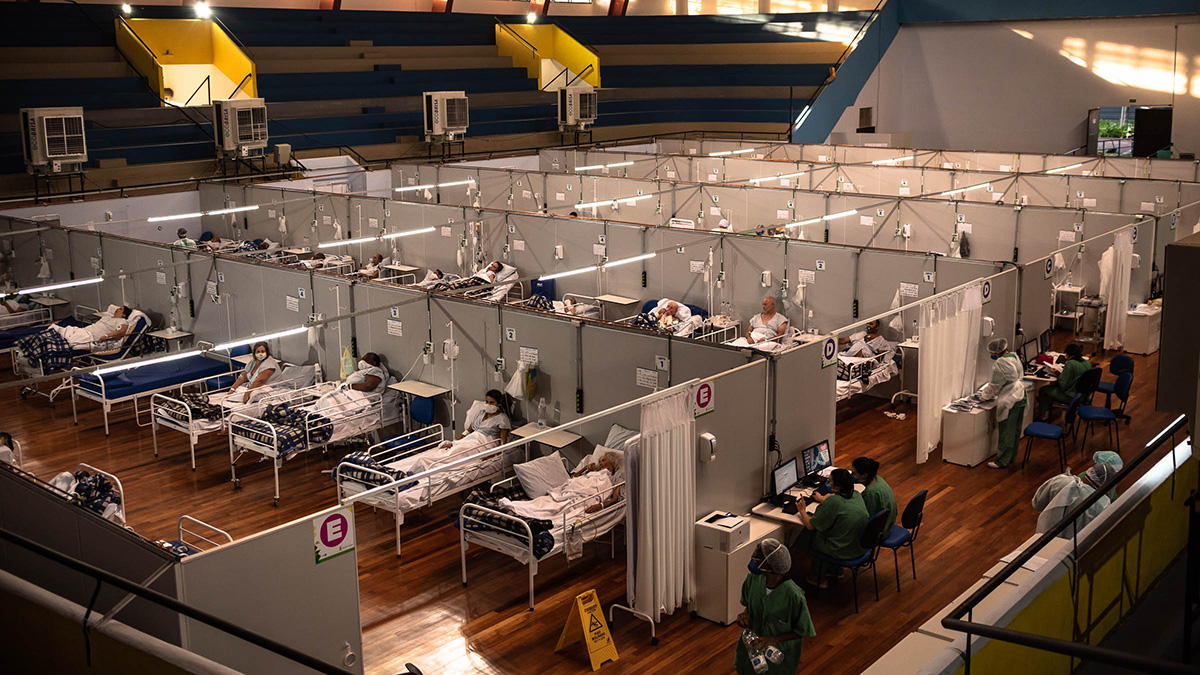
Diversos factores humanos y naturales están generando florecimientos de algas nocivas cada vez más frecuentes y prolongados. Estudios recientes han comenzado a revelar la magnitud del problema y nos informan sobre soluciones potenciales.
lakes
On-Again, Off-Again Lake Cahuilla Likely Enhanced Earthquakes in Southern California
The disappearance of the ephemeral lake has made earthquakes along the San Andreas Fault even more unpredictable.
Major Lakes Have Suffered Major Water Losses over the Past Few Decades
A new study shows that losses are global in both arid and humid regions and could have significant impacts on a quarter of Earth’s population.
The Greenhouse Gas Burden of Inland Waters
A global collaboration inventoried greenhouse gas emissions from rivers, lakes, and streams.
Neural Networks Map the Ebb and Flow of Tiny Ponds
Ponds play an outsized role in carbon emissions, but their size makes them hard to track. Enter machine learning.
Glacial Lakes Can Unleash Deadly Deluges. How Risky Are They?
Breaches in glacial lake dams threaten millions around the world, and scientists are investigating how climate change might affect that risk.
