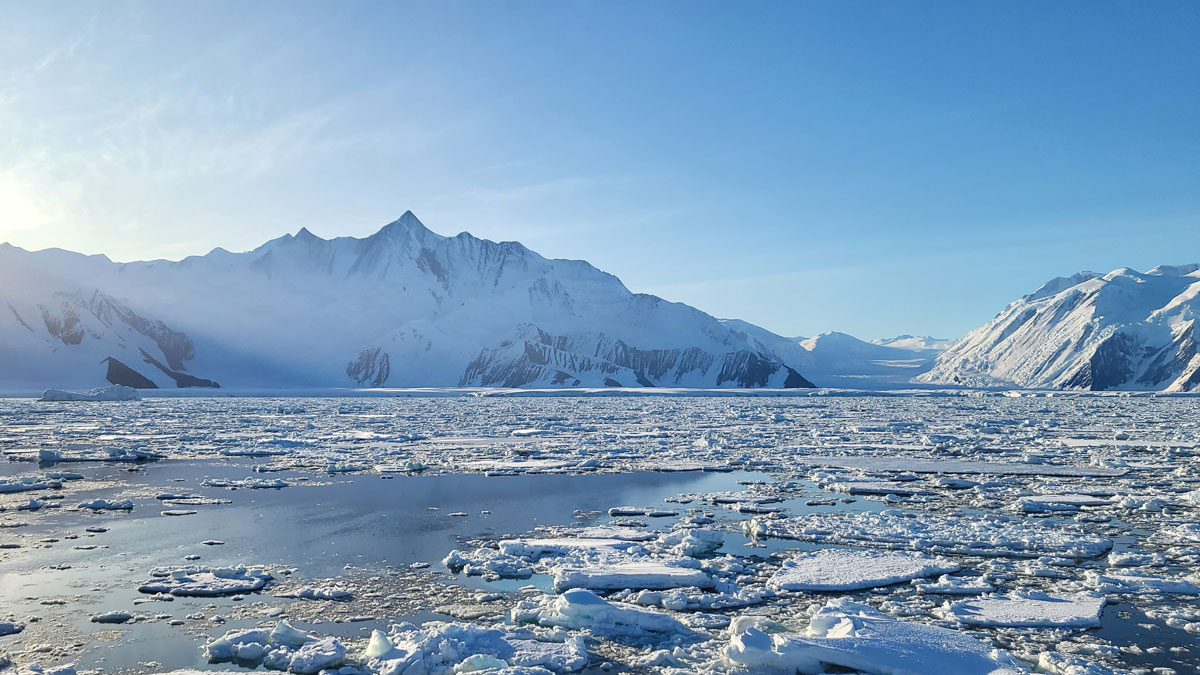
Scientists used sediments to create a millennia-long archive of Antarctic fast ice. Along the way, they discovered that the freezing and thawing of this enigmatic ice appear to be linked to solar cycles.
solar activity
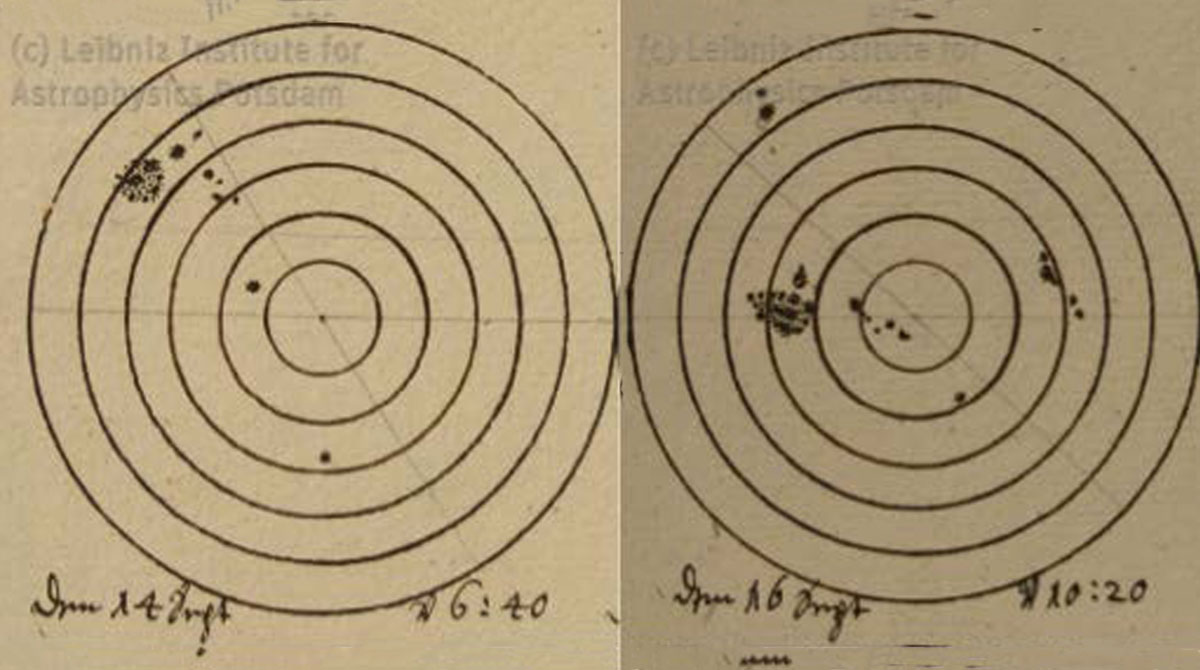
Sunspot Drawings Illuminate 400 Years of Solar Activity
A new computational framework is helping scientists sift through centuries of scientific illustration of the Sun’s spotty surface.
