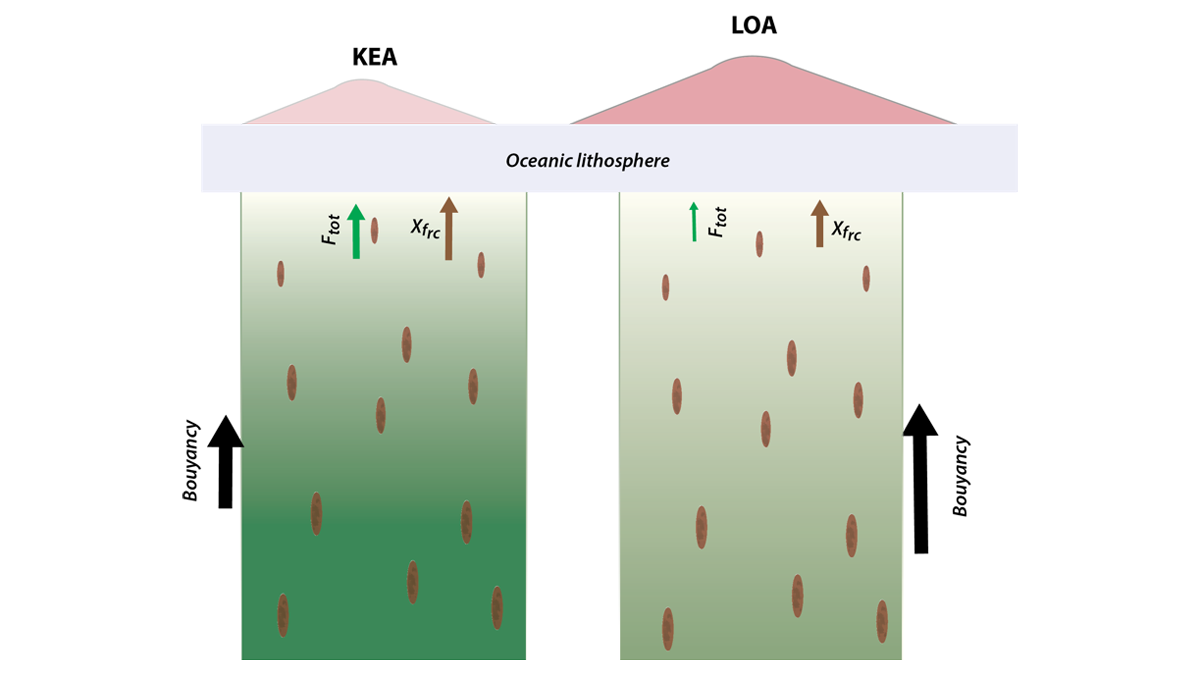
The source for the isotopically-enriched Hawaiian magmas contains peridotites that experienced near-surface melting prior incorporation in the plume.
Editors’ Highlights
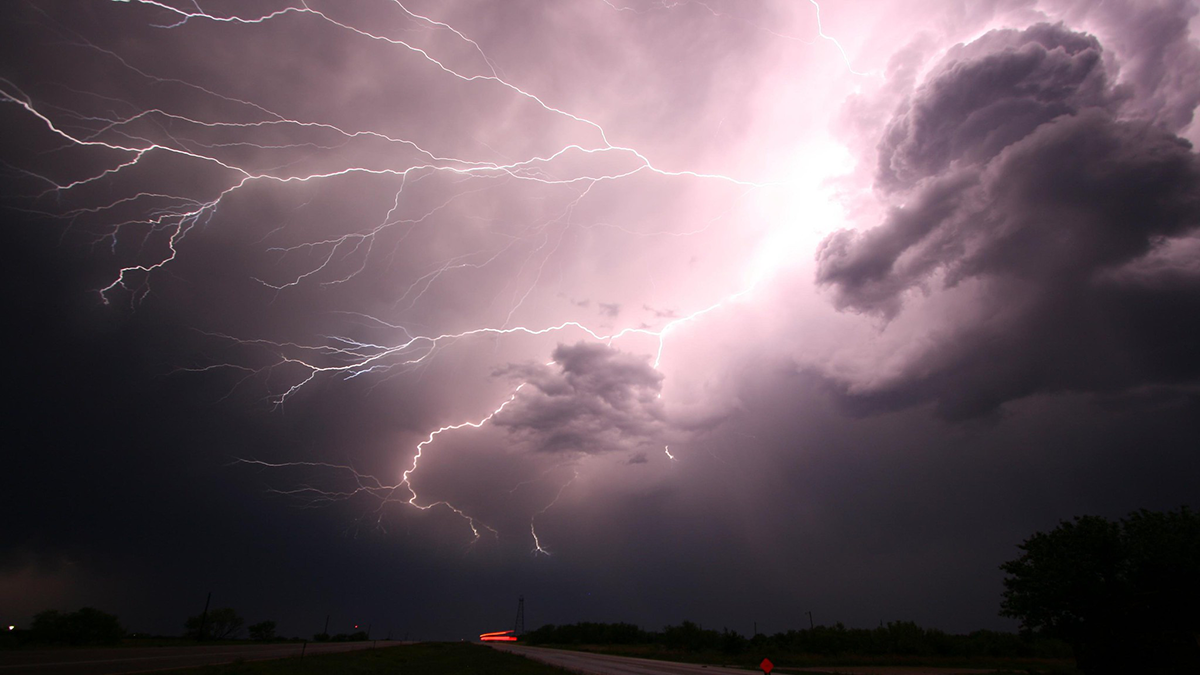
Rapid Thunderstorm Charging Produces Strong Gamma‐Ray Glows
A new study explains how thunderstorm electric fields produce strong gamma‐ray glows with oscillating gamma‐ray rates, and that these oscillations develop into intense pulse trains that closely resemble terrestrial gamma-ray flashes.
The Complex Evolution of Debris-Covered Glacier Surfaces
