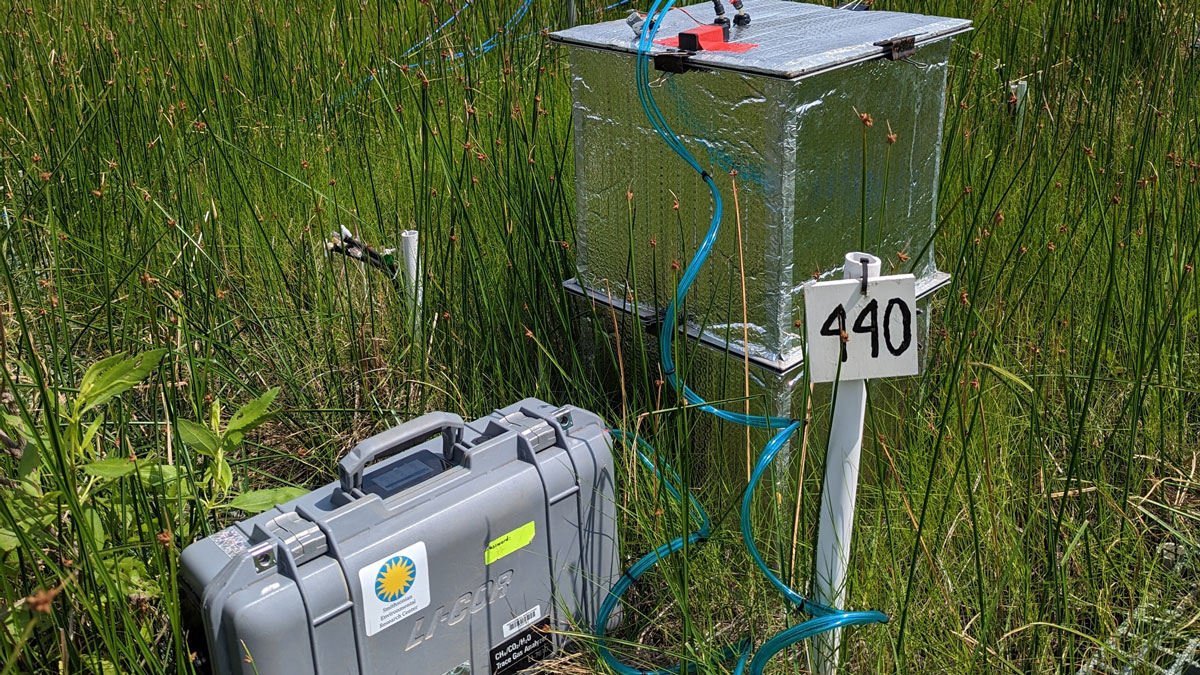
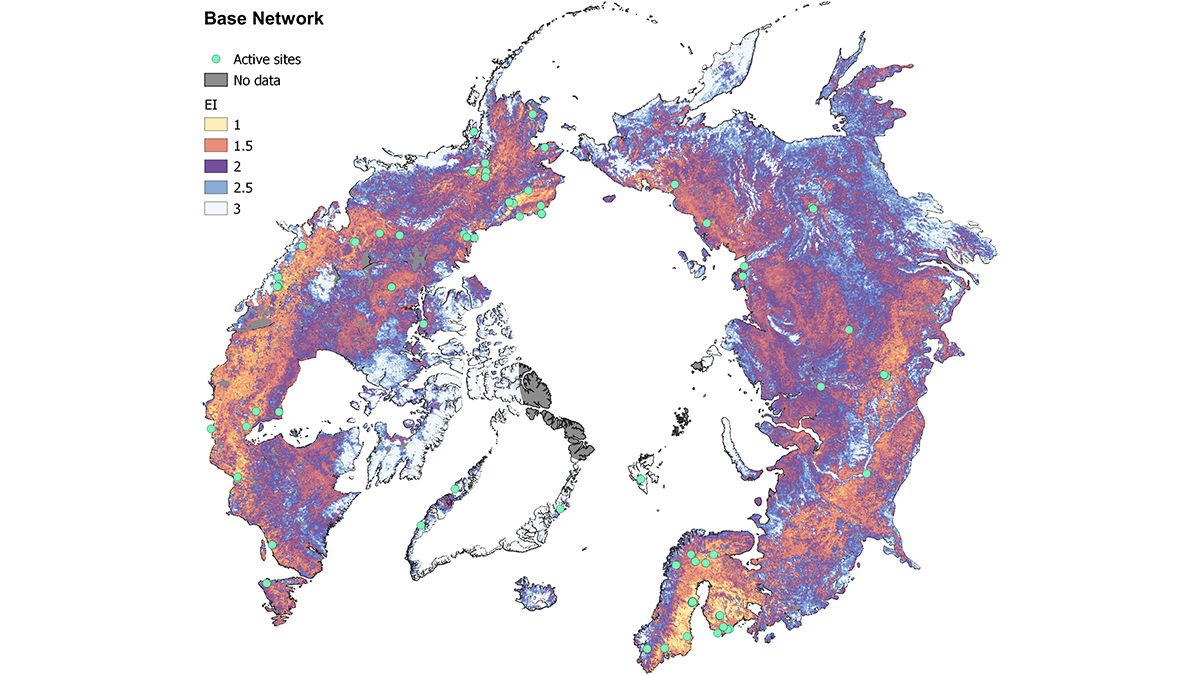
Filling the Gaps: Context and Design of Arctic Carbon Flux Measurement Networks
Large scale observational networks are necessary for understanding the impact of a warming climate in the Arctic, but critical tools are crucial to how those networks are designed.
