The Arctic is warming up, but instead of large rivers migrating faster, they’re actually slowing down because of shrubification.
temperature
El hierro está en el centro de este debate de las ciencias de la Tierra
Un nuevo estudio investiga el estado del hierro en el interior del planeta. Los hallazgos tienen repercusiones para comprender la estructura del núcleo interno.
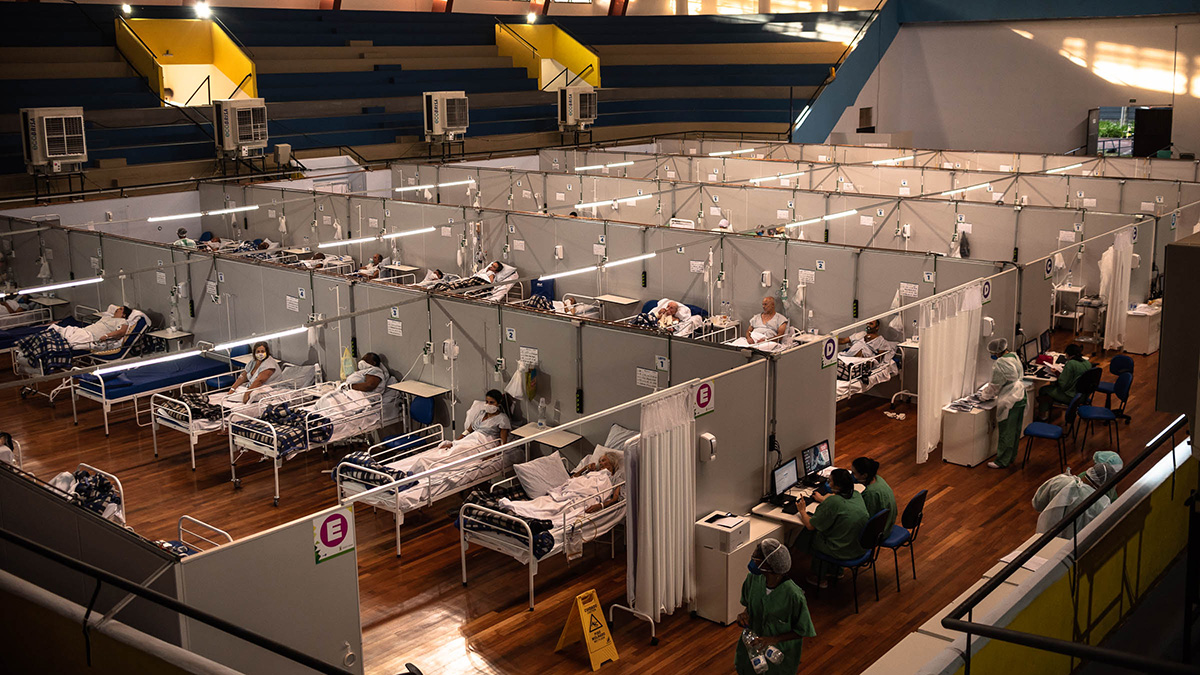
COVID-19 Got You Feeling Under the Weather? Maybe Blame…the Weather
High humidity and low temperature altered COVID-19 spread in Brazil, but only slightly.
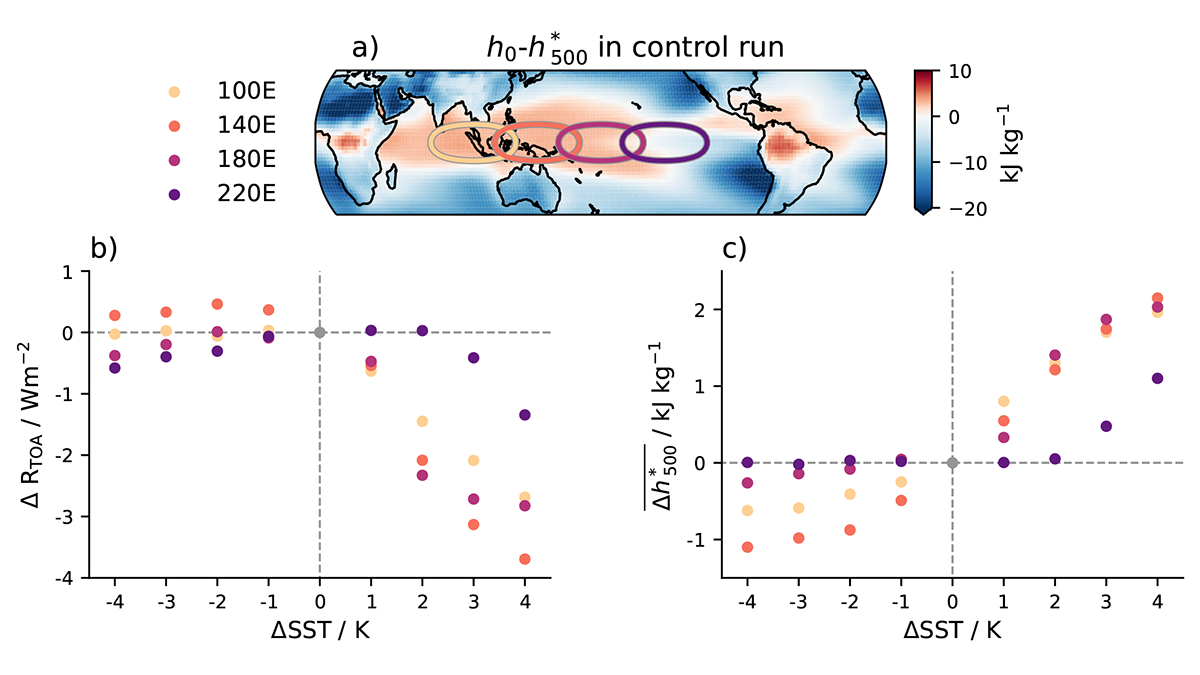
Non-Linear Climate Response to Tropical Sea Surface Temperatures
A new study shows the importance of considering non-linear responses to isolated sea surface temperature (SST) changes and the implications for the linear frameworks used to quantify the SST pattern effect.
