New research indicates climate change may thin the mixed layer and contribute to a reduction of sea surface temperature anomalies.
temperature
Arctic Ozone Loss Brings Warming to the Near Surface
New research confirms that ozone loss over the Arctic can lead to widespread warming near the Artic surface during late winter and early spring.
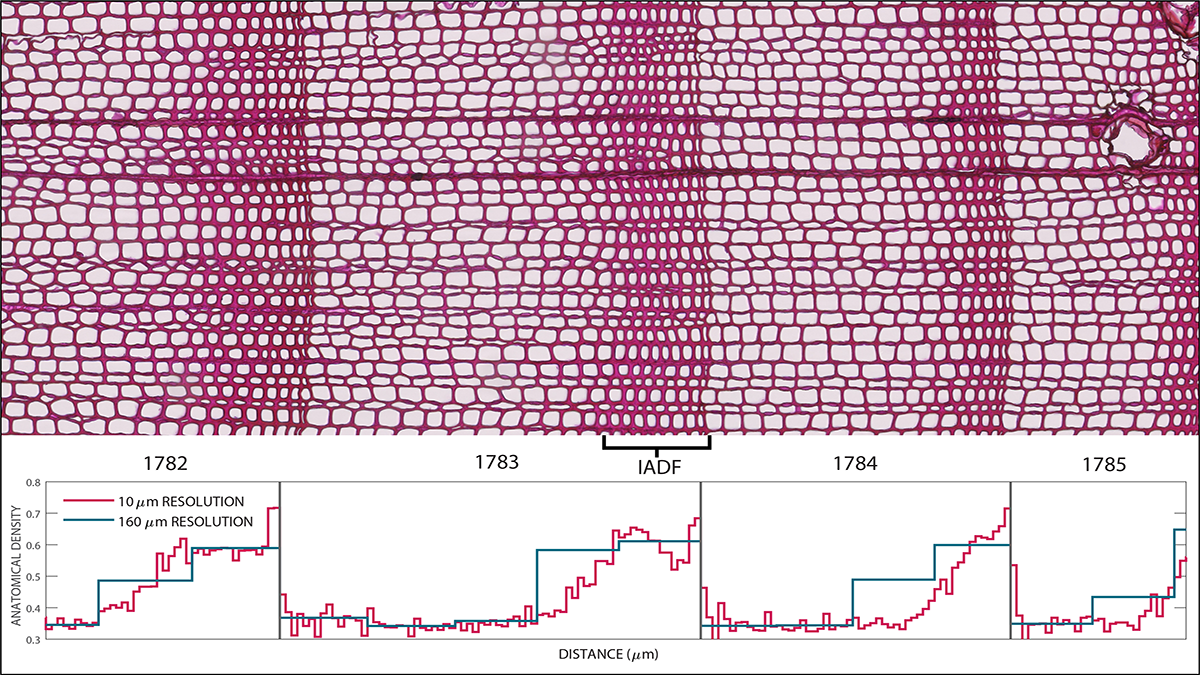
How Hot Was the Summer of 1783 Really? Trees Tell Tales
Volcanoes, heat waves, and tree rings – getting the seasonal story straight – a new study finds that volcanic fog lowered summer tree ring density despite the heat.