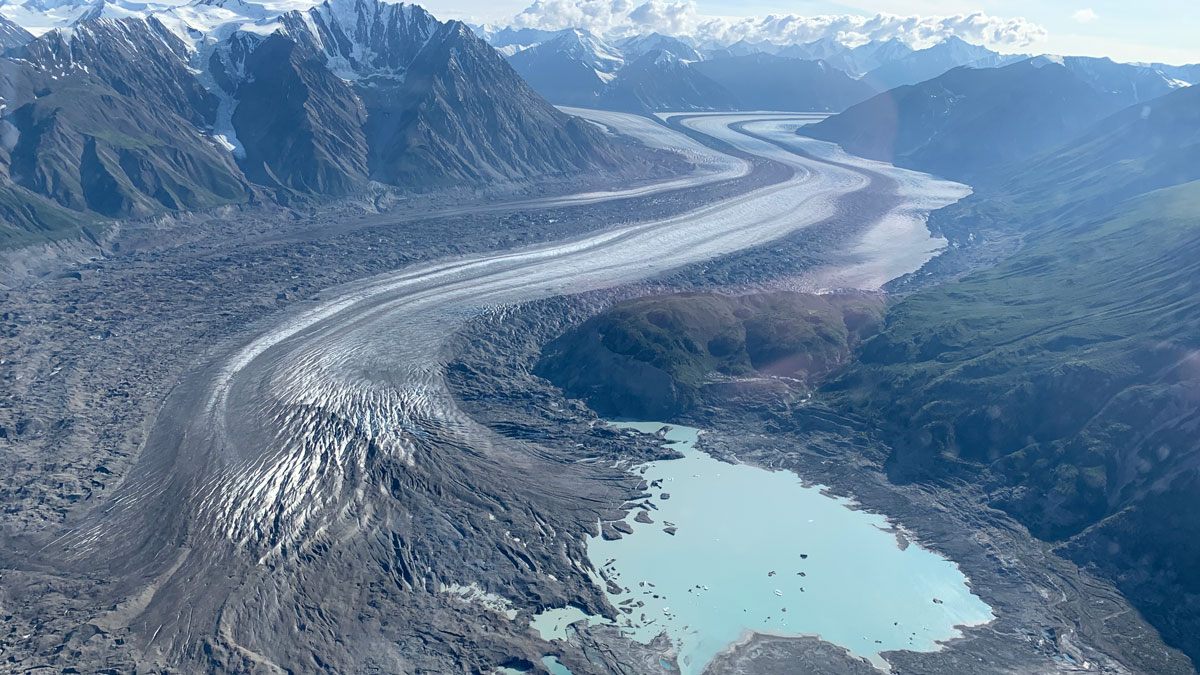
Lakes Can Change How Glaciers Move
Lakes forming from melted ice can have a big effect on their parent glacier, and more of these bodies of water are appearing under warming conditions.
Sedimentos lacustres registran el legado del carbón de Carolina del Norte
Los lagos contaminados con cenizas de carbón se encuentran en áreas residenciales y recreativas, provocando preocupaciones por la salud de los residentes locales y los ecosistemas.
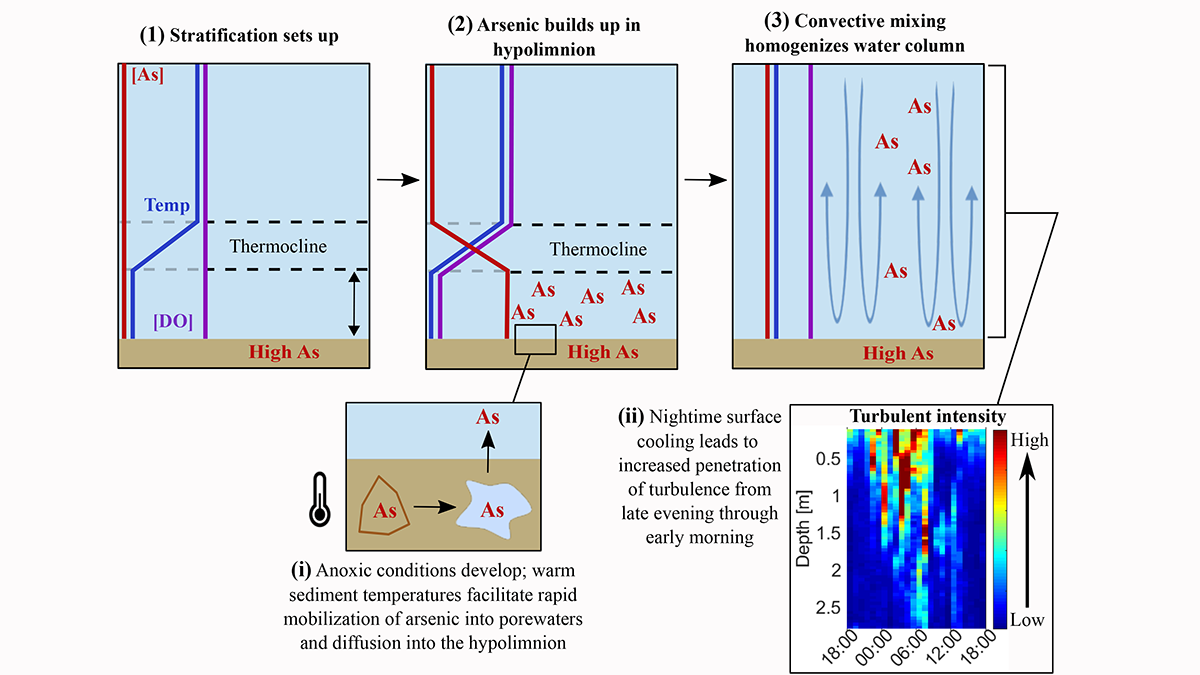
Understanding Enhanced Arsenic Pollution in Shallow Lakes
A new study explains why the arsenic that has accumulated in lake bottom sediments is more harmful to the lake ecosystems in shallow lakes.