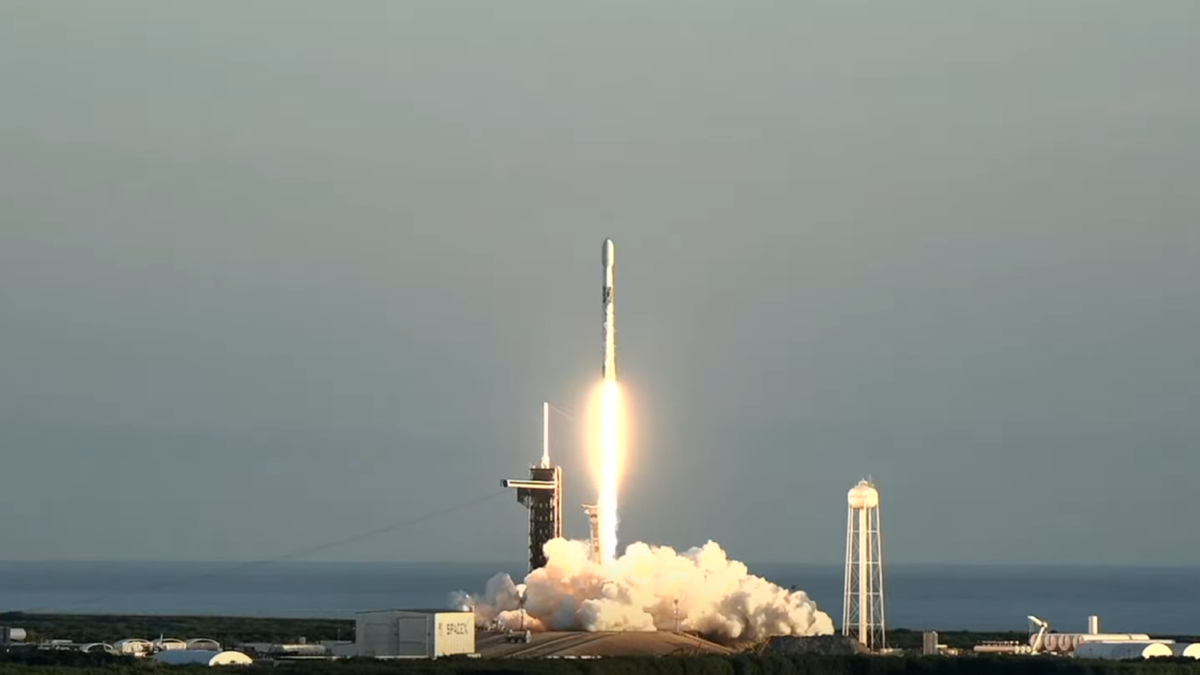
Trio of Space Weather Satellites Take Flight
These three satellites will that study the solar wind and its impacts.
U.K. Space Weather Prediction System Goes Operational
Officials now have access to a suite of models they can use to head off damage to critical infrastructure.
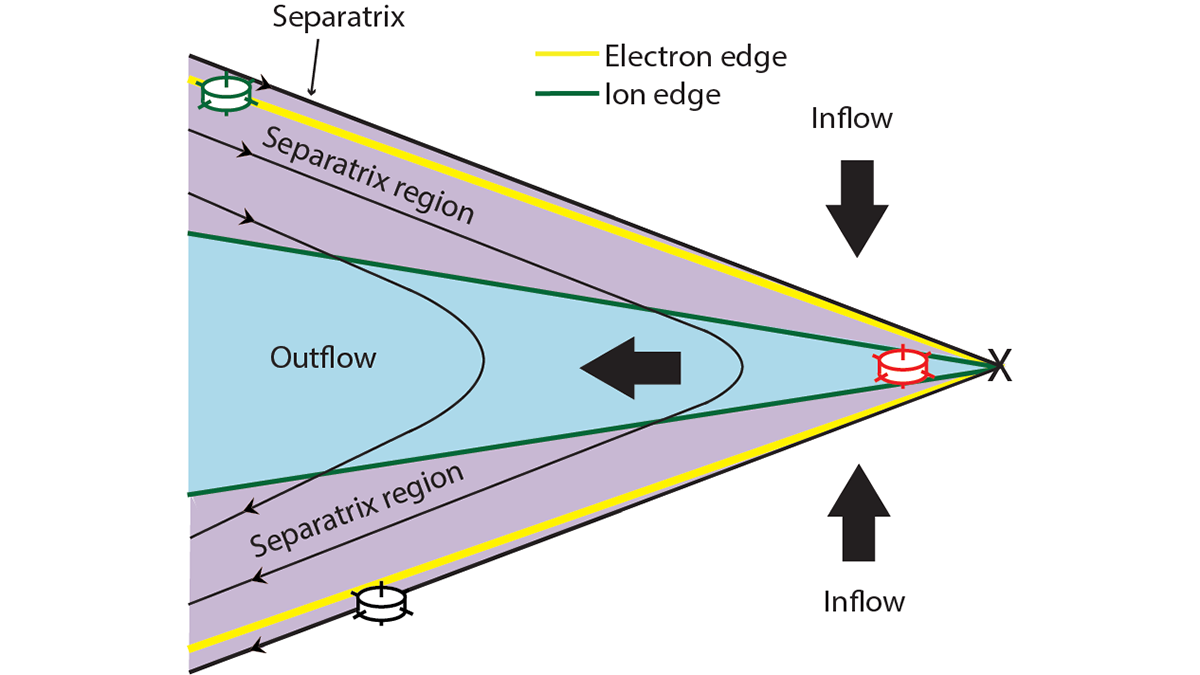
New Insights into an Enigmatic Form of Magnetic Reconnection
A new study deepens understanding of magnetic field behavior recently discovered by NASA in Earth’s magnetosphere.
