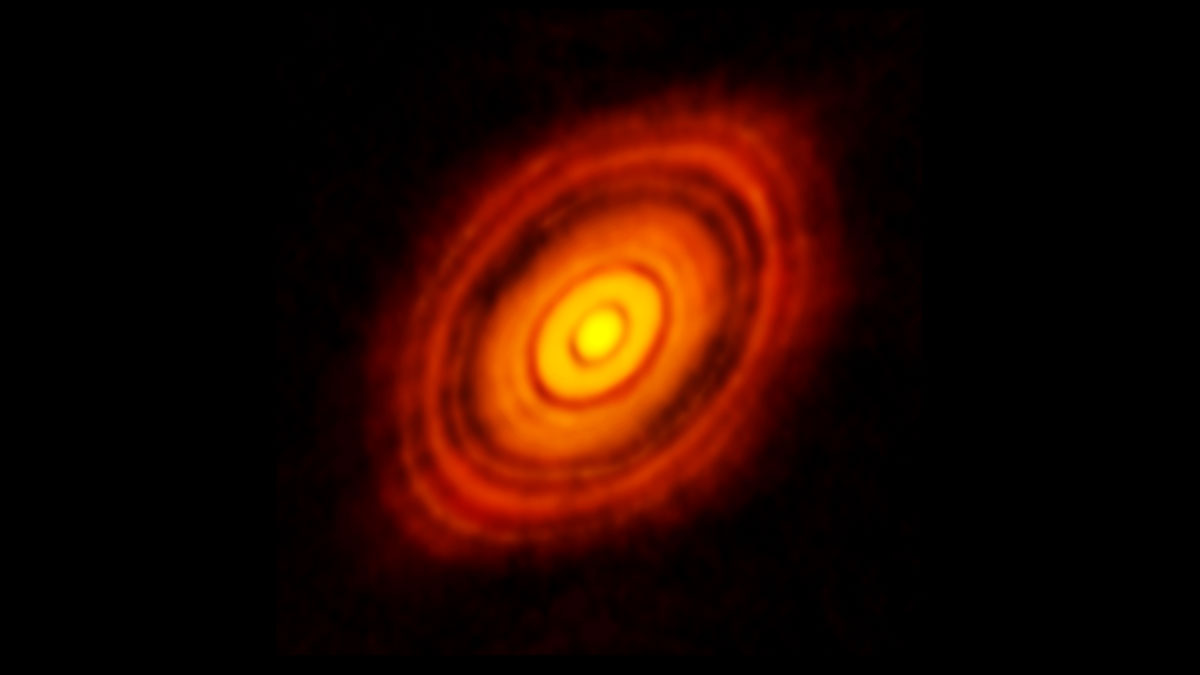
A liquid metal experiment has shown how magnetic rotational instability might allow dust to pool together in disks around young stars to form new worlds.
planets
Tilted Planet System? Maybe It Was Born That Way
New observations could shed light on the degree to which misalignment in a planet-forming disk contributes to skewed planetary orbits.
