The discovery of a decadal El Niño–like state associated with shifts in the Pacific trade winds could have important implications for predicting sea level in future decades.
wind
What Drives Surface Winds in a Deep Valley?
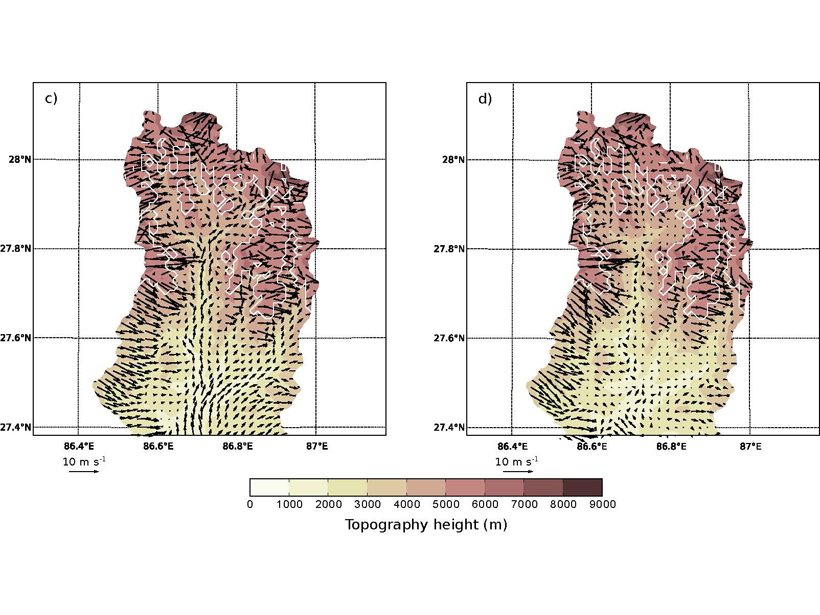
Surface winds in a Himalayan valley are found to vary daily and seasonally due to factors including pressure gradient, advection, turbulent vertical mixing, and the presence of glaciers.
Windy Weather in the Thermosphere
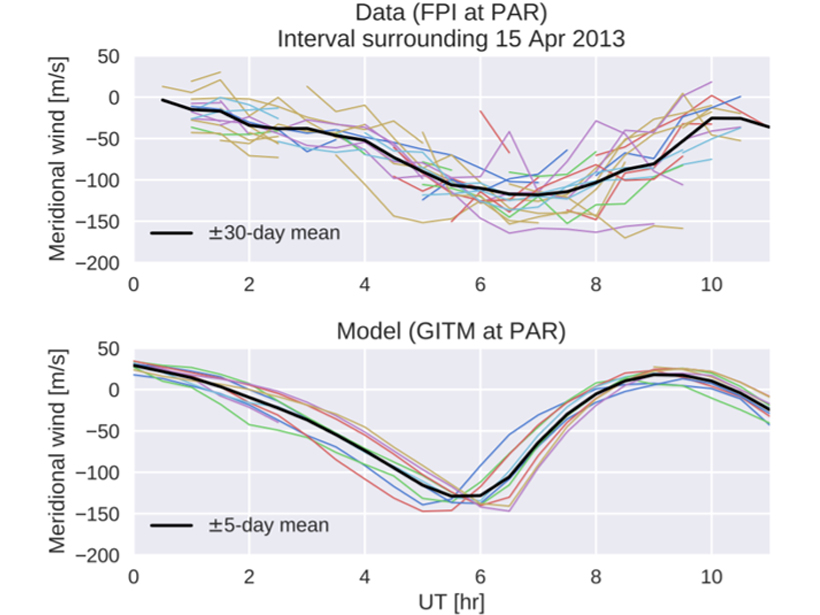
The weather in the thermosphere includes winds that buffet spacecraft as they orbit the Earth, but how well can these winds be modeled?
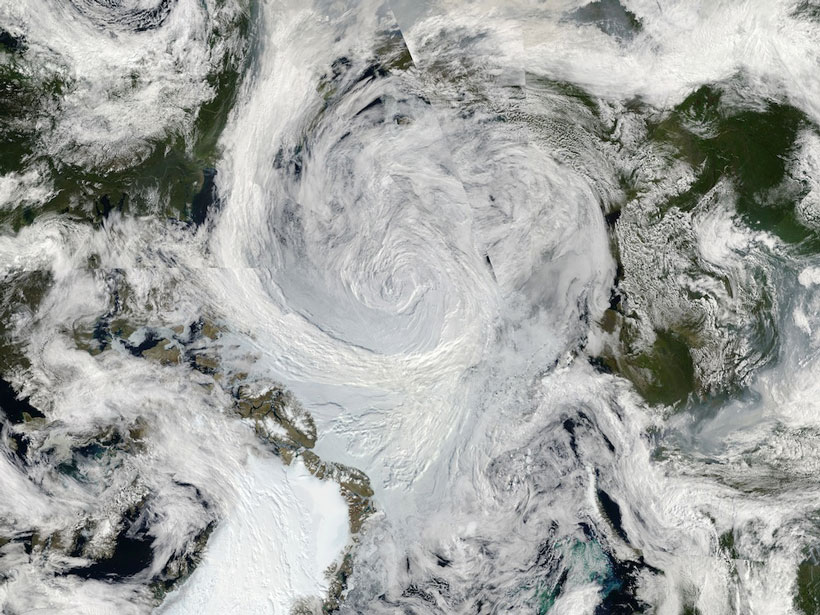
How Arctic Cyclones Change the Sea Ice
Whirlwinds disrupt the sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. Scientists are now beginning to understand how.
