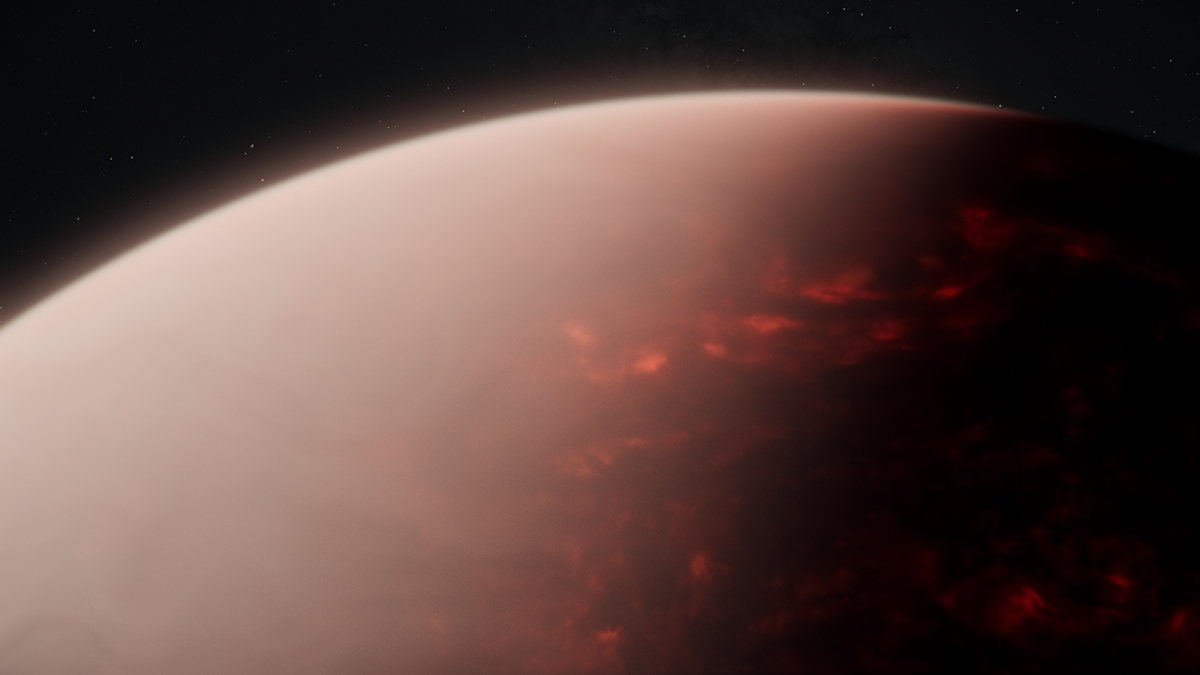
TOI-561 b, an exoplanet roughly 275 light-years away, seems to have a thick atmosphere despite being wildly irradiated by its host star.
planetary atmospheres
Trump Administration Plans to Break Up NCAR
The Trump administration is planning to dismantle the National Center for Atmospheric Research, one of the world’s leading climate and Earth science research laboratories, according to a statement from Russ Vought, director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, to USA Today.
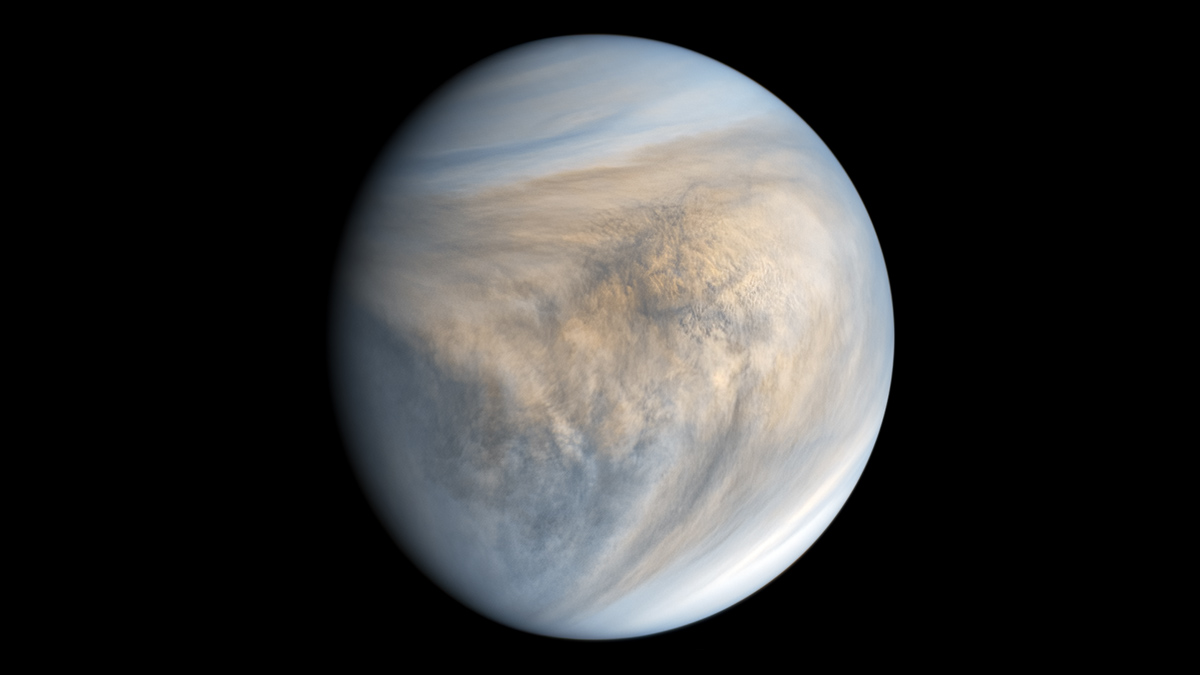