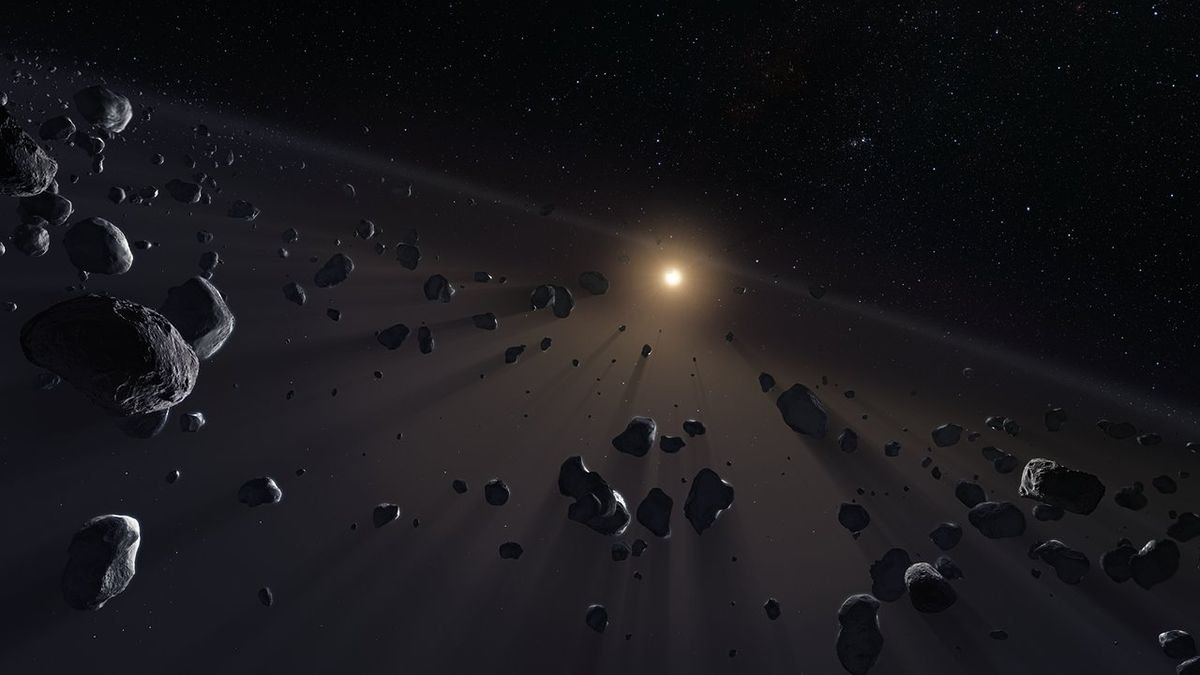
A Survey of the Kuiper Belt Hints at an Unseen Planet
An analysis of more than 150 objects in the far reaches of the solar system suggests that a planet more massive than Mercury could be lurking beyond the orbit of Pluto.
How an Interstellar Interloper Spurred Astronomers into Action
Valuable lessons from previous interstellar objects allowed scientists to develop a more rapid response when the third one arrived in July.
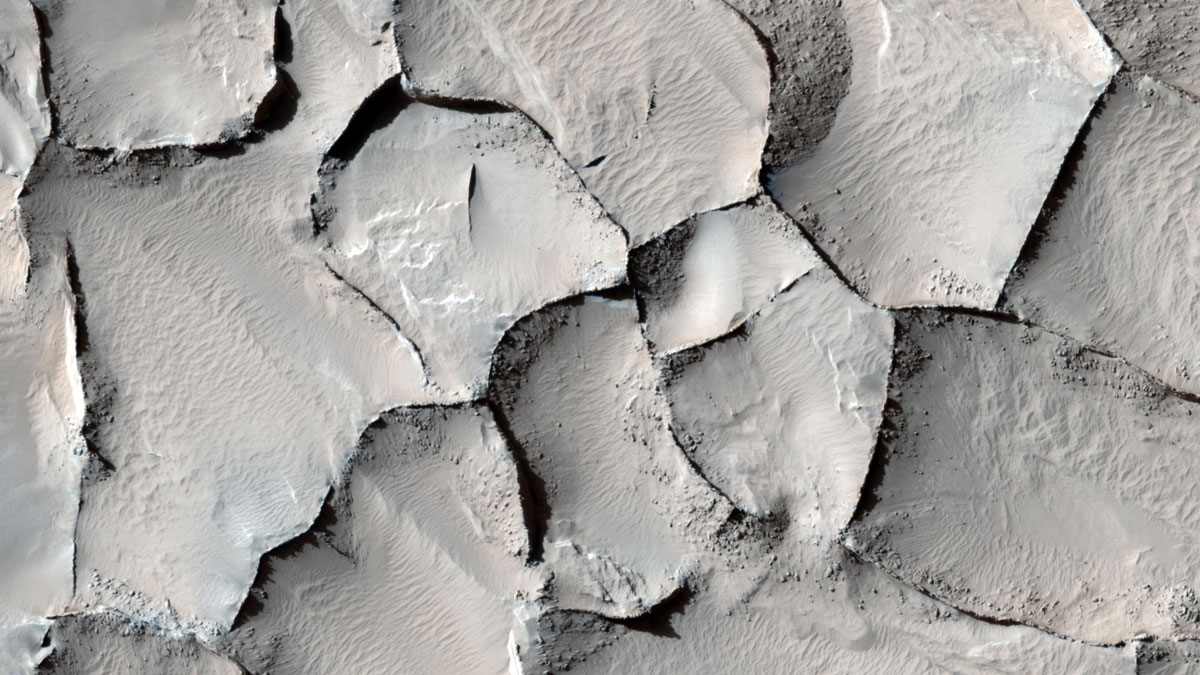
Cracks on Planetary Surfaces Hint at Water
Imagery of fractured terrain on Venus, Mars, and Jupiter’s moon Europa pinpoints environments influenced by water.