Fast Flows in Earth’s Magnetotail Surveyed by NASA Satellites
A survey of high-speed electron flow observed by NASA satellites in the Earth’s magnetotail is presented and related to the process of magnetic field line reconnection and particle acceleration.
Watching a Solar Event from All Angles
A fleet of spacecraft captured unprecedented details of the major solar outbursts in May and June 2024.
Blasts from the Past: New Insights from Old Space Storms
Reassessment and comparison of past space weather events highlight the potential for Earth to experience destructive geomagnetic disturbances.
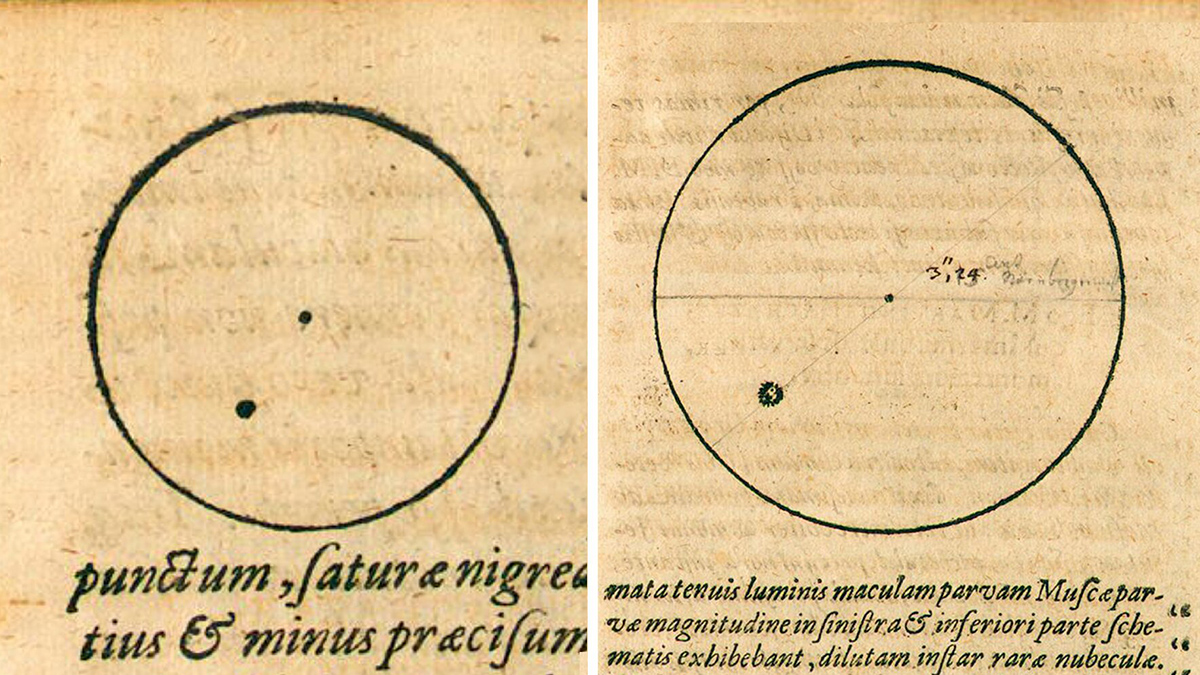
Kepler’s Drawings Might Reveal When the Sunspots Disappeared
Johannes Kepler’s landmark 1607 sunspot observations may have been made at the end of the solar cycle, helping constrain the start of the Maunder Minimum.
From Sun to Earth: A New Network for Comprehensive Space Weather Monitoring
The Chinese Meridian Project combines hundreds of instruments for a detailed, three-dimensional view of the solar-terrestrial environment.