Spacecraft observations and model simulations provide new insights into tidal patterns that transport momentum and energy into the planet’s upper atmosphere.
wind
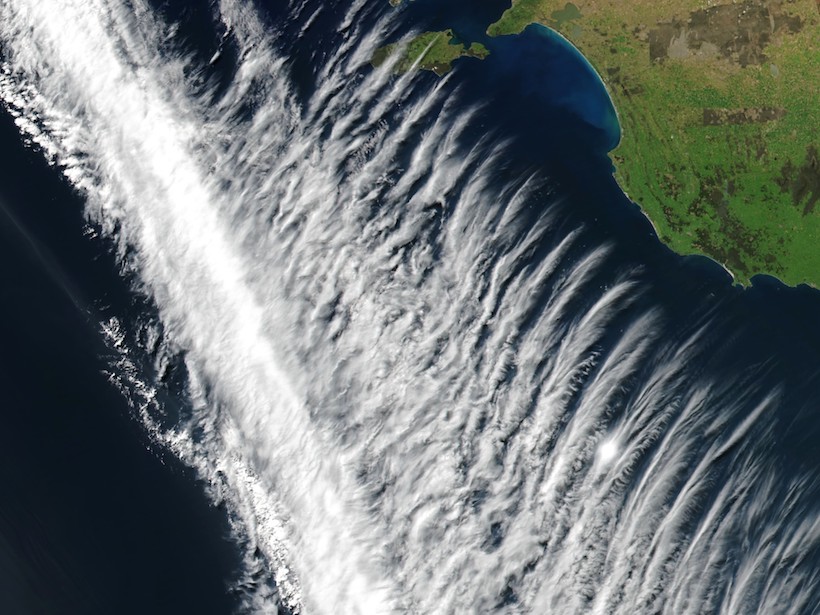
Successfully Simulating Atmospheric Gravity Waves
These waves are key to moving energy from the troposphere to the thermosphere, but until now they haven’t been well described at high altitudes in computer models.
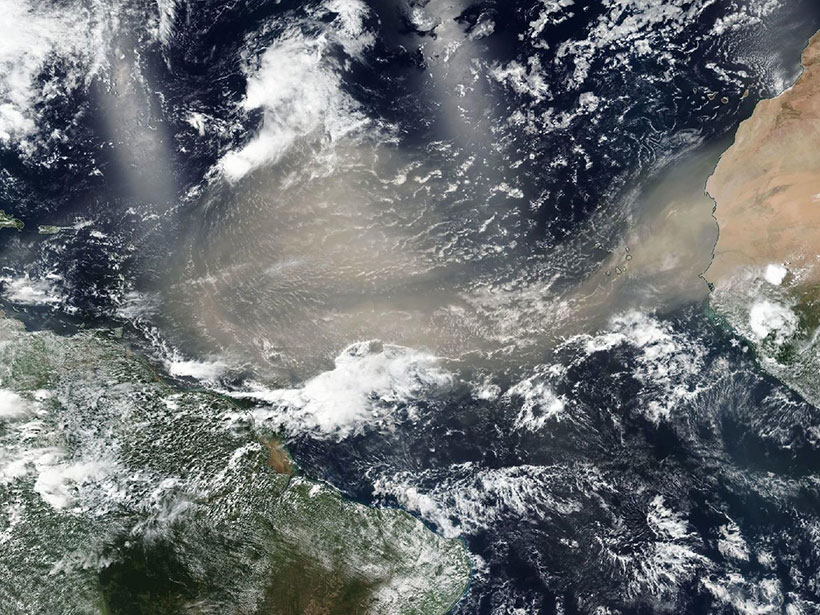
Trans-Atlantic Dusts May Not Enrich Amazon as Much as Thought
New research indicates that nutrient loads delivered to South American ecosystems by dust originating in Africa are far lower than suggested in previous studies.