Cinturones polvorientos ofrecen una visión más clara de la formación de exoplanetas
Las observaciones en longitudes de onda milimétricas de polvo y guijarros en 74 sistemas estelares sugieren que las migraciones planetarias podrían ser más comunes de lo que pensábamos.
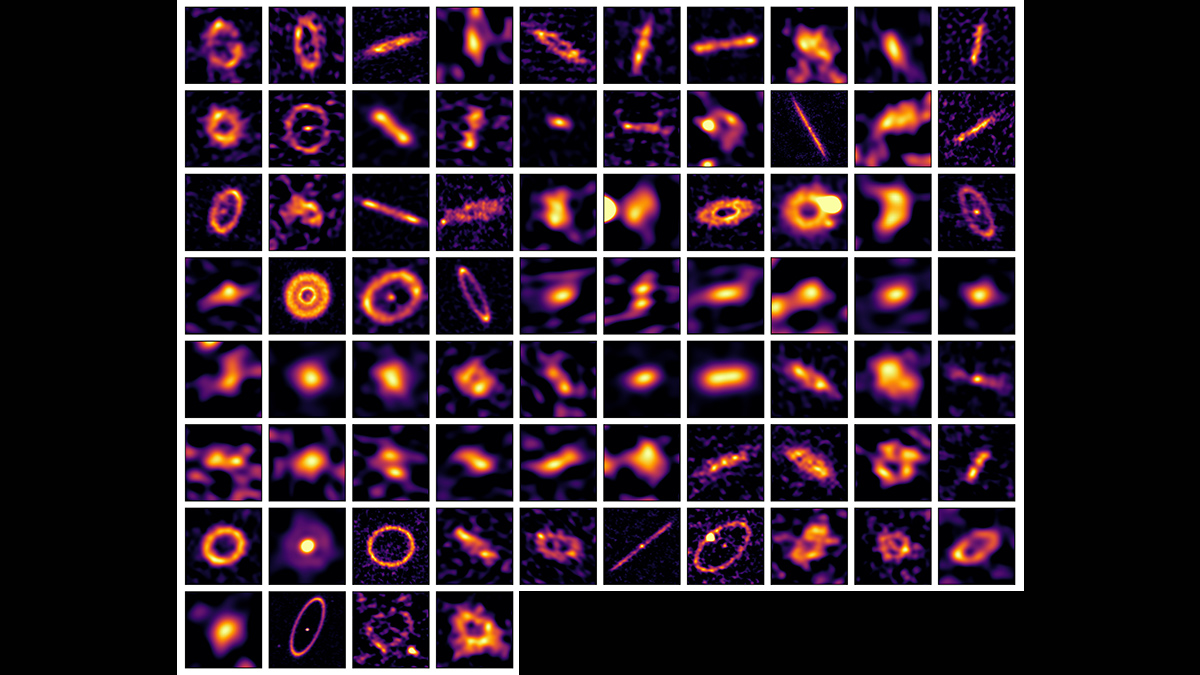
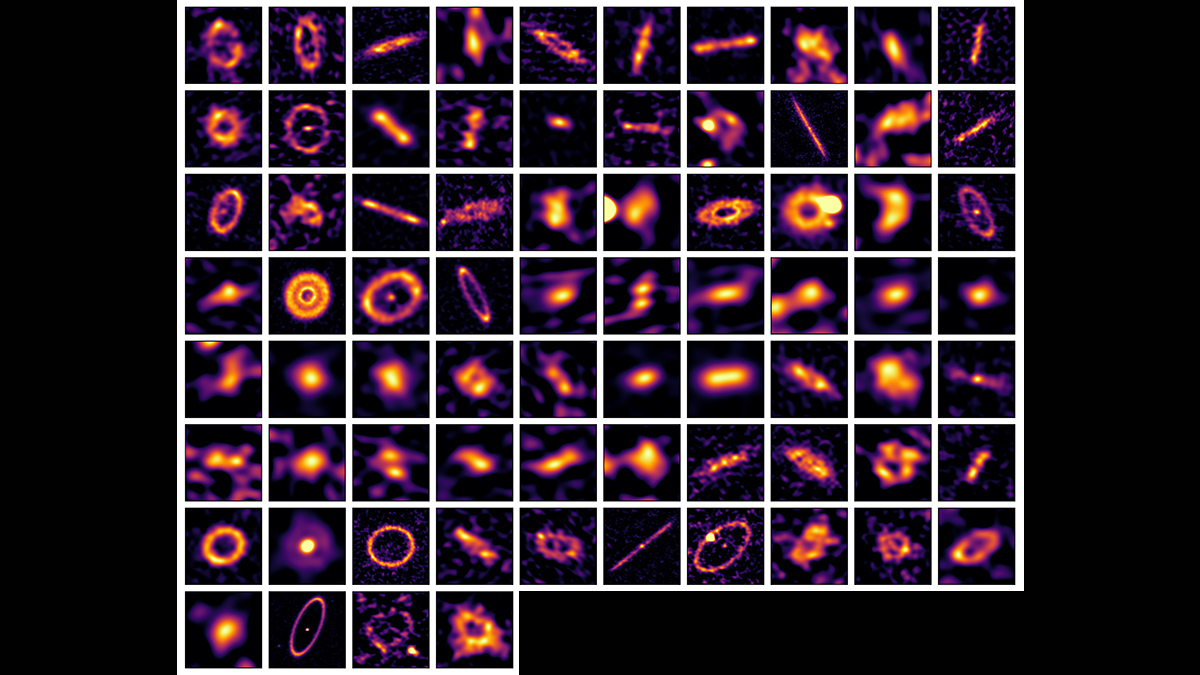
