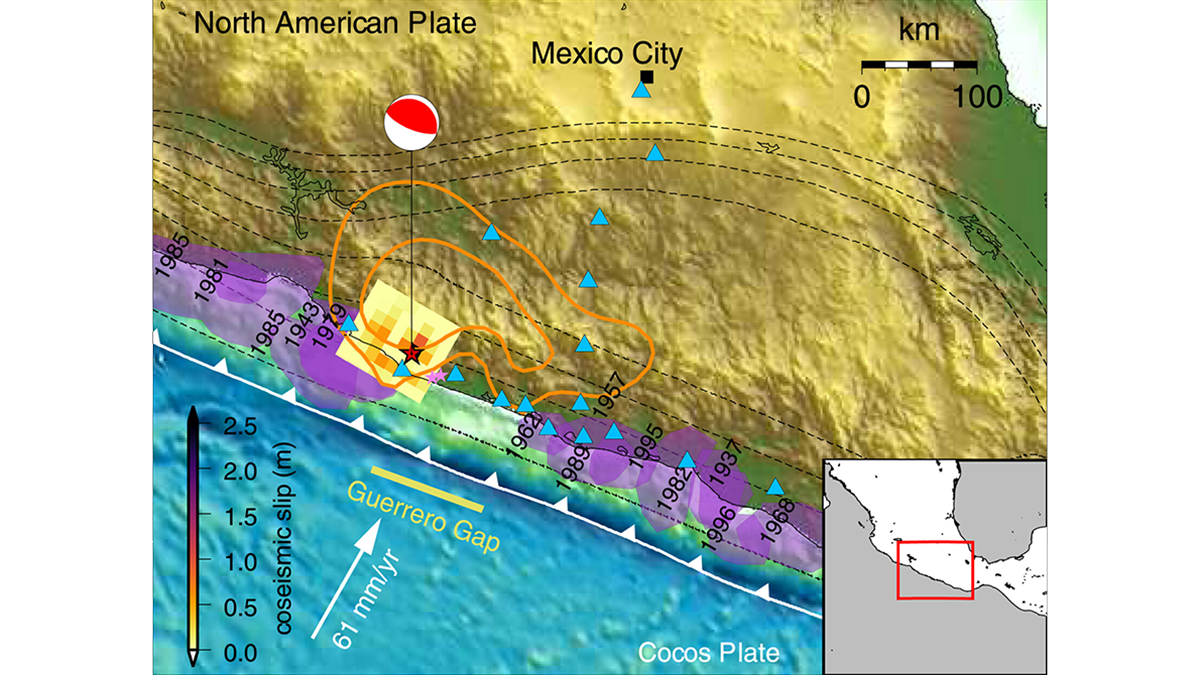
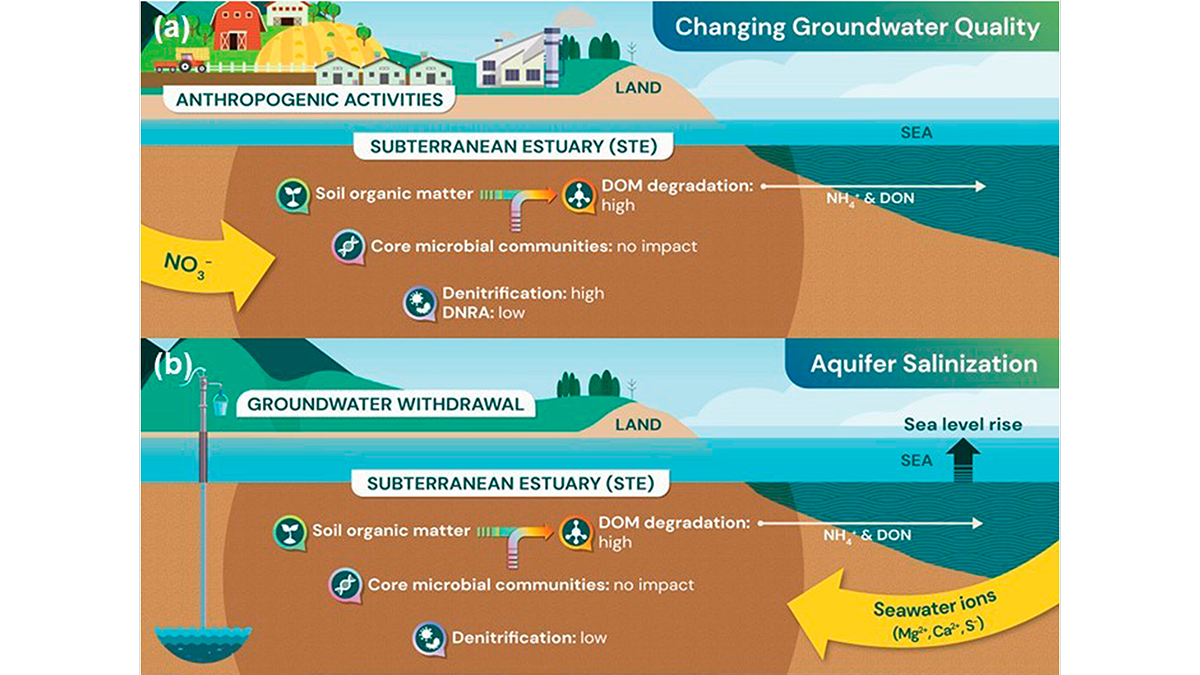
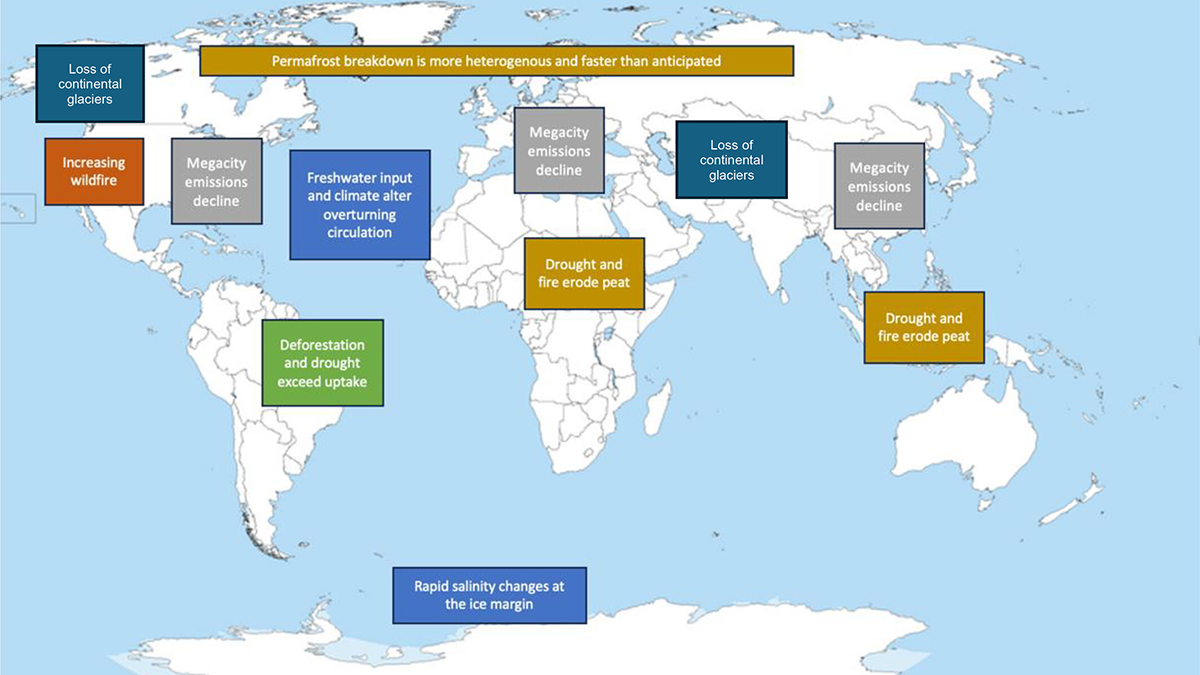
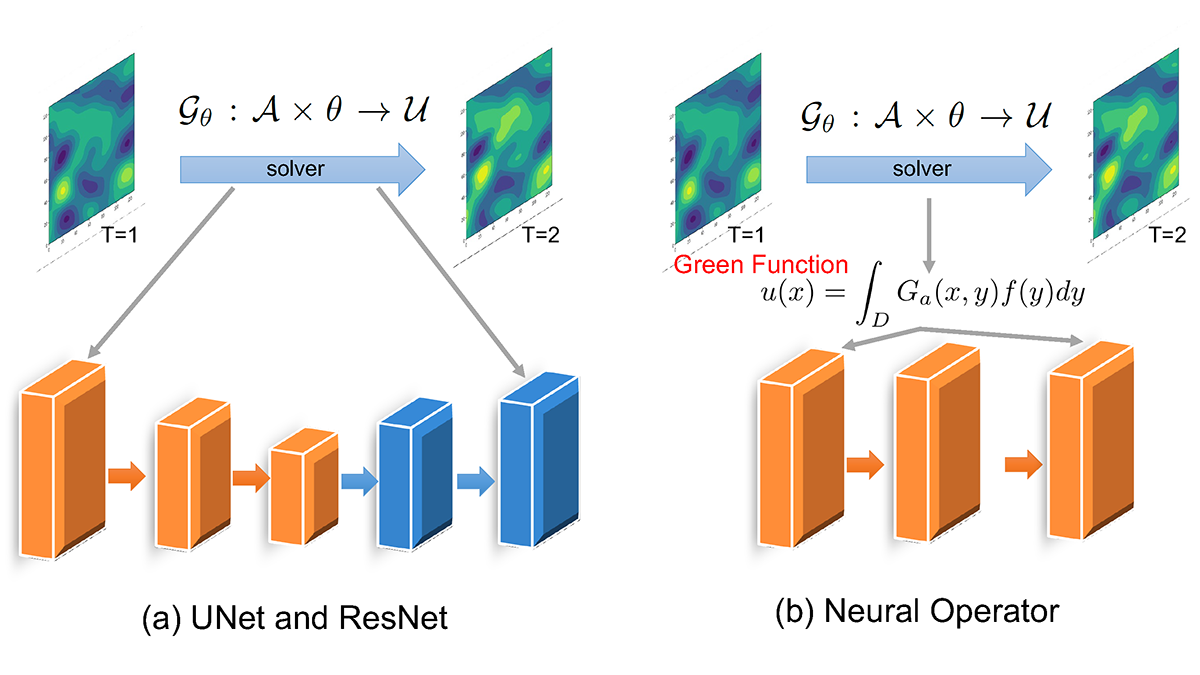
A new generation of physics-based models that integrate temporal slip evolution over decades to seconds opens new possibilities for understanding how large subduction zone earthquakes occur.
Editors’ Highlights
The Unexplored Microbial Life in Subterranean Estuaries
A new study reveals that microbial life in subterranean estuaries is threatened by anthropogenic activities.
How Earthquakes Grow from a Tiny Fracture to a Catastrophic Event