What 92 Years of Data Say About Ice Cover
New research on Mohonk Lake in New York investigates how changing ice phenology alters temperature dynamics in lakes.
New Software Package Helps Scientists Find Flux
An easy-to-use R package offers a more efficient way to sort through and analyze data about greenhouse gas levels collected in static chamber experiments.
Improvements to Measuring the Ups and Downs of the Landscape
If you are a jazz fan, you may be familiar with Ella Fitzgerald singing ‘How deep is the ocean, how high is the sky’. Using data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission we now know how high the land really is.
Machine Learning Enhances Image Analysis in Biogeosciences
Machine learning can enhance our ability to identify communities of microorganisms and how they change in response to climate change over time.
Insights Biogeoquímicos de um Importante Rio Amazônico
Sub-representados nos orçamentos globais de carbono, rios tropicais como o Tocantins, no Brasil, necessitam de estudos para estabelecer suas características de base face às crescentes mudanças globais.
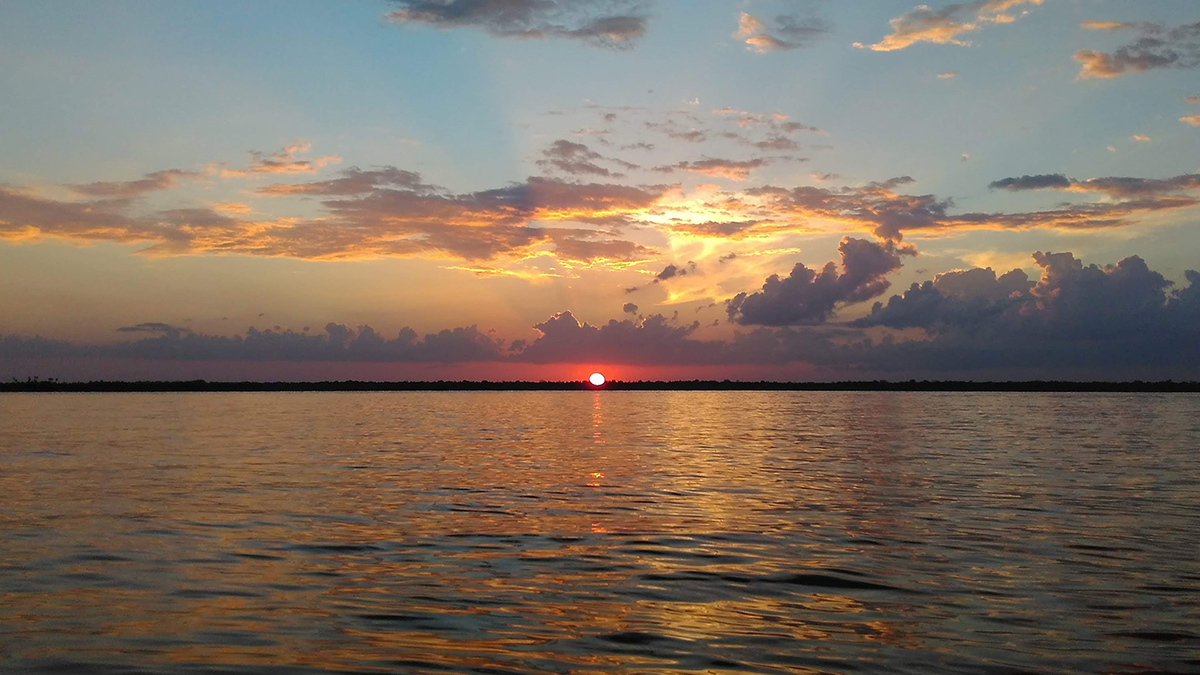
New Insights into a Blind Spot in Aquatic Carbon Dioxide Exchange
Multi-annual measurements across Lake Superior indicate remarkable similarities between large lakes and ocean CO2 exchange during the ice-free season.
Lifting the Veil of Journal Editing
AGU Publications is excited to announce Early Career Editorial Fellow programs for JGR: Biogeosciences and GeoHealth for mentoring the next generation of journal editors.
The Many Adventures of Nitrogen in the Arctic Ocean
New research reviews how our atmosphere’s most abundant element cycles through the Arctic Ocean—and how climate change could affect the process.