Key Driver of Extreme Winds on Venus Identified
A new study suggests that a once-daily atmospheric tidal cycle may be a bigger driver of rapid Venusian winds than previously thought.
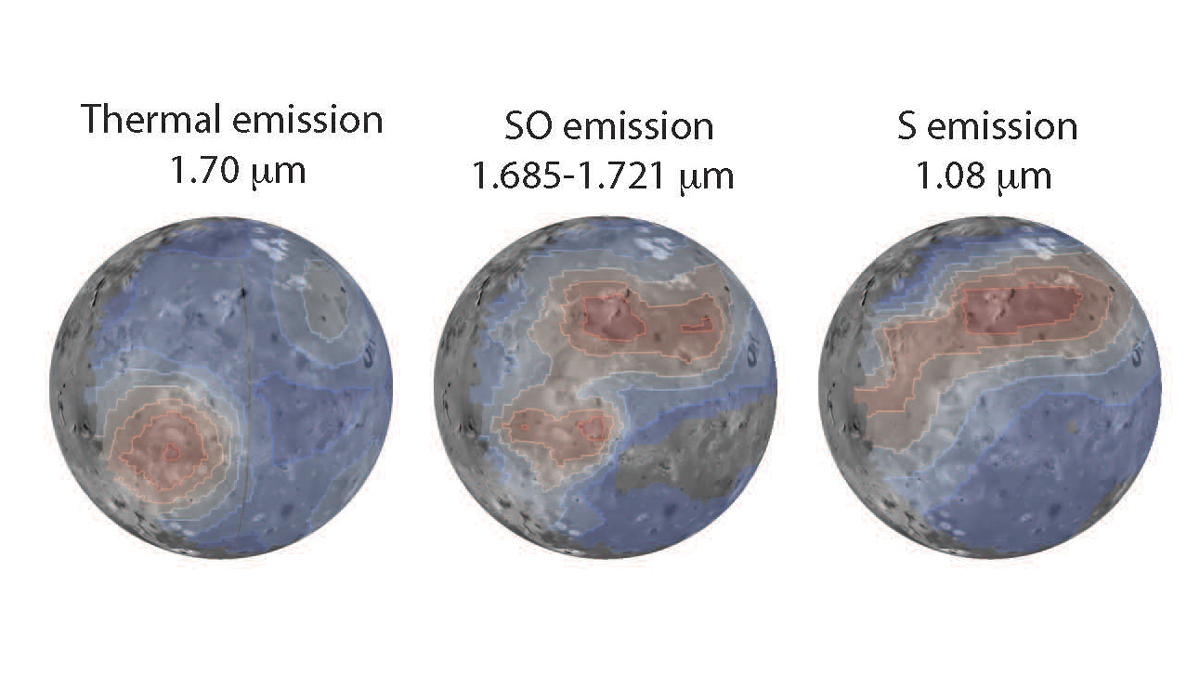
Webb Telescope Spies Io’s Volcanic Activity and Sulfurous Atmosphere
New James Webb Space Telescope images reveal cooling lava, volcanic sulfur monoxide gas, and sulfur gas emissions created by interactions between plasma and the moon’s atmosphere.
¿Pueden los microorganismos prosperar en la atmósfera terrestre o simplemente sobreviven allí?