State-of-art numerical simulations illustrate how a small-scale shear instability can become a giant earthquake in a manner that is consistent with seismological observation.
Framing the Next Decadal Survey for a Warming World
The next decadal survey (DS28) will be framed by a rapidly changing world, and will be critical to consider observational needs of the 2030s-2040s, a world increasingly dominated by climate extremes.
What’s Hot in Iceland? A Close Up View of Hotspot-Ridge Interaction
New seafloor magnetic data help scientists retrace the evolution of the Reykjanes Ridge, lending insights into the effects of a mantle plume on mid-ocean ridge organization and evolution.
Machine Learning Accelerates the Simulation of Dynamical Fields
Fourier neural operator solvers accurately emulate particle-resolved direct numerical simulations and significantly reduce the computational time by two orders of magnitude.
Where and How Sea-Level Rise Threatens Coastal Areas and Communities
To better understand how sea-level rise threatens coastal areas, scientists propose a new indicator to estimate the risk of coastal flooding under climate change.
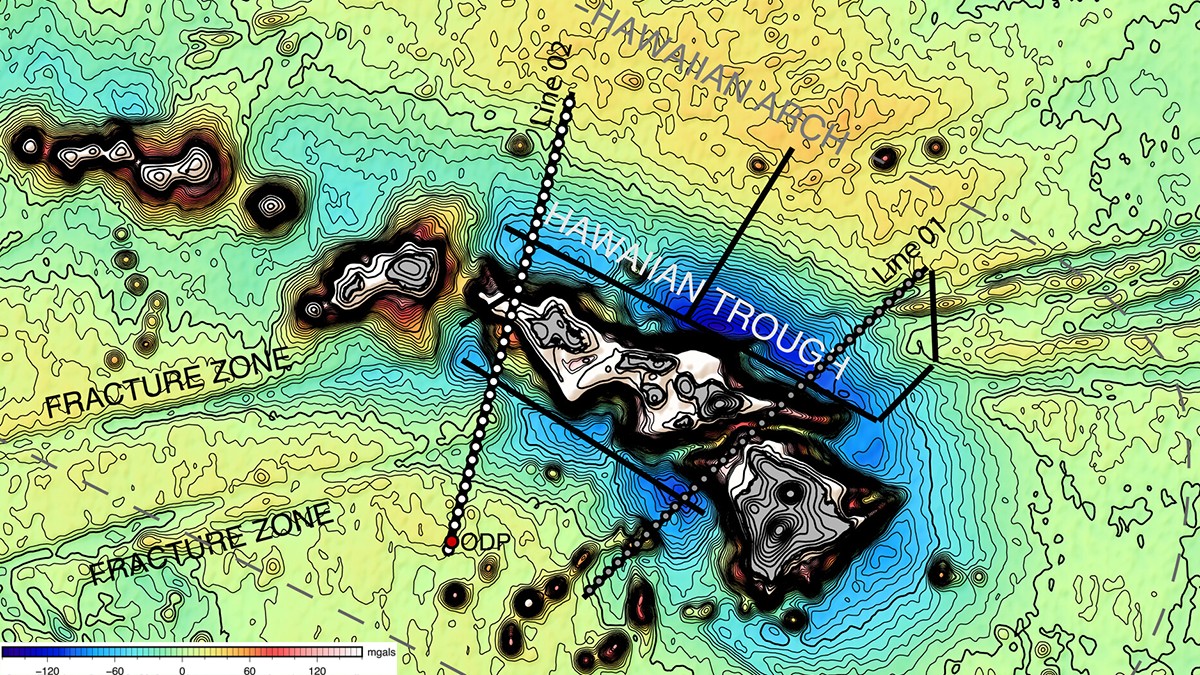
A Strong Pacific Plate Bends Under the Hawaiian Volcanic Chain