Dusty Belts Provide Clearer Insights into Exoplanet Formation
Millimeter-wavelength observations of dust and pebbles in 74 star systems hint that planetary migrations might be more common than we realized.
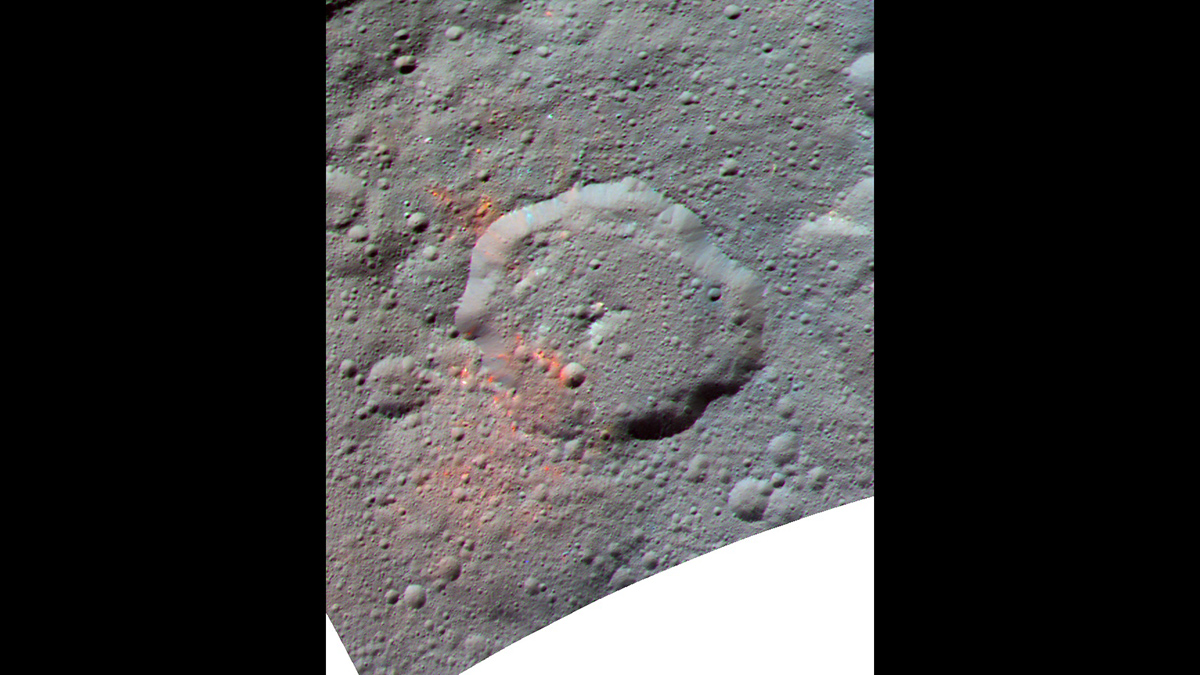
Ceres’s Organics Might Not Be Homegrown After All
