不同的指标以不同的方式变化,但是气候模型显示出一个明显的趋势,那就是热应力的增加。
temperature
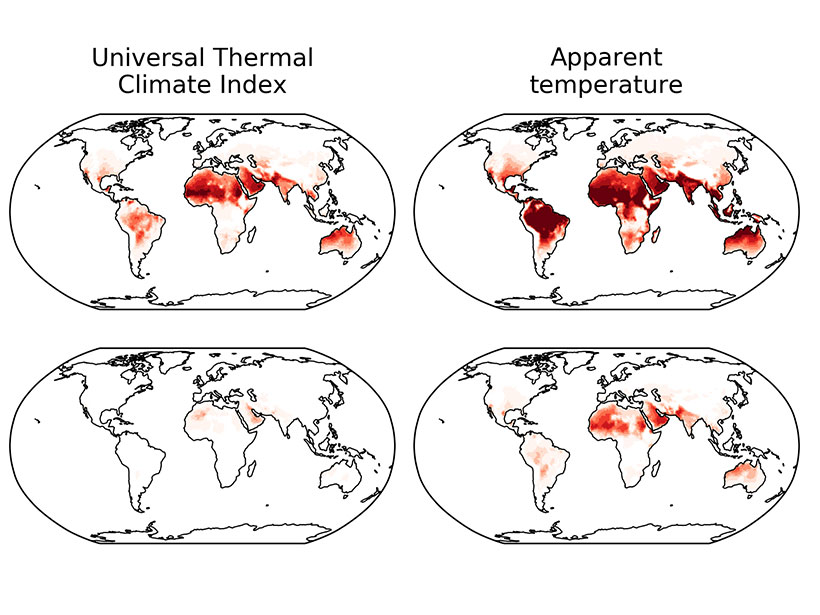
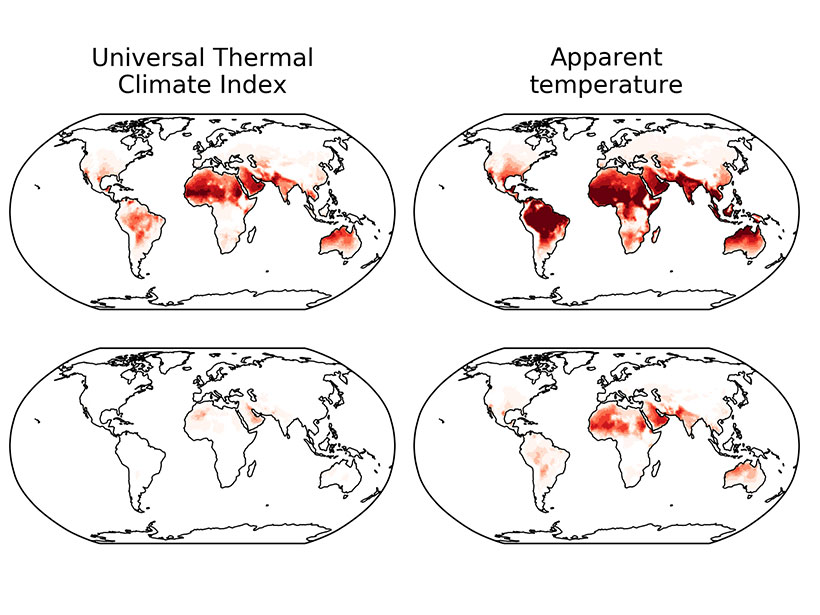
Global Warming Causes Uneven Changes in Heat Stress Indicators
Different indicators change in different ways, but climate models project a clear trend of increasing heat stress.
New Land Surface Air Temperature Global Dataset
The fifth major update of land surface air temperature data from the Climatic Research Unit and the Met Office has extended the time series, included more stations, and used better processing methods.
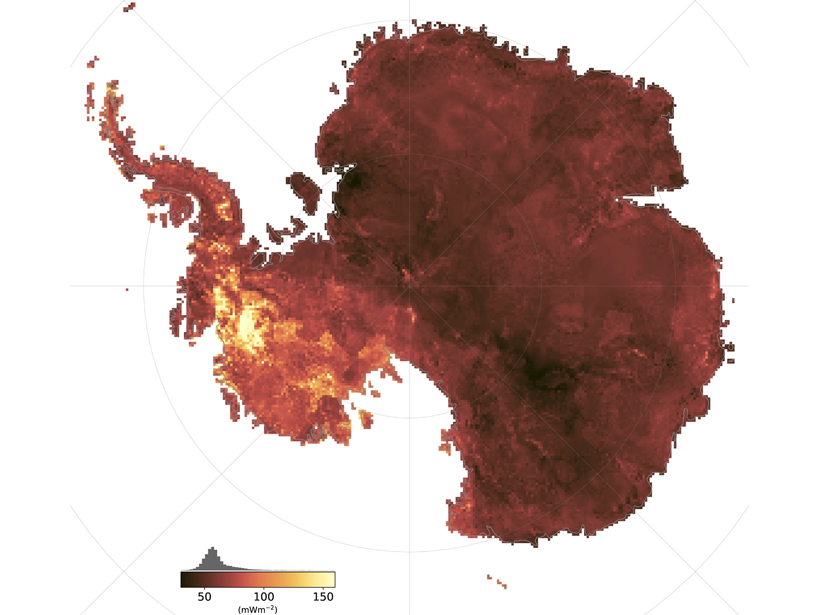
Taking the Temperature of Antarctica’s Crust
How do you measure the geothermal heat flux in a continent covered by an ice-sheet? A new study uses correlations of diverse global observables and produces a heat flow map of the entire Antarctica.
New Global Surface Temperature Dataset Spans 170 Years
HadCRUT5, the new version of the Met Office Hadley Centre/Climatic Research Unit global surface temperature dataset from 1850 to 2018, has extended and improved the previous temperature record.
Thawing Permafrost May Cause Streams to Cool
Permafrost thawing associated with climate warming increases contributions to streamflow by deeper, cooler groundwater flow paths, which may result in lower summer stream temperatures.
Ice Age Testing Reveals Challenges in Climate Model Sensitivity
Increased reflection of incoming sunlight by clouds led one current-generation climate model to predict unrealistically cold temperatures during the last ice age.
Tracing the Moisture That Nourishes the World’s Highest Glacier
Using data from weather stations on and around Mount Everest, scientists find that the Khumbu Glacier receives most of its moisture from the Bay of Bengal.
Coastal Brazil Is Likely to Face More Heat Waves and Droughts
In 2014, São Paulo experienced its greatest water crisis ever, caused by an intense drought. New research indicates that it is likely to happen again and be even more severe.
Will Rising Temperatures Make Rice Too Toxic?
Greenhouse experiments reveal how higher temperatures act to elevate arsenic levels in rice and may help focus efforts to solve a crisis threatening food systems around the world.