Ice Cores Record Long-Ago Seasons in Antarctica
Researchers used ice core data to reconstruct seasonal temperatures throughout the Holocene. The results link especially hot summers with patterns in Earth’s orbit.
Iron Is at the Core of This Earth Science Debate
A new study investigates iron’s form at the planet’s interior. The findings have repercussions for understanding the inner core’s structure.
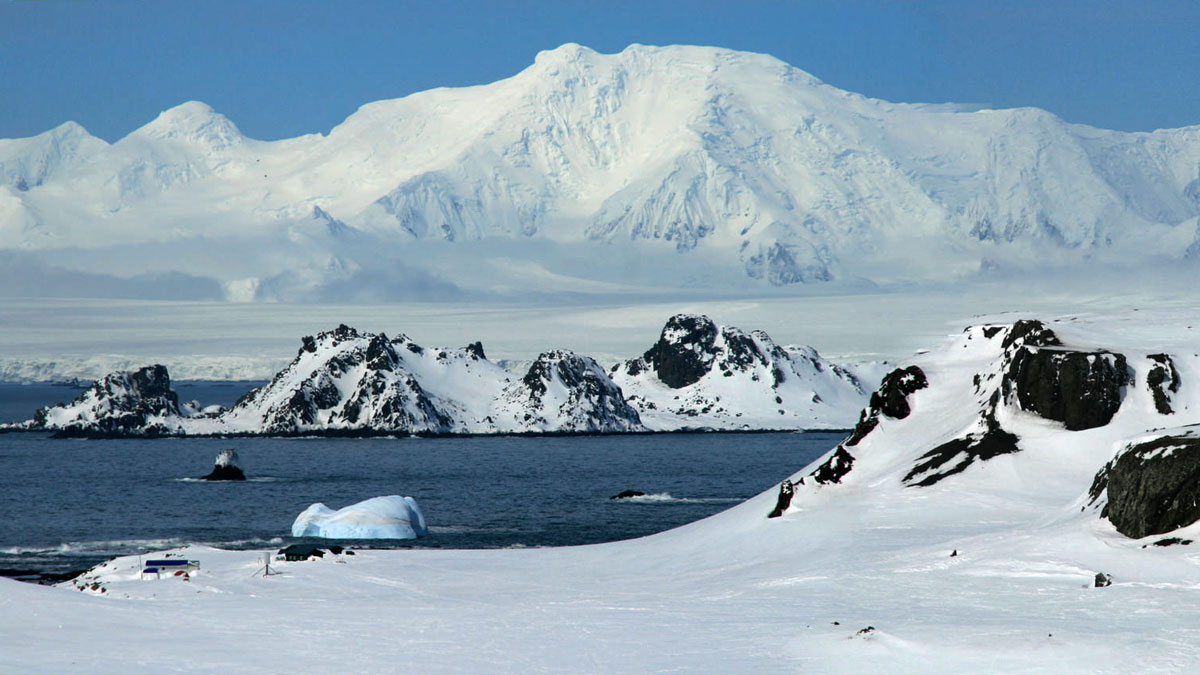
A Deeper Dive into Wintry, Carbon-Absorbing Antarctic Waters
Cold surface water in the Southern Ocean is a critical component in ocean carbon uptake. A new study profiles it using state-of-the-art research techniques.
Silicate Weathering Throttles the Global Thermostat
The natural breakdown of some rocks sucks carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. Knowing how quickly it happens could help scientists engineer solutions to the climate crisis.
Landfall Temperature of Atmospheric Rivers on the US West Coast
Atmospheric rivers that start in warm areas of the North Pacific generally stay warm, leading to warmer landfall temperatures in the western United States.
Ants Aren’t Adapting to Warmer Temperatures
Foraging in hotter-than-desired temperatures could negatively affect ants’ biology and the forest ecosystems that they support.