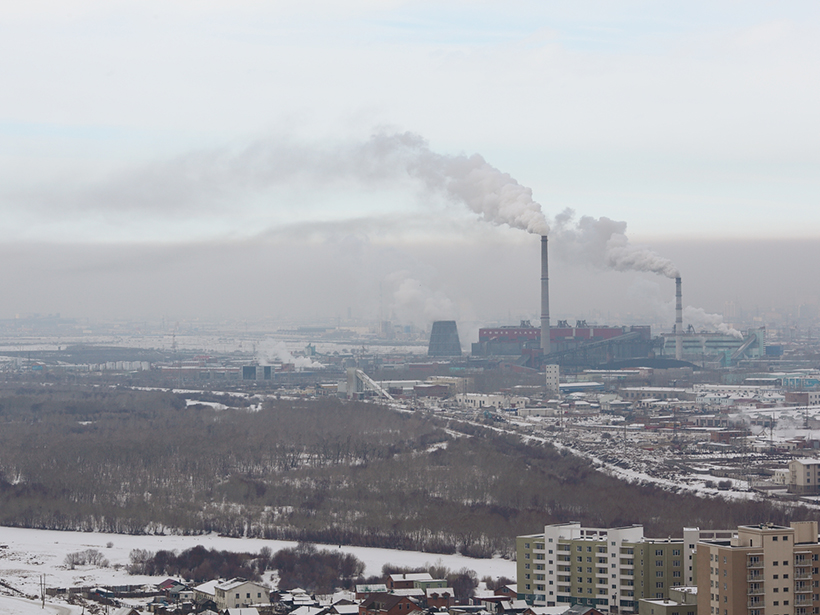
How a husband-and-wife team created the world's first open access, open source international air quality data hub—a global resource for health organizations, policy makers, and others.
CC BY-NC-ND 2016
Carbon Dioxide Frost May Keep Martian Soil Dusty
Temperature readings acquired from orbit show that Mars's surface gets cold enough at night to allow layers of solid carbon dioxide frost up to several hundred micrometers thick to build up near the equator.
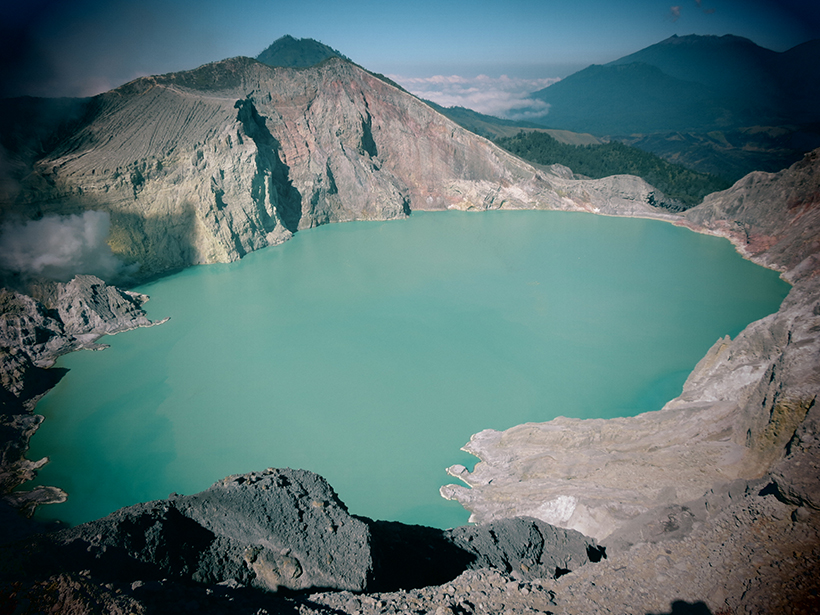
A New Tool to Better Forecast Volcanic Unrest
In a retrospective study of volcanic unrest at Indonesia's Kawah Ijen, a new model was able to pick up on the rising probability of eruption 2 months before authorities were aware of the risk.