A first look at how the surfaces of debris-covered glaciers evolve over time from six years of drone surveys in the Nepal Himalaya.
Carbon-Nutrient Ratios Drive Nitrate Removal in Mediterranean Streams
The type of organic matter, and ratio of nutrients to carbon, impact the ability of heterotrophic bacteria to effectively remove certain forms of nitrogen pollution (nitrate) from streams.
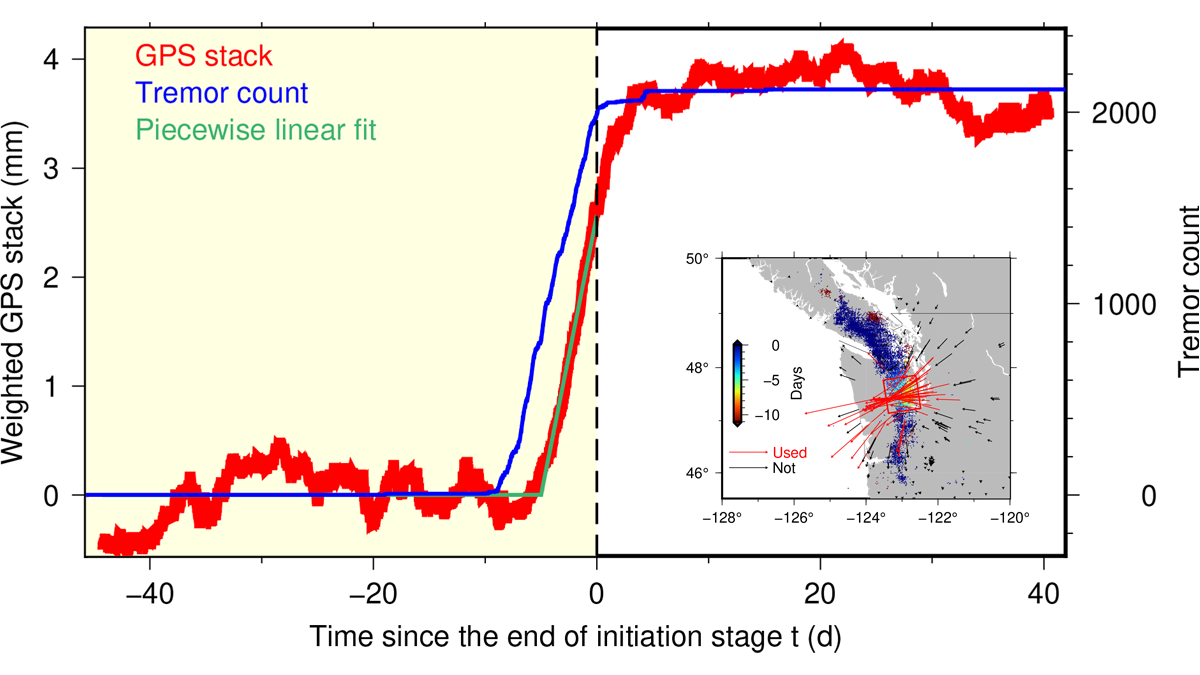
How (Slow) Earthquakes Get Going
Non-volcanic tremor ramp up precedes slow slip in Cascadia by about a day, indicating that brittle-creeping process interactions control nucleation.