Un enfoque de modelización ascendente podría acercar a los científicos a la comprensión de las comunidades de microbios en la atmósfera.
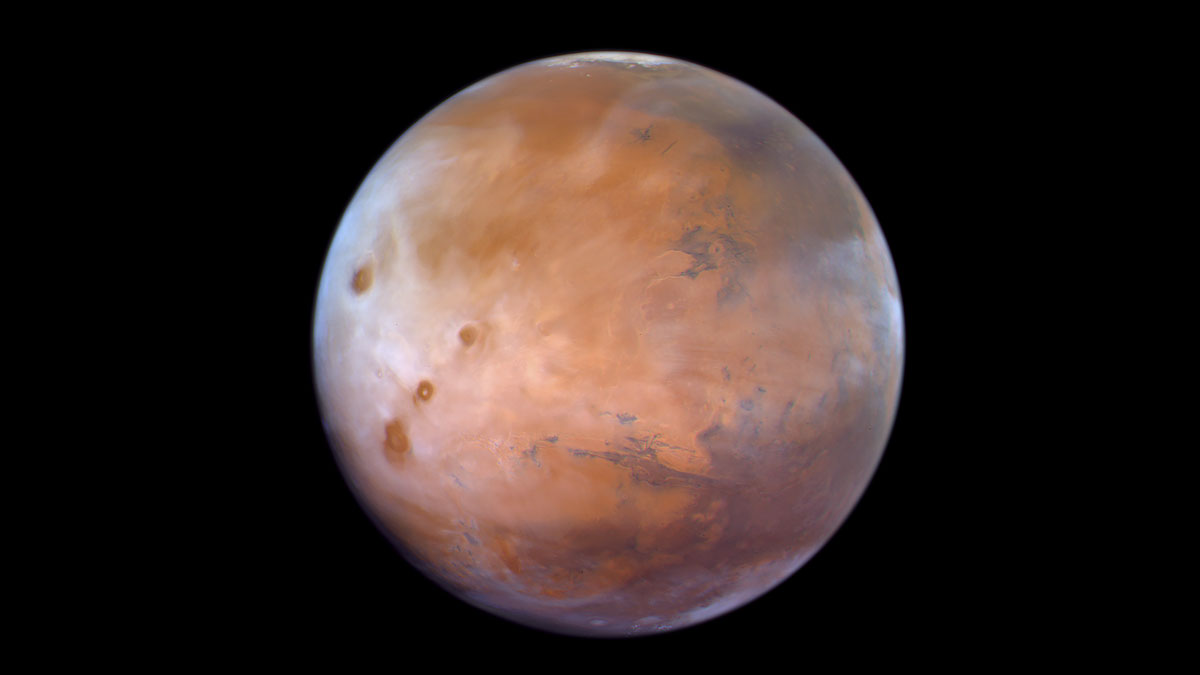
First Complete Picture of Nighttime Clouds on Mars
Data captured by the Emirates Mars Mission reveal that clouds are typically thicker during Martian nighttime than daytime.
Can Microorganisms Thrive in Earth’s Atmosphere, or Do They Simply Survive There?
A bottom-up modeling approach could bring scientists closer to understanding communities of microbes in the atmosphere.
