Research unveiled a surprising plateau in plants’ ability to absorb carbon through stomata, which could mean more carbon left in the atmosphere.
Modeling
Arctic Ice Loss Could Shorten Winter Feeding Time for Zooplankton
The Arctic’s thinning sea ice allows more light to penetrate deeper into the ocean, holding zooplankton far beneath the surface.
Flowing Crust Pushes Faults on Their Backs
Puzzlingly shallow faults in western Türkiye are likely getting a boost from below.
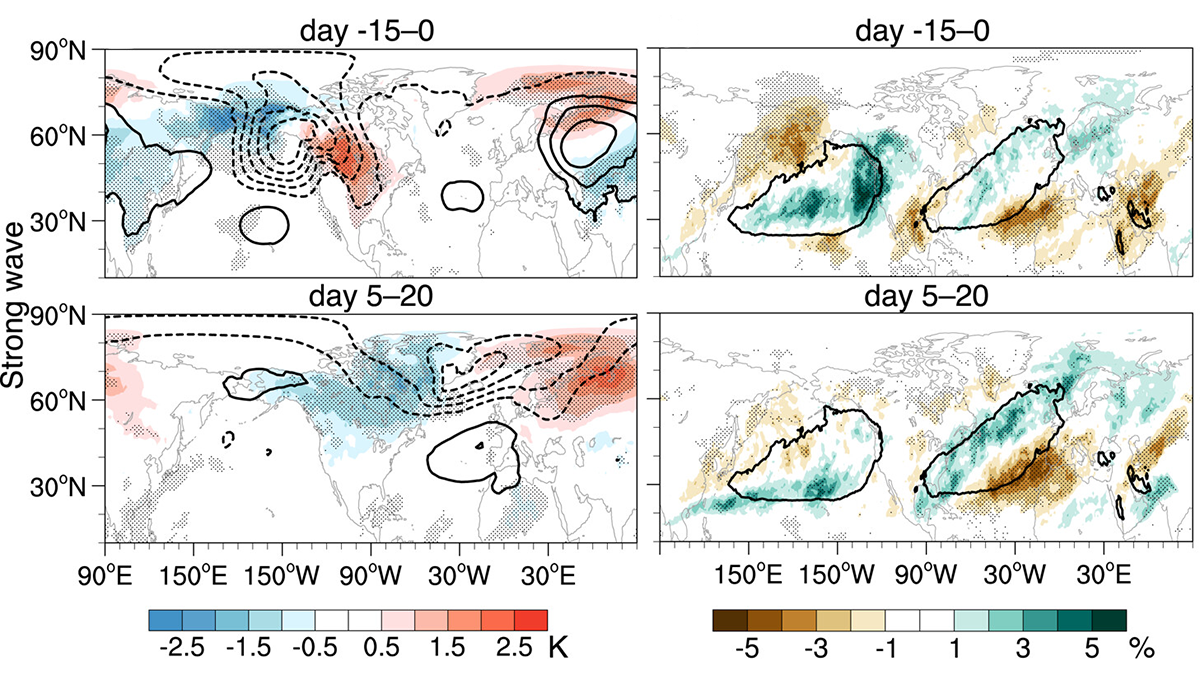
Modeling Stratospheric Impacts on North American Extreme Events
A new study quantifies the tropospheric and surface impacts of extreme stratospheric wave events and evaluates their representation in state-of-the-art climate models.
La desigualdad del estrés por calor
Residentes de vecindarios históricamente marginalizados enfrentan mayor estrés por calor que los de otras áreas.
Observing the Impact of Convective Aggregation on Water Vapor
Remote sensing measurements for water vapor isotopic composition enable us to assess how convective aggregation influences the atmospheric hydrological cycle.
Exploring Just How Extreme Future Storms Could Get
A novel approach to storm simulations could help prepare for increasingly heavy precipitation events.