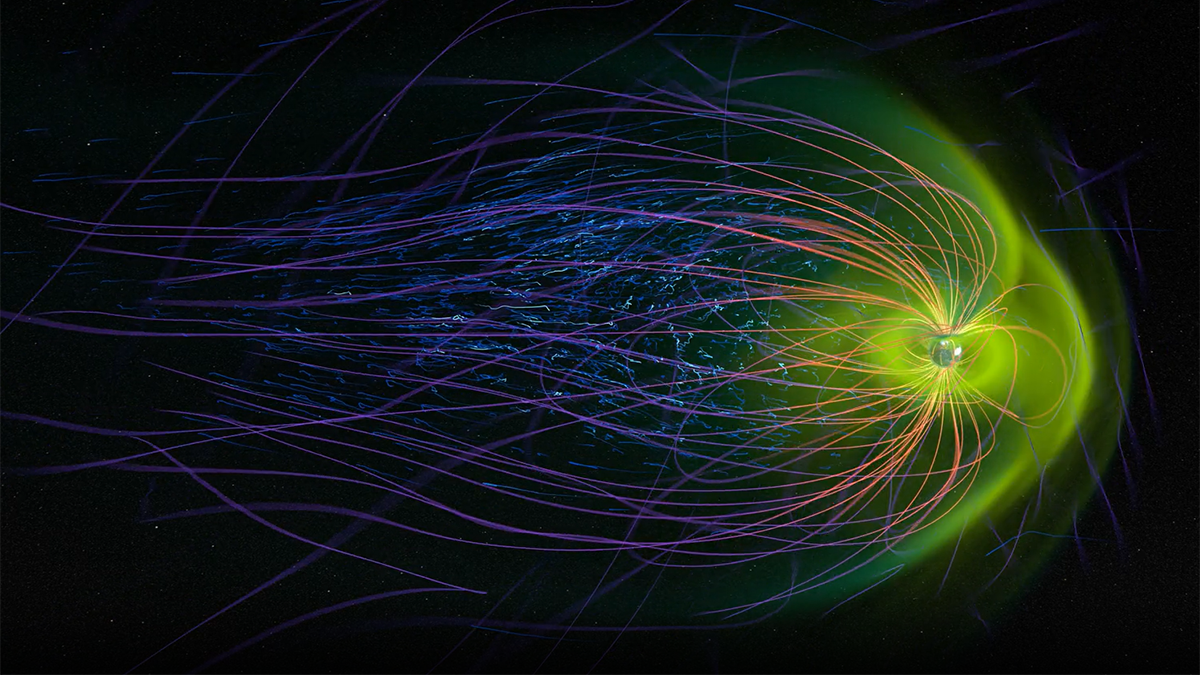
Explaining Mars’ Mysteriously Magnetic Crust
Fluid-rock interactions on ancient Mars may have produced abundant magnetic minerals that preserved unusually intense records of the planet’s now-extinct magnetic field.