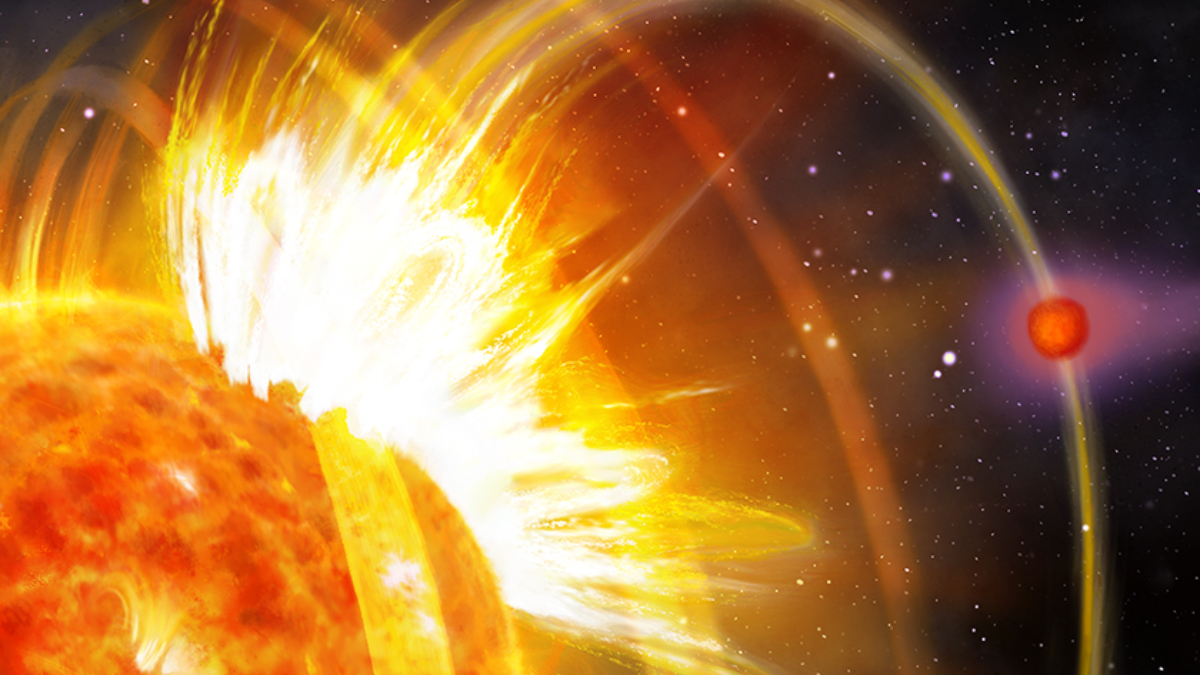
Exoplanet Triggers Stellar Flares and Hastens Its Demise
HIP 67522 b can’t stop blasting itself in the face with stellar flares, a type of magnetic interaction that scientists have spent decades looking for.
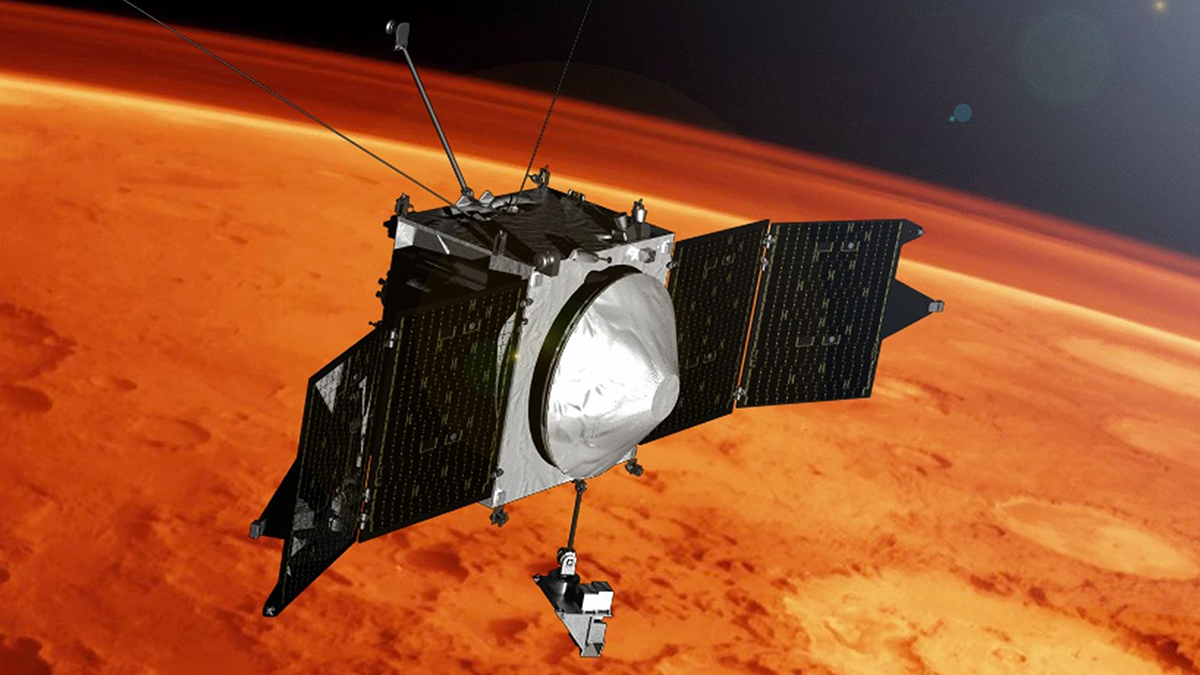
Scientists Spot Sputtering on Mars
Nearly a decade’s worth of data went into the first direct observation of sputtering on Mars, which researchers believe contributed to the loss of the Red Planet’s atmosphere.