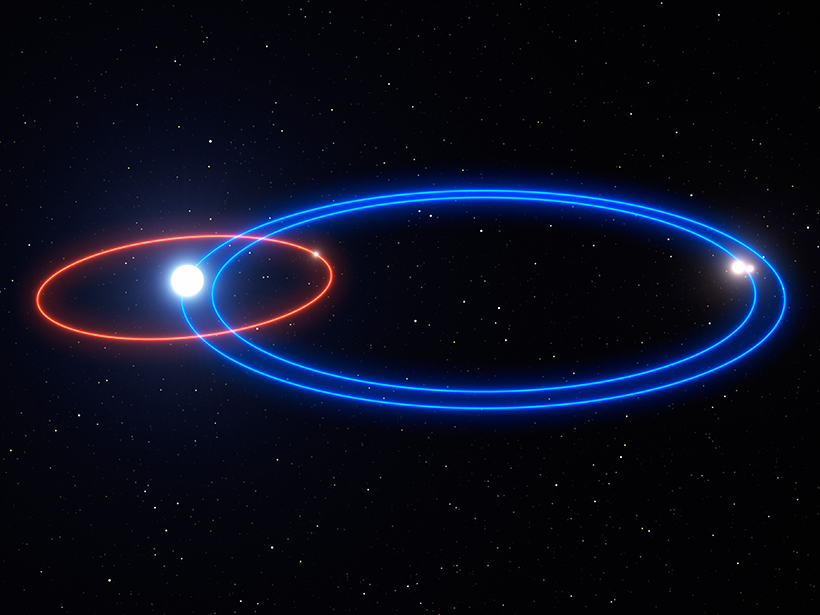
Exoplanet Found in Curious Triple-Star System
The newly discovered planet balances precariously in orbit within the star system, puzzling scientists.
Integrated Marine Research for Sustainable Ocean Development
Sustainable Ocean Development—A Perspective from Former, Current and Future Kiel Marine Scientists; New York, 28–30 September 2015
Former Academy Head Predicts Few Obstacles for Female Successor
Prior to retiring last week as president of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, Ralph Cicerone said the academy is ready for its new leader to be a woman and a younger person.
Juno Spacecraft Nails Its Orbit Around Jupiter
The mission will spend 20 months collecting data on the planet's core, its magnetic field, and the composition of its atmosphere.
Arctic Survey Hunts for Missing Nitrogen and Phosphorus
A new survey of ocean waters flowing in and out of the Arctic may shed light on how dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus contribute to nutrient cycling in the Arctic.
Telica Volcano Rested Quietly Right Before Spewing Ash
The length of quiet periods predicts the severity of eruption events, according to a new model that might soon help forecast explosions worldwide.
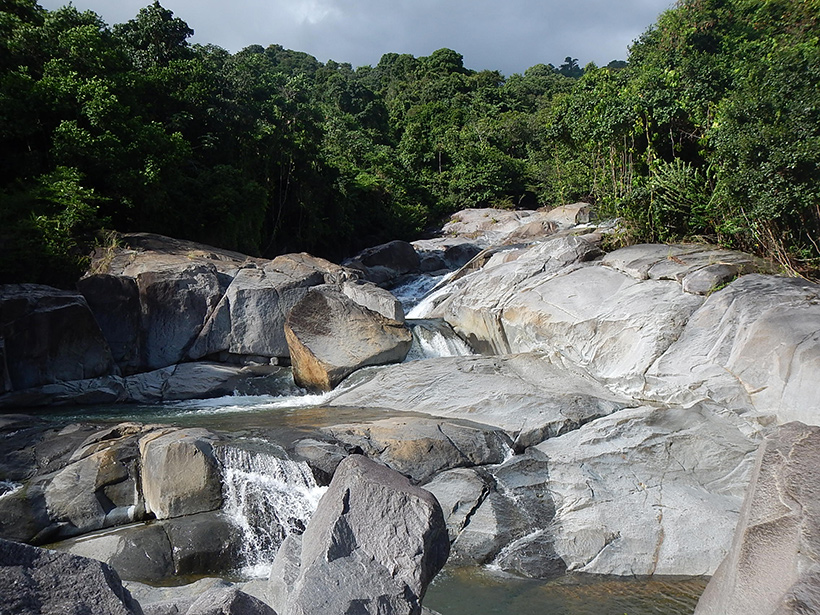
How Do Tropical Forests Slow Knickpoints in Rivers?
Using Puerto Rico's Luquillo Mountains as a case study, scientists use the region's geological history to study how knickpoints—areas where there's a sharp change in the river's slope—move over time.