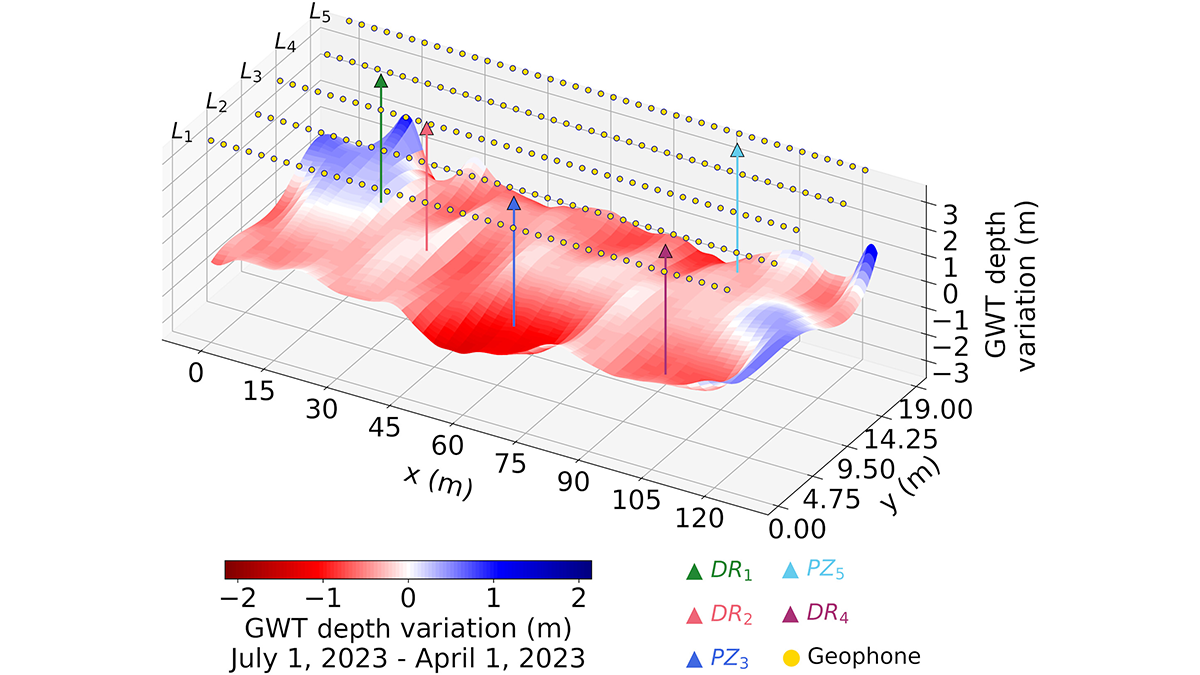
Listening to Groundwater Dynamics
Deep learning from shallow passive seismic data reveals groundwater table depth information in space and time.
Ionospheric Changes Following the Geomagnetic Storm of May 2024
A new study finds that unique ionospheric changes occurred in the upper atmosphere in response to the May 2024 geomagnetic superstorm.
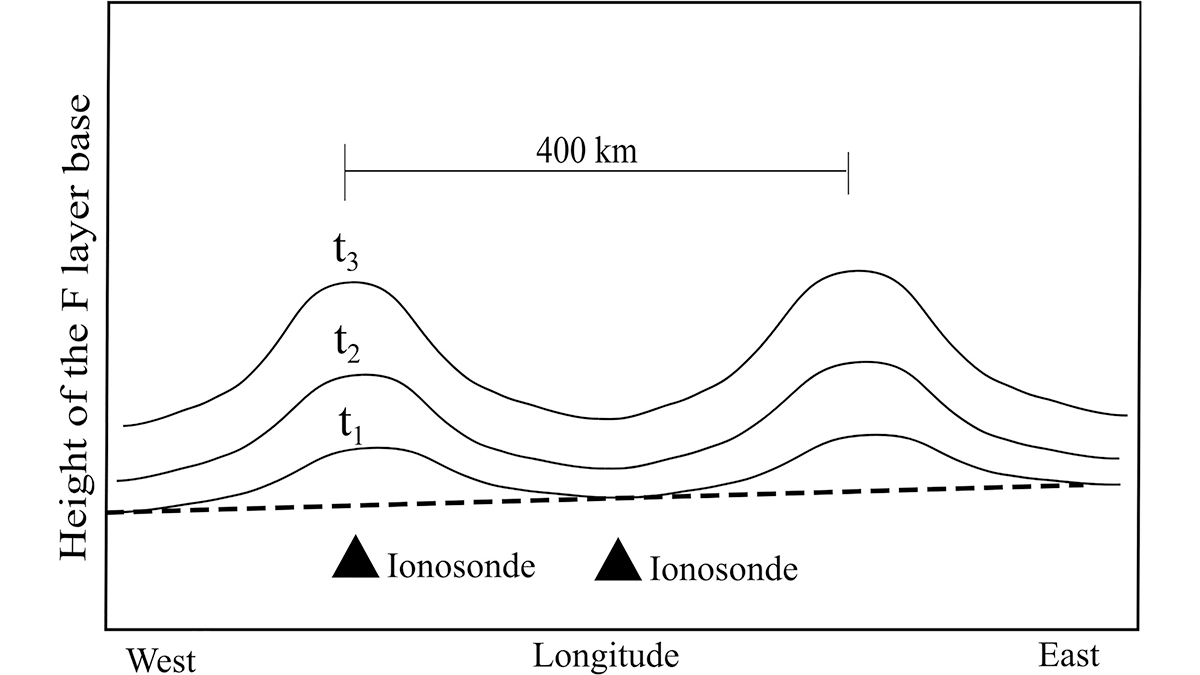
Prediction of Equatorial Plasma Bubbles for Navigation and Communication
