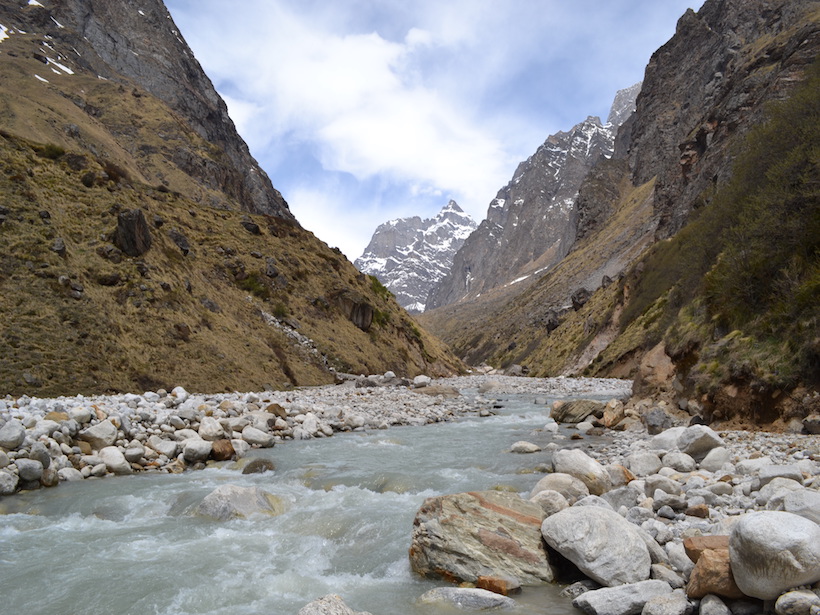
Las muestras de agua de 25 ríos en el centro de Cuba están dominadas por signos de erosión de las rocas en lugar de la escorrentía de fertilizantes, según muestran investigadores que trabajan en instituciones cubanas y estadounidenses.
Water quality
An Unfought Geoscience Battle in U.S. Prisons
Prisoners, activists, and lawyers are fighting to protect incarcerated people from pollution and the dangers of climate change. There’s a place for geoscientists in the fight too.
Biggest Risk to Surface Water After a Wildfire? It’s Complicated
Whether you’re considering short-term or long-term changes to water quality after a wildfire, scientists agree that sedimentation is a big concern.
Tracking Trace Elements in the Ganga River
Levels of dissolved trace and heavy metals, which can be toxic, are highly variable across the river basin, concentrating in urban areas with high pollution but diluted by inflow from tributaries.
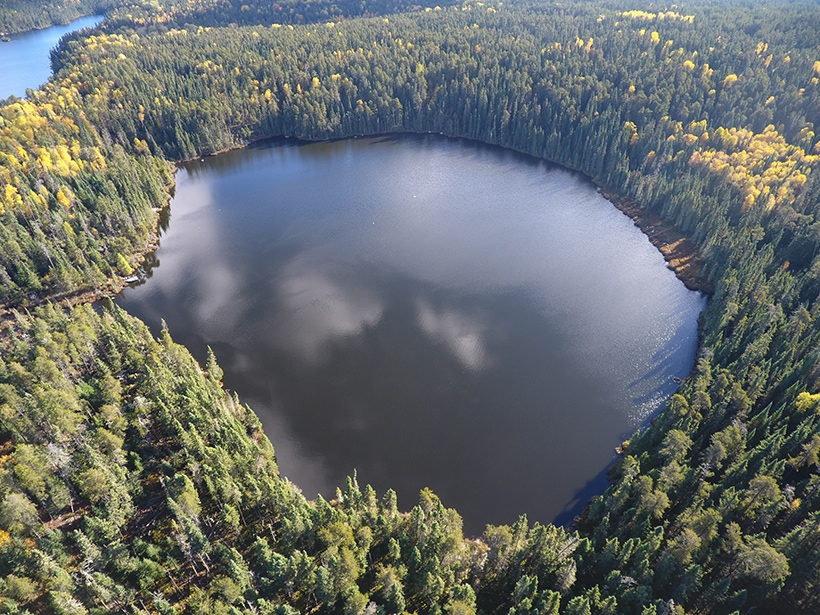
The Lasting Legacy of Phosphorus Buried in Lakes
Research at an experimental lake suggests that phosphorus inputs from runoff may affect the health of aquatic ecosystems long after external additions of the nutrient are reduced.