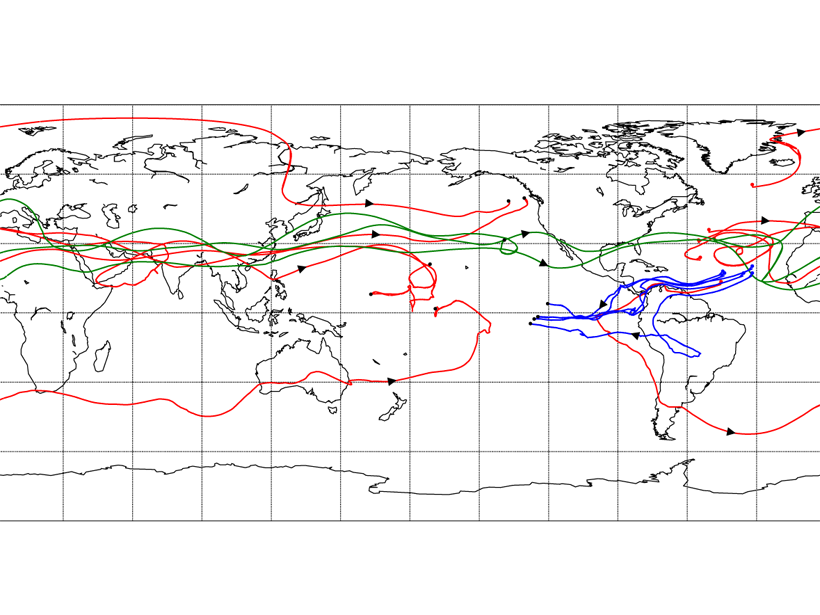
A New Perspective on a Classic Climate Conundrum
The Lagrangian method applied to tracking water transport between the Atlantic and Pacific basins reveals a larger contribution by mid-latitude westerly winds across Eurasia than previously thought.
Megaripple Migration Offers Insights into Martian Atmosphere
The movement of large sand ripples, documented for the first time, suggests Mars is windier than we thought.
Lifting the Veil on Martian Dust Storms
A special collection in JGR Planets presents insights from a long-awaited global dust storm on Mars in 2018 that was closely scrutinized by five orbiting and two landed spacecraft.
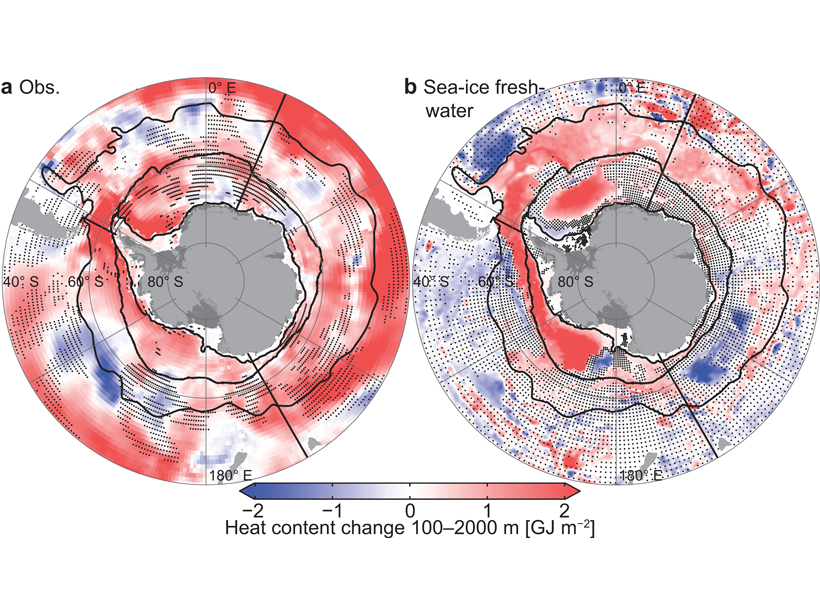
Explaining Cold and Fresh Southern Polar Ocean Surface Waters
Global climate models do not reproduce observed trends of the Southern polar ocean surface, but an increase in wind-transported sea ice that melts and inhibits mixing may account for the disparity.