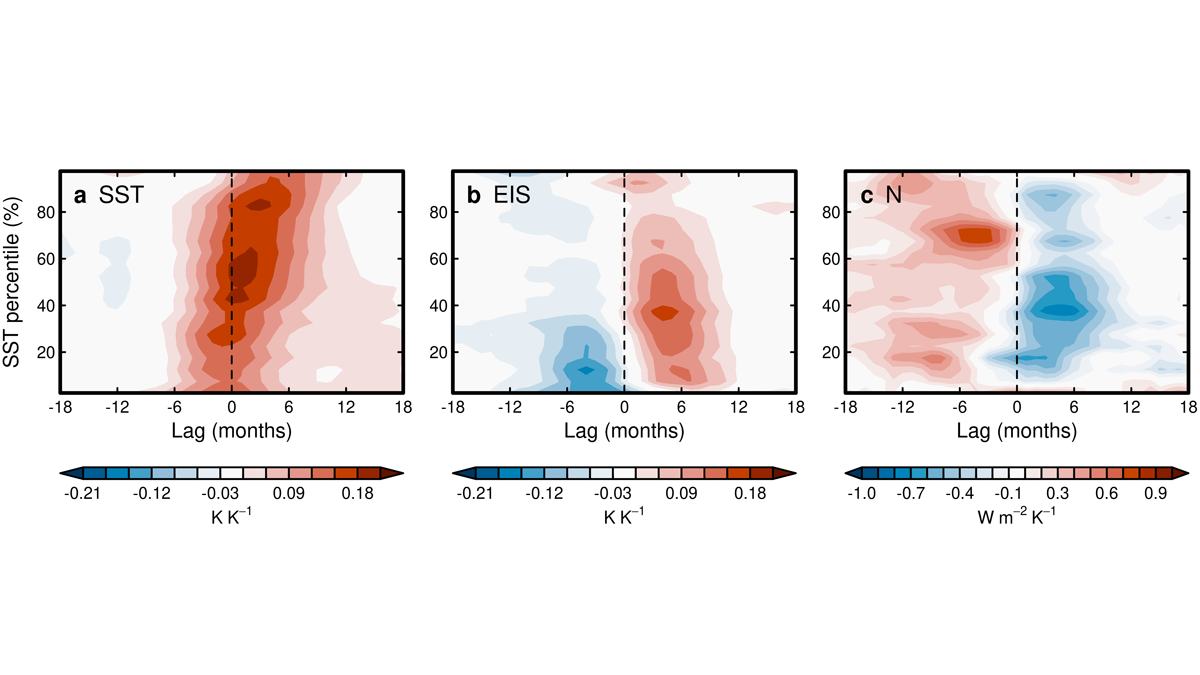
El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Radiation Two-Way Coupling
Changes in sea surface temperature during ENSO events and radiation are related, suggesting a two-way coupling between sea surface temperature and radiation in coupled climate variability.
Lasers and Ultracold Atoms for a Changing Earth
Applying new technology rooted in quantum mechanics and relativity to terrestrial and space geodesy will sharpen our understanding of how the planet responds to natural and human-induced changes.
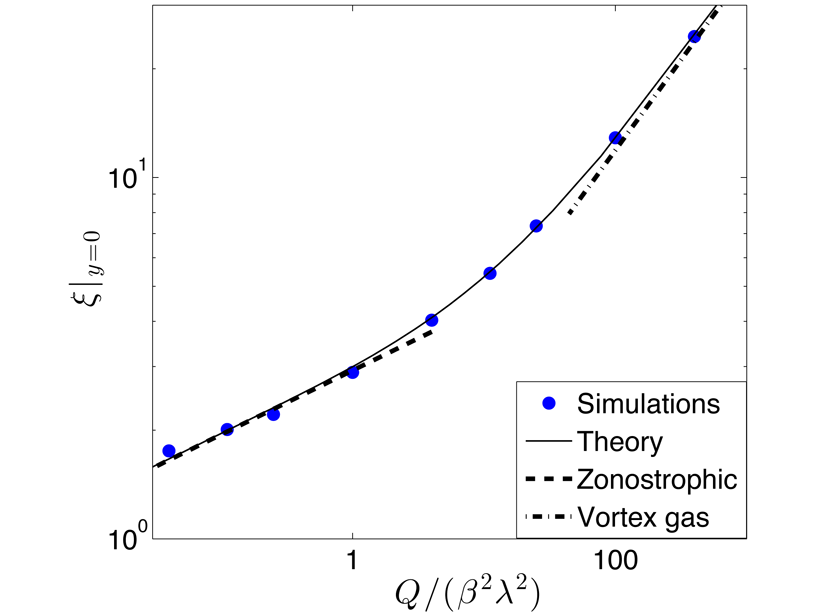
Order in Turbulence
Extracting order from turbulence is difficult, even under the most idealized conditions. A new scaling theory quantifies how eddies influence temperature gradients in geophysical turbulence.