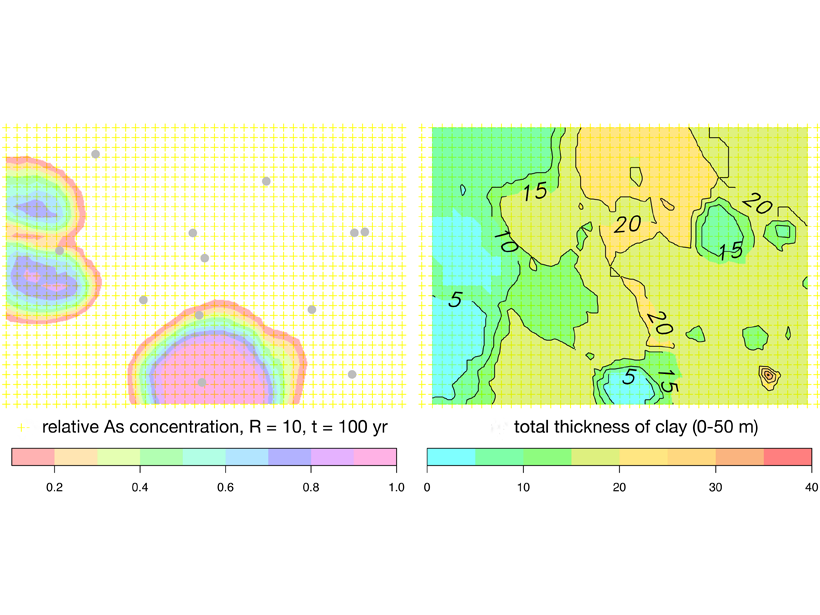
Arsenic Pollution in Bangladesh is Catching Up with Deeper Wells
Inhabitants of Bangladesh have deepened drinking water wells to avoid extracting arsenic-rich groundwater from shallow aquifers, but these may not be free from pollution either.
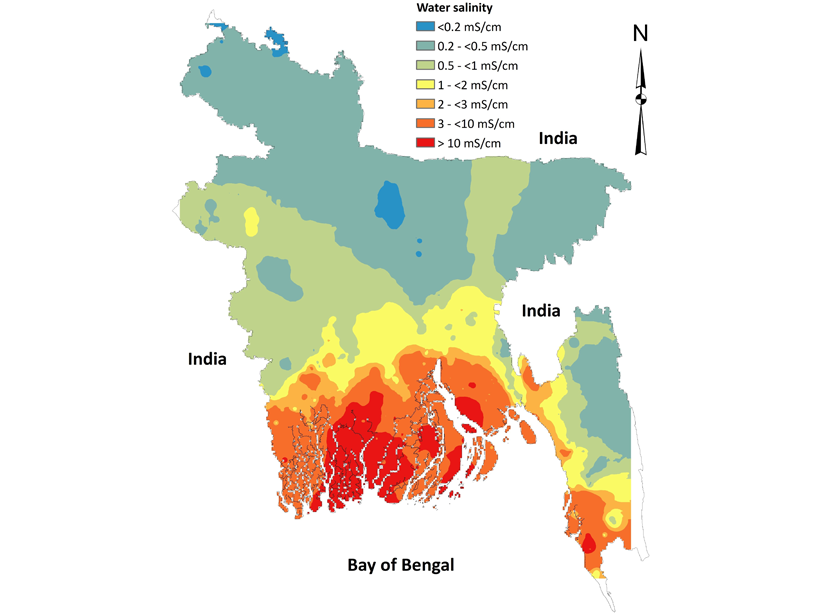
Does Drinking Water Salinity Affect Child Mortality?