Scientists have been unable to determine whether the dwarf planet’s organics were produced by its own chemical processes or delivered by asteroids. New evidence implicates asteroids.
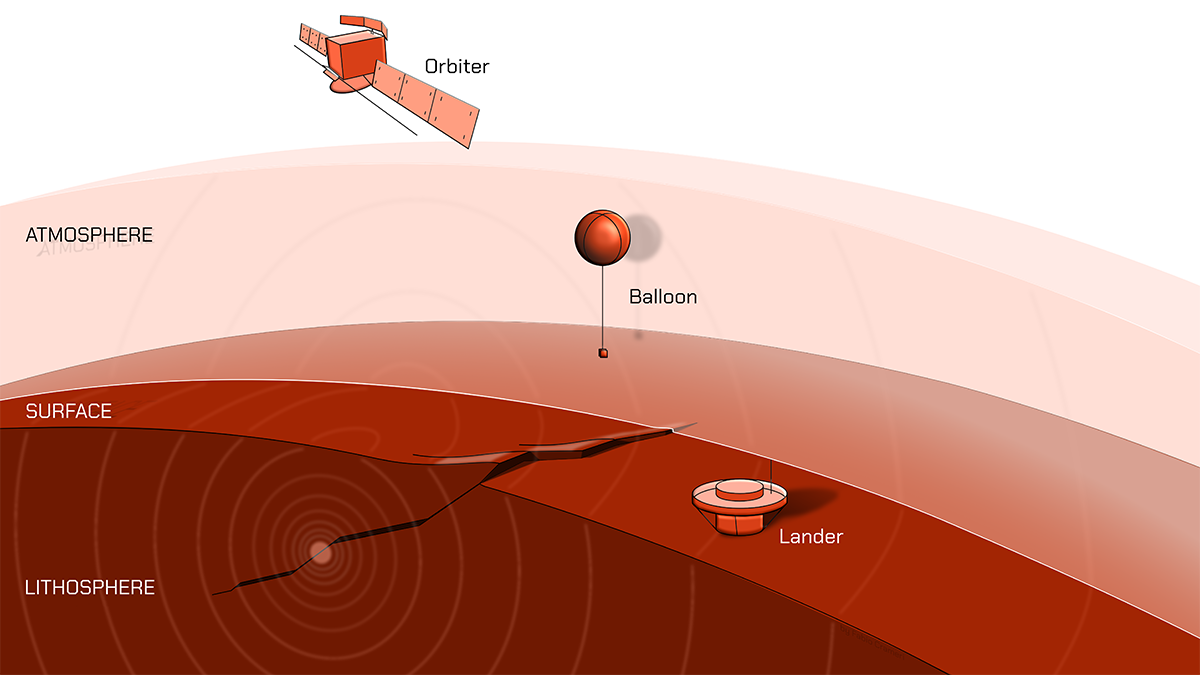
Three Ways to Track Venusquakes, from Balloons to Satellites
The planet’s harsh conditions make studying seismicity challenging, but it is likely possible.