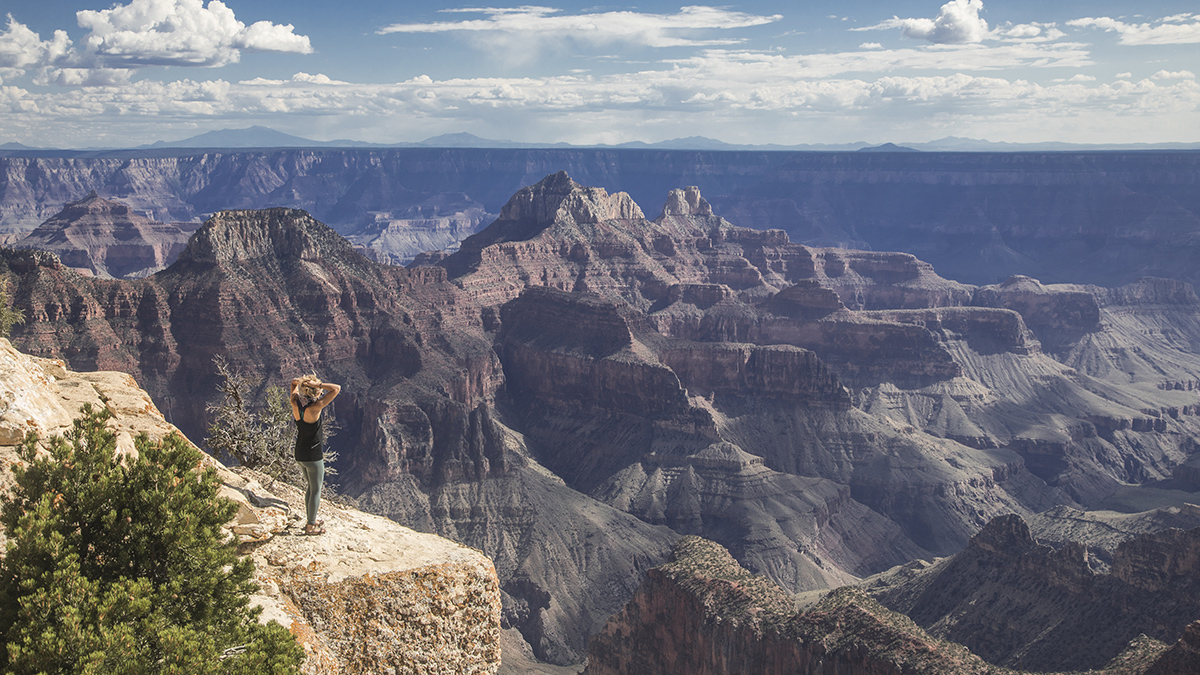
Grand Canyon Heat May Become More Dangerous
Climate change may double the risk of heat-related illness at Grand Canyon National Park by the end of the century.
Better Bottom-Up Estimates of Wetland Methane Emissions
Limited monitoring of methane emissions from tropical wetlands could be obscuring these environments’ role in climate change.
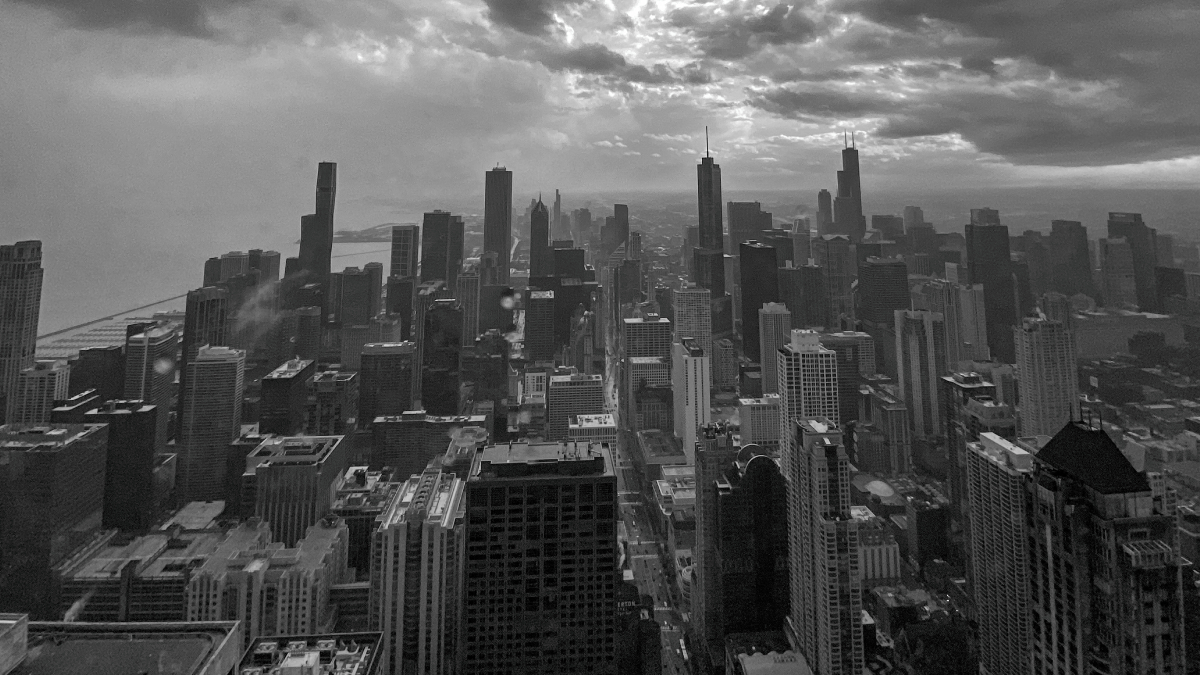
Underground Heat Could Be a Problem, or a Perk, for Chicago Buildings
Heat released by old and inefficient Chicago buildings could, if harnessed, be an energy solution.