Scientists demonstrate a new technique to predict the formation of equatorial plasma bubbles, a crucial space weather phenomenon affecting satellite-based communication and navigation systems.
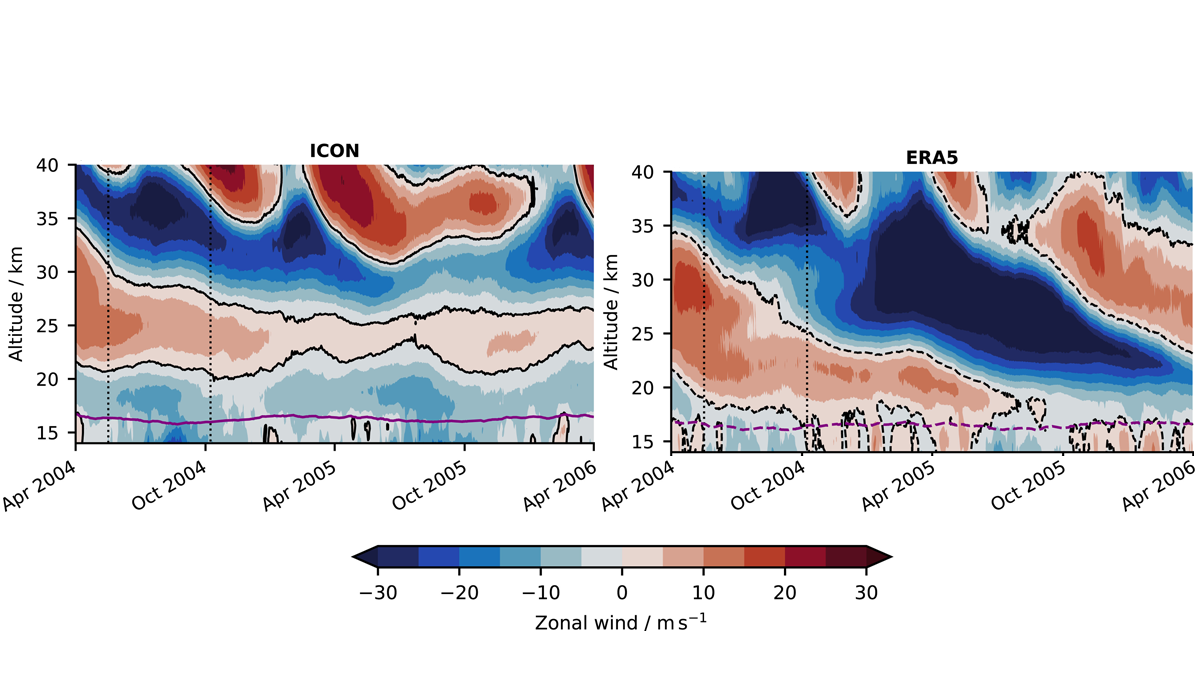
Simulating a Unique Wind System in a Kilometer-Scale Model
A new study shows that a kilometer-scale model can directly simulate aspects of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation.