Solving the case of ocean eddy death could help climate modelers better represent the effect of wind.
wind
Raising Central American Orography Improves Climate Simulation
Elevation of Central American orography significantly reduces the pervasive tropical rainfall bias by blocking the easterlies and consequently warming the northeastern tropical Pacific.
After the Dust Cleared: New Clue on Mars’ Recurring Slope Lineae
An imaging campaign after the 2018 planet-encircling dust storm on Mars revealed a significant increase in detections of enigmatic recurring slope lineae and new insights into how they might form.
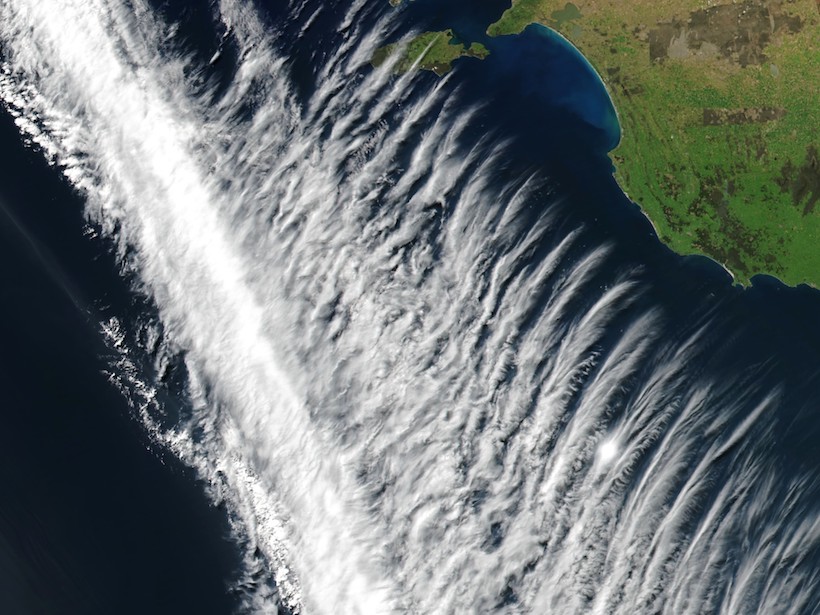
Atmospheric Turbulence May Promote Cloud Droplet Formation
Turbulence causes local variations in relative humidity, which can push particles past a critical saturation threshold for droplet nucleation.
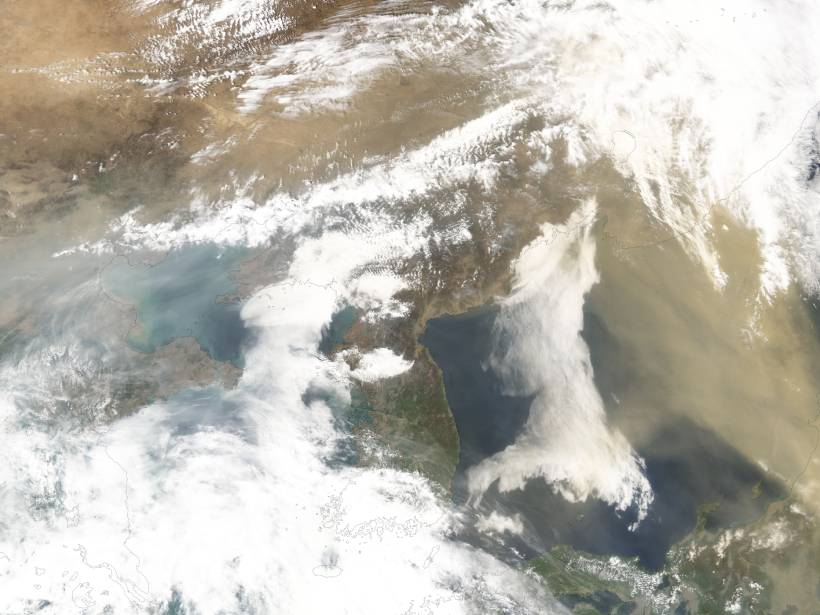
Dust on the Wind
A new study confirms that an important wind system is shifting due to climate change.
Wind Stress is not the Ceiling of Momentum Flux to the Ocean
The ocean is mainly driven by wind stress, but simultaneous observations show that the gain of momentum flux by the ocean can be larger than the wind stress due to the influence of ocean waves.
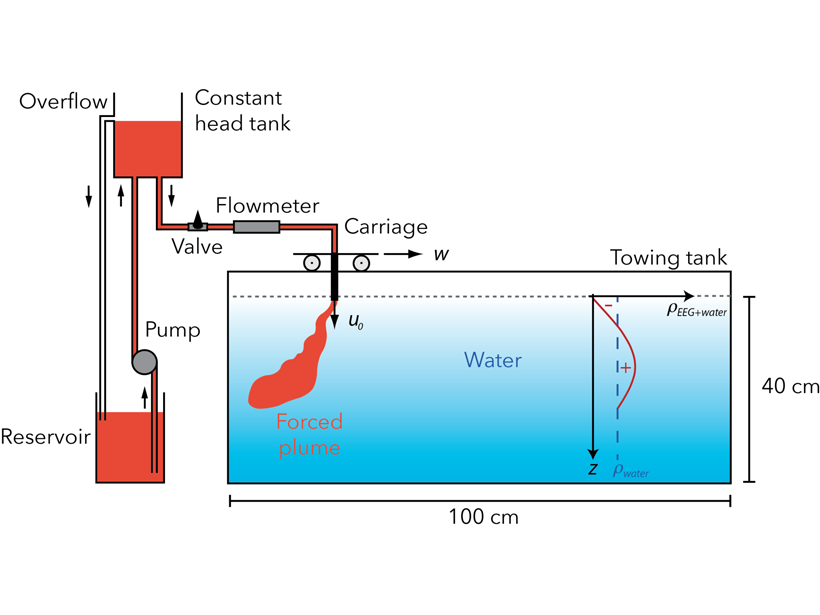
The Importance of Wind for the Fate of Volcanic Eruption Columns
A theoretical model coupled to lab experiments on turbulent jets with reversing buoyancy sheds new light on the role of wind in controlling the dynamics of volcanic eruptive columns.
Post-Tropical Cyclones Influence on European Windstorm Risk
Comparing the importance of midlatitude cyclones and post-tropical cyclones on European windstorms during the Atlantic hurricane season using ERA-5 reanalysis.
Capturing Heat-Driven Atmospheric Tides on Mars
Spacecraft observations and model simulations provide new insights into tidal patterns that transport momentum and energy into the planet’s upper atmosphere.
Successfully Simulating Atmospheric Gravity Waves
These waves are key to moving energy from the troposphere to the thermosphere, but until now they haven’t been well described at high altitudes in computer models.