An association between drinking water salinity and neonatal and infant mortality in Bangladesh indicates the critical role of water salinity on child health.
AquaSat Gives Water Quality Researchers New Eyes in the Sky
A new data set combining sample data and remote sensing could give scientists the power to make accurate predictions at a global scale.
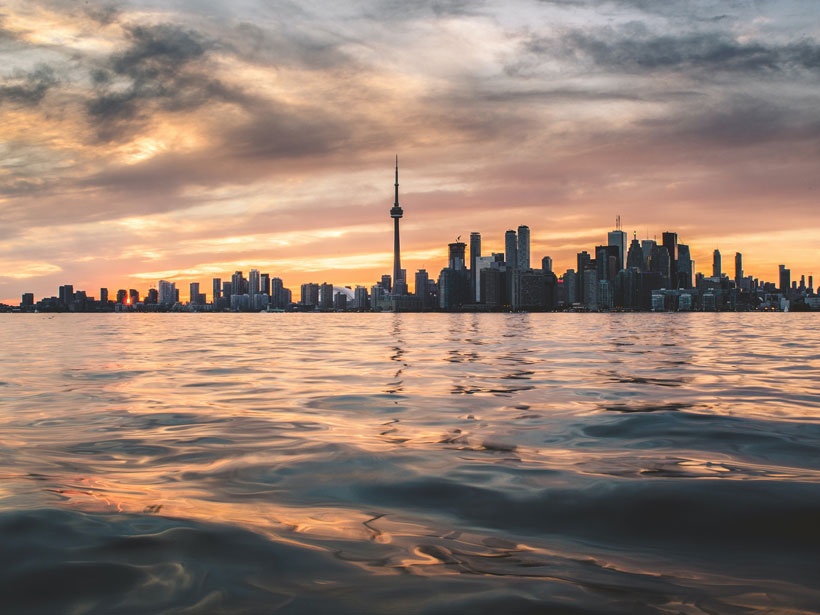
Great Lakes Cities’ Sewer Designs Mean Waste in the Waters
In older cities, a single system of pipes may transport sewage and stormwater runoff. As the climate crisis brings more intense storms, urban areas like Toronto are overhauling their drainage systems.
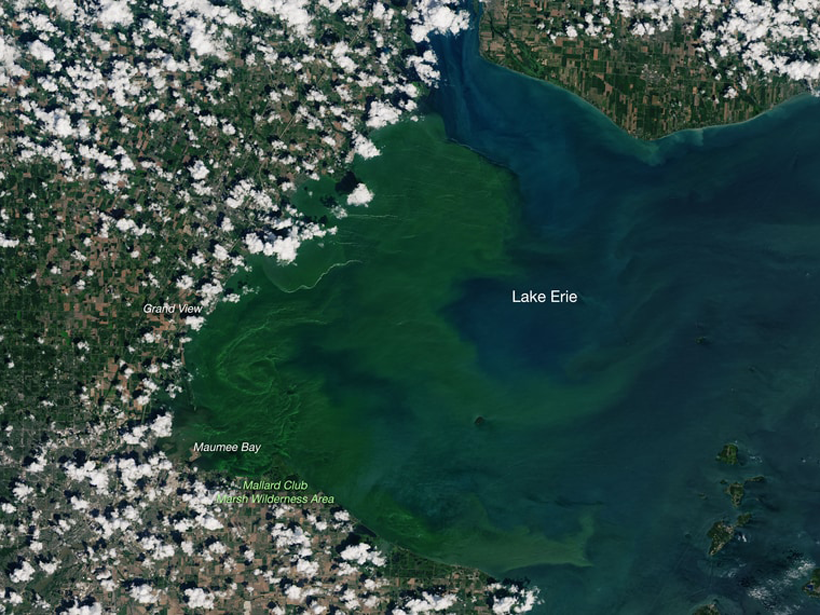
Mapping Nutrient Inputs in the Great Lakes Basin
A new tool links nitrogen and phosphorus applications to land use classifications to better understand where and how much of the nutrients enter watersheds in the U.S. Great Lakes Basin.