Two seismic studies reveal the volcanic loads and resulting flexure of the Pacific plate at the Hawaiian Ridge and, surprisingly, show no magmatic underplating.
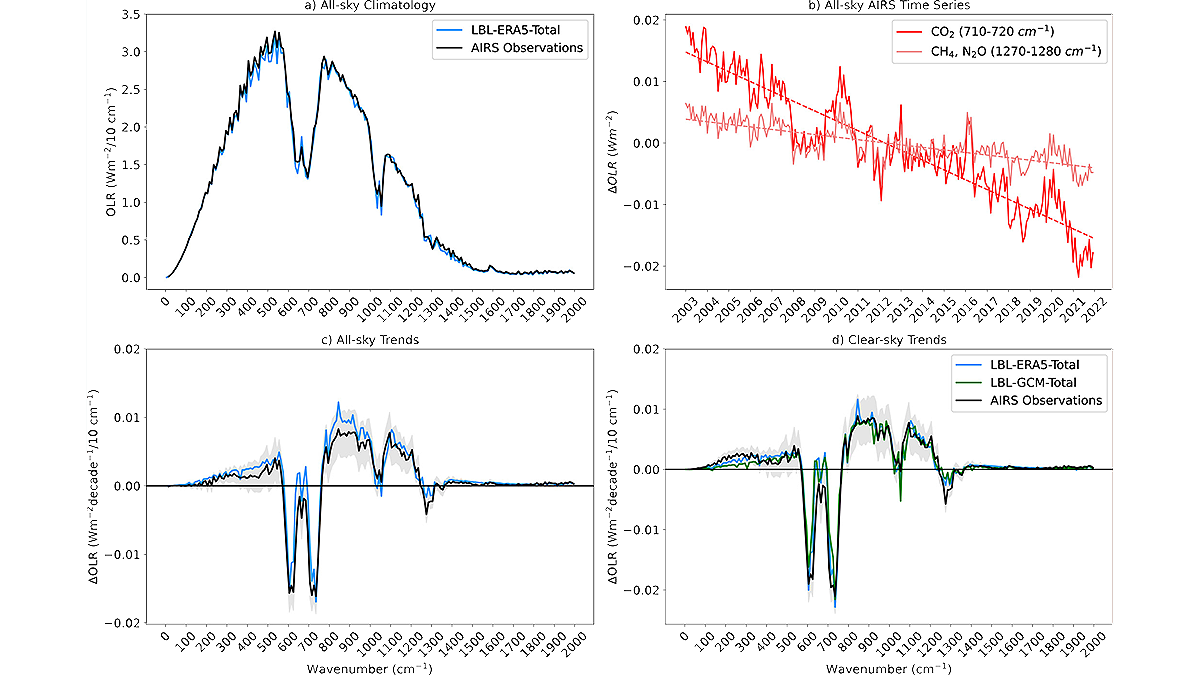
Using Satellite Observations for Attribution of Radiation Changes
Analysis of infrared satellite measurements identifies the climate response to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Speed of Ice Shelf Rifting Controlled by Ocean-Ice Interactions
Scientists report the fastest rate of rift extension yet observed for an Antarctic floating ice shelf and explain why it is far slower than rates expected for brittle ice deformation.