How Ningaloo Niño Supercharges the El Niño–Southern Oscillation
The warm current cools the tropical Pacific and strengthens trade winds.
Satellite Observations of Ocean Surface Winds and Currents
Florida State University workshop on Satellite Observations of Ocean Surface Winds & Currents; La Jolla, California, 18–19 May 2018
Eddy Generation in the Central Bay of Bengal
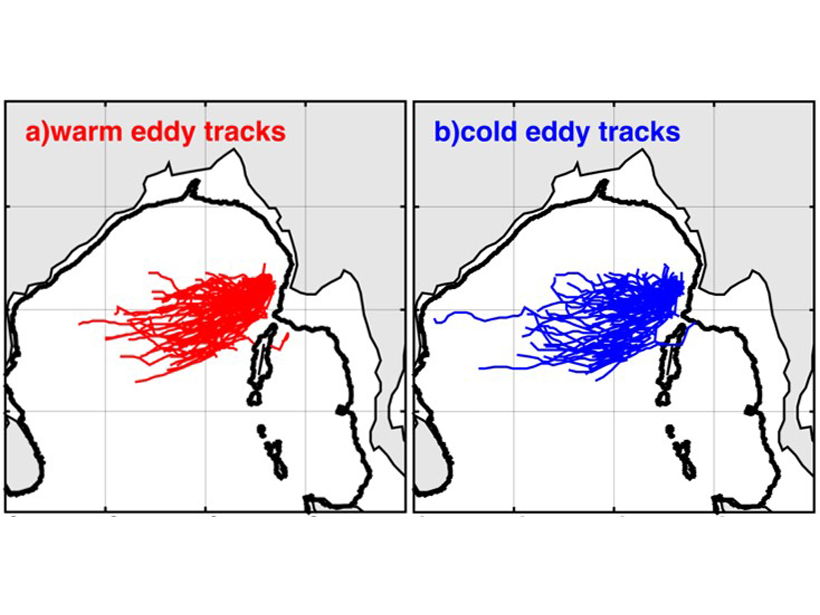
Eddies in the central Bay of Bengal are generated near the eastern boundary of the basin, related to equatorial wind forcing, nonlinearity, and the topographic “bump” of Myanmar.
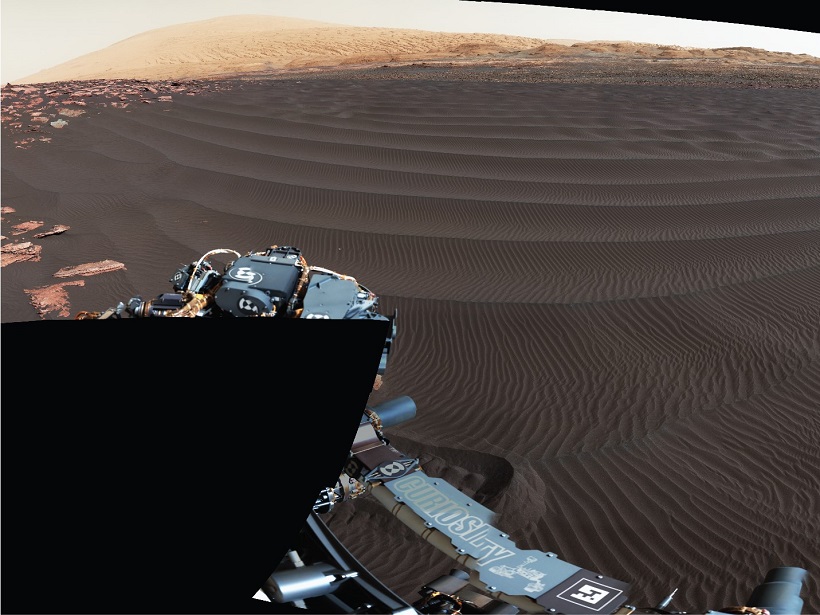
Seeing Mars in a Grain of Sand
The second phase of Curiosity’s campaign at the Bagnold Dunes brought new observations of windblown sands during Mars’s windy season.
Wind Speed Governs Turbulence in Atmospheric Inversions
Measurements made during a field campaign in Idaho indicate that the speed of winds 2 meters above Earth’s surface determines the type of turbulence present in nighttime inversions.
High-Altitude “Wind Walls” Discovered near Magnetic Poles
Satellite imaging reveals two narrow channels of extreme winds surrounded by gentle opposing flow 140–250 kilometers above sea level.