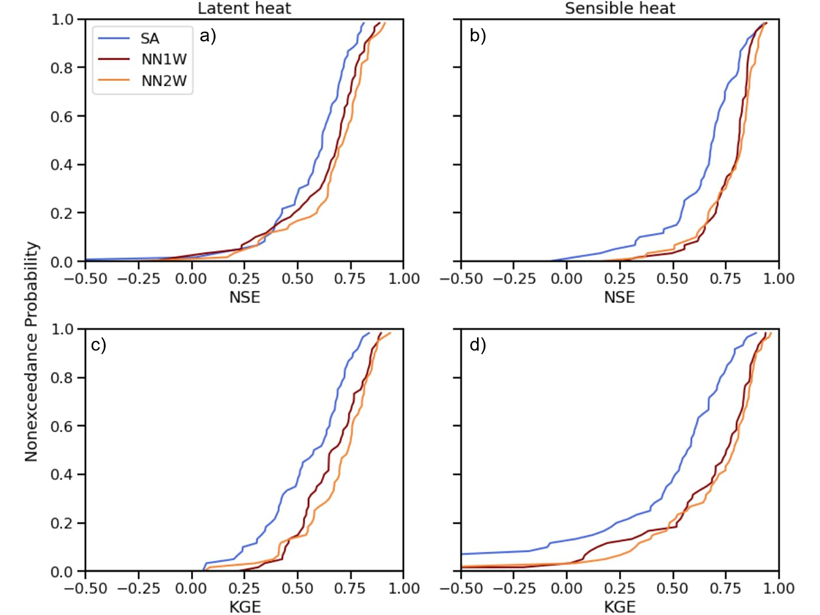
Combining Deep Learning Methods with Process-based Models
Using turbulent heat fluxes as an example, a new study shows that exchange of information between process-based models and deep learning methods may lead to improved predictions.
Calculating Human Health Risks with General Weather Data
Gridded climate data sets are just as effective as weather station data at assessing human mortality risk related to heat and cold, researchers suggest.
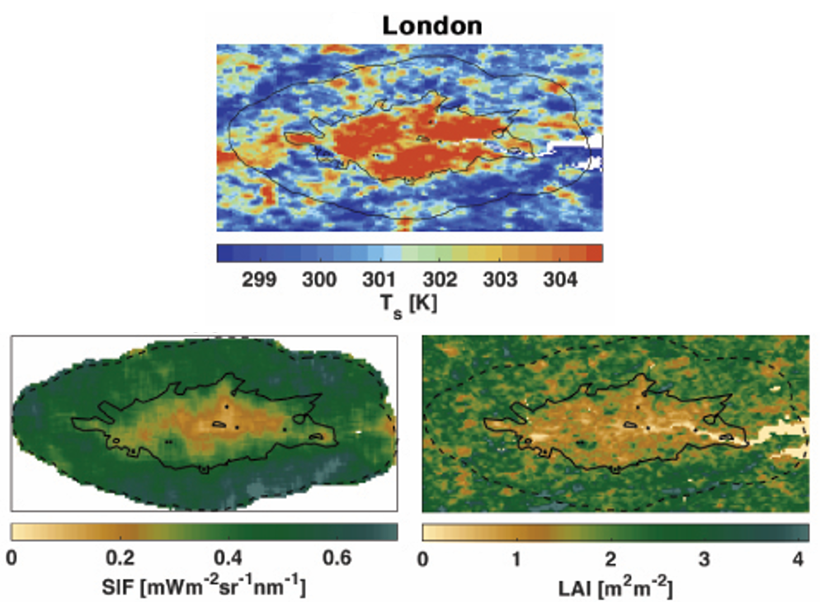
Urban Vegetation Key Regulator for Heat Island Intensity
Satellite data reveals that urban vegetation, especially urban forests, is the most important factor regulating Urban Heat Island intensity.