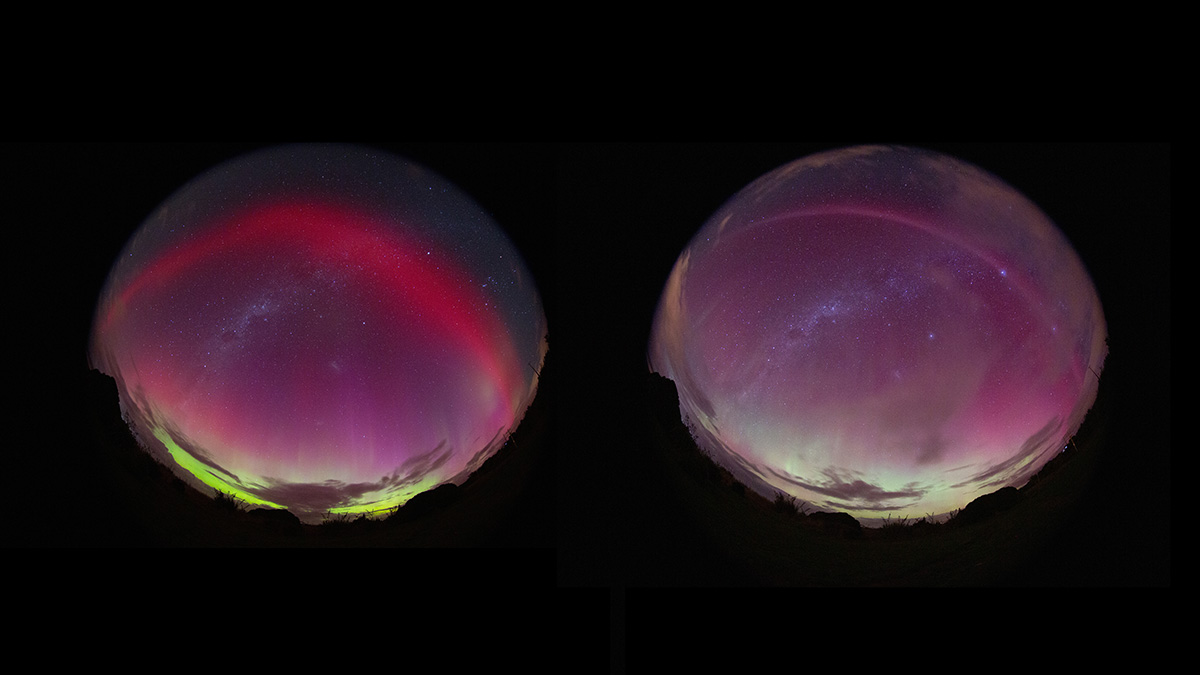
A new study reports the first observation of a stable auroral red arc evolving into a strong thermal emission velocity enhancement during a geomagnetic storm.
Alexandra K. Scammell
COPY joined Eos as the associate editor in 2021 after more than 5 years working at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) as a writer and associate editor. She has a M.A. in science writing from Johns Hopkins University and a B.A. in communications from the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences at Cornell University.
Los efectos del cambio climático en las tasas de suicidio en los EE.UU.
La incidencia del suicidio podría incrementarse hasta a 1660 casos anuales, dependiendo de qué tanto cambie el clima.
The Effects of Climate Change on U.S. Suicide Rates
Suicide incidence could increase by up to 1,660 cases annually, depending on how much the climate changes.
Kimberley Miner: Preserving Earth’s Biodiversity and Integrity
From Antarctica to the Arctic, Miner’s career as a climate scientist has taken her to Earth’s frozen areas to study the effects of climate change.
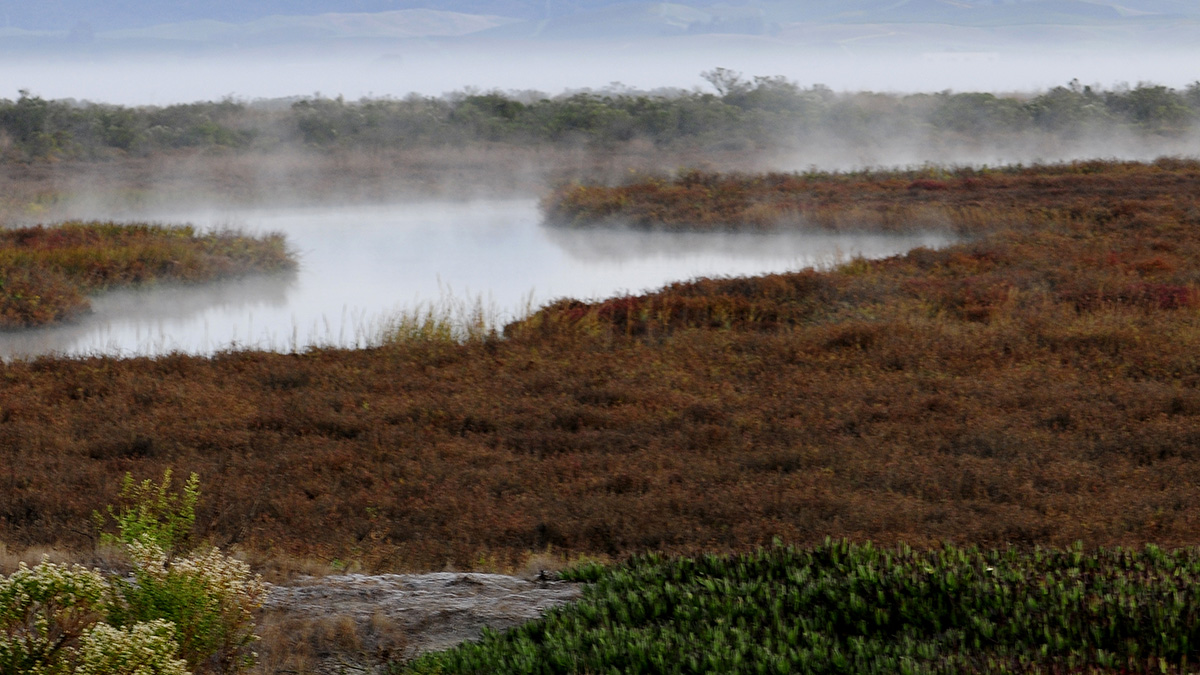
Atmospheric Rivers Help Coastal Wetlands Build Up Sediment
Accounting for these storms and flooding can help experts predict and respond to rising sea levels.
Hidden Upwelling Systems May Be Overlooked Branches of Ocean Circulation
New research suggests that overlooked upwelling systems in western boundary currents play a role in transporting nutrients, carbon, and heat in the global ocean.
A Simple Model Predicts Household Lead Exposure Risk
Using both sample data and crowdsourced science, a new model effectively identified houses at risk for higher concentrations of lead.
Air Pollution Poses Inequitable Health Risks in Washington, D.C.
Certain health risks are greatest in neighborhoods with higher proportions of people of color and lower levels of income and education.