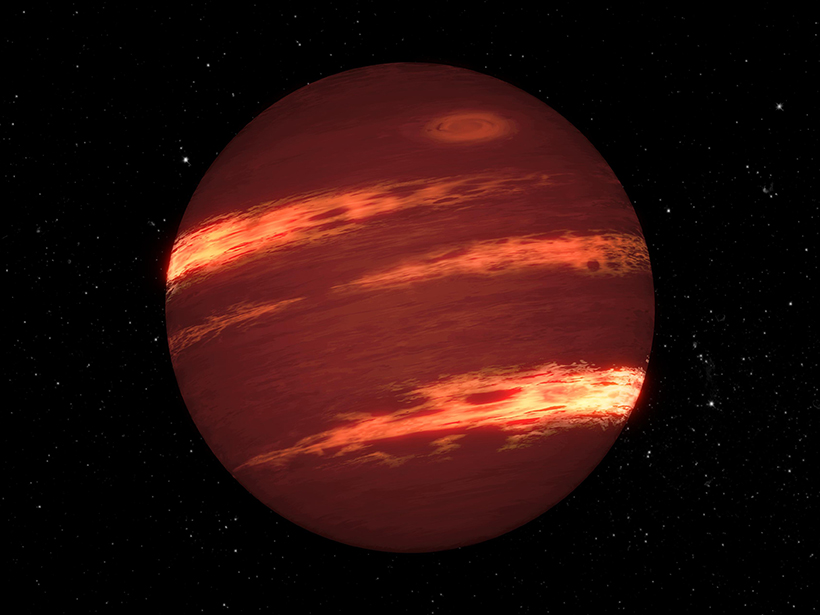
Record-Setting Winds on a Nearby Brown Dwarf
Infrared and radio observations reveal zonal winds moving faster than 2,000 kilometers per hour on a “failed star” in our celestial neighborhood.
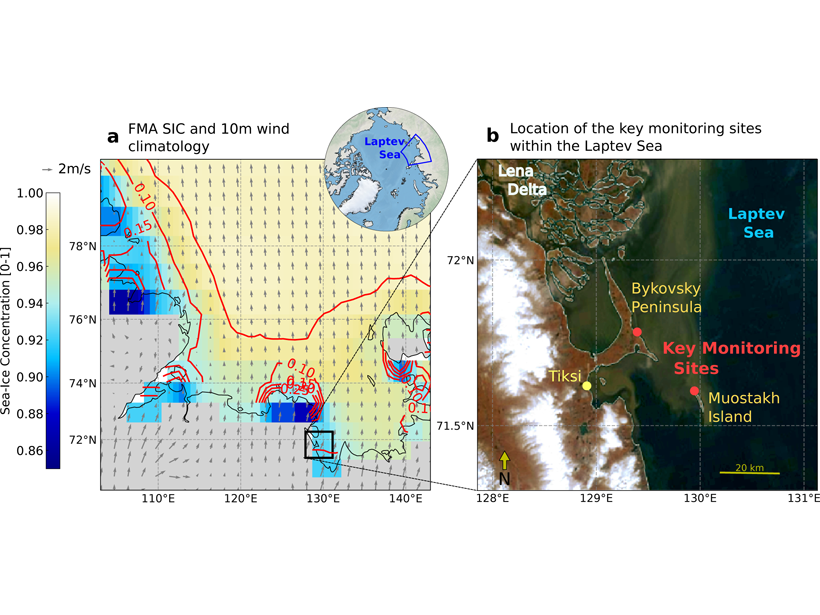
Arctic Coast Erosion Linked to Large-Scale Climate Variability
Changes in rates of Arctic coastal erosion detected from multi-decadal measurements are attributed to the shorter duration in the winter sea ice coverage and large-scale changes in the wind patterns.
Climate Change Is Intensifying Arctic Ocean Currents
Melting ice means that strong Arctic winds create more energetic currents in the Beaufort Gyre.