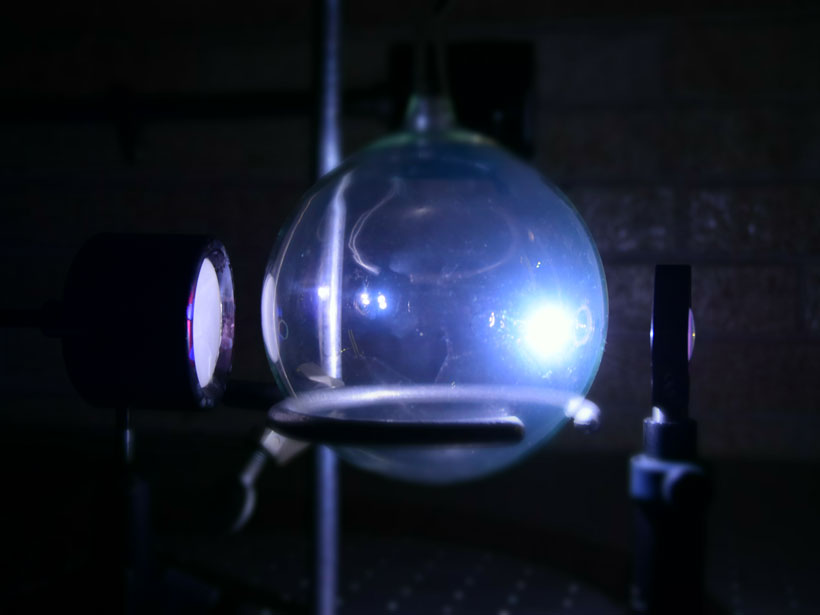
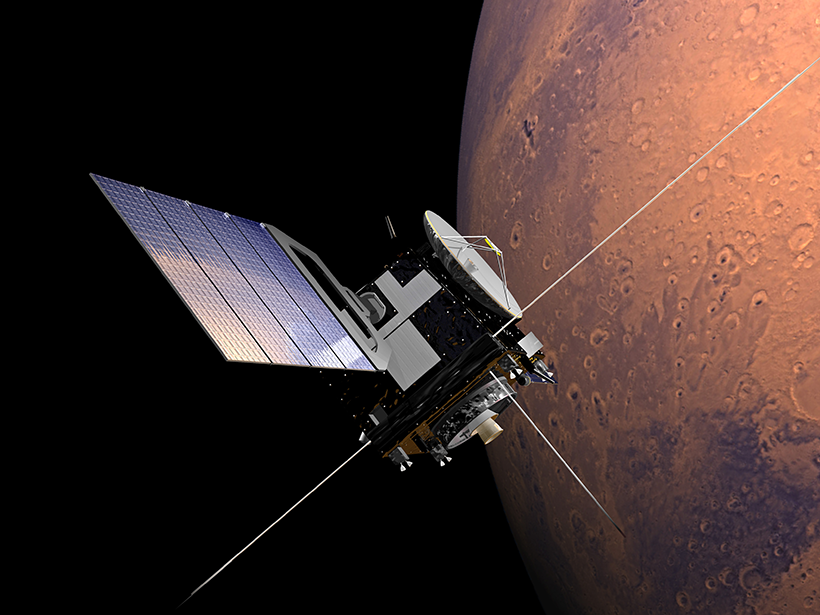
Sediments from the Curiosity rover and experiments using tanks of gas and laser beams helped reveal how water continued to flow on Mars after the planet lost its atmospheric carbon dioxide.
CC BY-NC-ND 2019
The Accidental Particle Accelerator Orbiting Mars
The radar aboard the Mars Express spacecraft can generate ion beams arcing through space above the planet, which could lead to a new way of studying the plasma surrounding it.
Subglacial Water Can Accelerate East Antarctic Glacier Flow
Airborne radar from the Recovery Glacier system demonstrates the importance of characterizing the underlying causes of ice flow speedup to understand how glacial discharge could change in the future.
Weather-Induced Tsunami Waves Regularly Roll Up on U.S. Shores
Roughly 25 meteotsunamis strike coastlines between Maine and Puerto Rico each year, tide gauge data reveal.
Ice Drove Past Indo-Pacific Climate Variance
Researchers used both terrestrial and marine proxy data to reconstruct the dramatic and dynamic climatic changes.
Spruce Beetle Slows Snow Sublimation in Wyoming’s Mountains
A new study investigates changing water dynamics after a pest infestation in the Rocky Mountains.
North Atlantic Circulation Patterns Reveal Seas of Change
New evidence suggests the eastern Atlantic may be the site of major overturning.
Compiling a Census for SEAFLEAs
Collaboration to Compile Open-Source Sites of Seafloor Fluid Expulsion Anomalies, AGU Fall Meeting 2018; Washington, D.C., 14 December 2018
Sea-Surface Carbon Patterns Linked to Large-scale Climate Modes
A new 34-year global time series of observed sea surface partial pressure of CO2 links regional variation to major climate modes.
Ocean Warming Resumes in the Tropical Pacific
The discovery of a decadal El Niño–like state associated with shifts in the Pacific trade winds could have important implications for predicting sea level in future decades.